6. Status Codes¶
6.1. Status Codes Overview¶
This specification defines the status code architecture that is required for an implementation of the Platform Initialization (PI) specifications (hereafter referred to as the “PI Architecture”). Status codes enable system components to report information about their current state. This specification does the following:
Describes the basic components of status codes
Defines the status code classes; their subclasses; and the progress, error, and debug code operations for each
Provides code definitions for the data structures that are common to all status codes
Provides code definitions for the status code classes; subclasses; progress, error, and debug code enumerations; and extended error data that are architecturally required by the PI Architecture.
The basic definition of a status code can be found in the Terms section.
6.1.1. Organization of the Status Codes Specification¶
This specification is organized as listed below. Because status codes are just one component of a PI Architecture-based firmware solution, there are a number of references to the PI Specifications throughout this document.
Book |
Description |
|---|---|
Status Codes Overview |
Provides a high level explanation of status codes and the status code classes and subclasses that are defined in this specification |
Status Code Classes |
Provides detailed explanations of the defined status code classes |
Code Definitions |
Provides the code definitions for all status code classes subclasses extended error data structures and progress error and debug code enumerations that are included in this specification |
6.2. Terms¶
The following terms are used throughout this document:
- debug code¶
Data produced by various software entities that contains information specifically intended to assist in debugging. The format of the debug code data is governed by this specification.
- error code¶
Data produced by various software entities that indicates an abnormal condition. The format of the error code data is governed by this specification.
- progress code¶
Data produced by various software entities that indicates forward progress. The format of the progress code data is governed by this specification.
- status code¶
One of the three types of codes: progress code, error code, or debug code.
- status code driver¶
The driver that produces the Status Code Runtime Protocol (
EFI_STATUS_CODE_PROTOCOL). The status code driver receives status codes and notifies registered listeners upon receipt. Status codes handled by this driver are different from theEFI_STATUSreturned by various functions. The term EFI_STATUS is defined in the UEFI Specification.
6.3. Types of Status Codes¶
For each entity classification (class/subclass pair) there are three sets of operations:
Progress codes
Error codes
Debug codes
For progress codes, operations correspond to activities related to the component classification. For error codes, operations correspond to exception conditions (errors). For debug codes, operations correspond to the basic nature of the debug information.
The values 0x00-0x0FFF are common operations that are shared by all subclasses in a class. There are also subclass-specific operations/error codes. Out of the subclass-specific operations, the values 0x1000-0x7FFF are reserved by this specification. The remaining values (0x8000-0xFFFF) are not defined by this specification and OEMs can assign meaning to values in this range. The combination of class and subclass operations provides the complete set of operations that may be reported by an entity. The figure below demonstrates the hierarchy of class and subclass and progress, error, and debug operations.
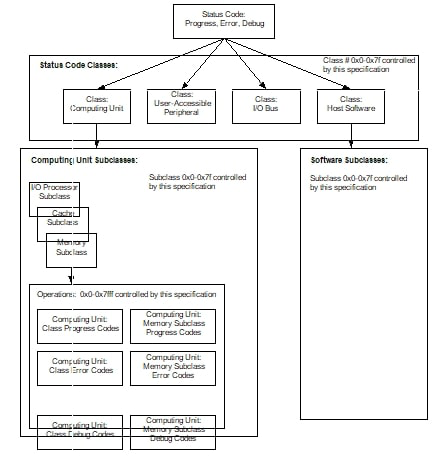
Fig. 6.1 Hierarchy of Status Code Operations¶
The organization of status codes, progress versus error, class, subclass, and operation facilitate a flexible reporting of status codes. In the simplest case, reporting the status code might only convey that an event occurred. In a slightly more complex system, it might be possible to report the class and if it is a progress, error, or debug Code. In such a case, it is at least possible to understand that the system is executing a software activity or that an error occurred with a computing unit. If more reporting capability is present, the error could be isolated to include the subclass–for example, an error occurred related to memory, or the system is currently executing the PEI Foundation software. If yet more capability is present, information about the type of error or activity is available–for example, single-bit ECC error or PEIM dispatch in progress. If the reporting capability is complete, it can provide the detailed error information about the single-bit ECC error, including the location and a string describing the failure. A large spectrum of consumer capability can be supported with a single interface for the producers of progress and error information.
6.3.1. Status Code Classes¶
The PI architecture defines four classes of status codes–three classes for hardware and one class for software. These classes are listed in the table below and described in detail in the rest of this section. Each class is made up of several subclasses, which are also defined later in this section.
See Code Definitions for all the definitions of all data types and enumerations listed in this section.
Type of Class |
Class Name |
Date Type Name |
|---|---|---|
Hardware |
Computing Unit |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT |
User-Accessible Peripheral |
EFI_PERIPHERAL |
|
I/O Bus |
EFI_IO_BUS |
|
Software |
Host Software |
EFI_SOFTWARE |
Class/subclass pairing should be able to classify any system entity, whether software or hardware. For example, the boot-strap processor (BSP) in a system would be a member of the computing unit class and host processor subclass, while a graphics processor would also be a member of the computing unit class, but a member of the I/O processor subclass.
6.3.2. Instance Number¶
Because a system may contain multiple entities matching a class/subclass pairing, there is an instance number. Instance numbers have different meanings for different classes. However, an instance number of 0xFFFFFFFF always indicates that instance information is unavailable, not applicable, or not provided.
Valid instance numbers start from 0. So a 4-processor server would logically have four instances of the class/subclass pairing, computing unit/host processor, instance numbers 0 to 3.
Due to the complexity of system design, it is outside of the scope of this specification how to pair instance numbers with the actual component–for instance, determining which processor is number 3. However, this specification mandates that the numbering be consistent with the other agents in the system. For example, the processor numbering scheme that is followed by status codes must be consistent with the one followed by the ACPI tables.
6.4. Hardware Classes¶
6.4.1. Computing Unit Class¶
The Computing Unit class covers components directly related to system computational capabilities. Subclasses correspond to types of computational devices and resources. See the following for the computing unit class:
Instance Number
Progress Code Operations
Error Code Operations
Defined Subclasses
6.4.1.1. Instance Number¶
The instance number refers to the computing unit’s geographic location in some manner. An instance number of 0xFFFFFFFF means that the instance number information is not available or the provider of the information is not interested in providing the instance number.
6.4.1.2. Progress Code Operations¶
All computing unit subclasses share the operation codes listed in the table below. See Progress Code Definitions in Code Definitions: Computing Unit Class for the definitions of these progress codes.
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|
EFI_CU_PC_INIT_BEGIN |
General computing unit initialization begins. No details regarding operation are made available. |
See subclass. |
EFI_CU_PC_INIT_END |
General computing unit initialization ends. No details regarding operation are made available. |
See subclass. |
0x0002 0x0FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification for Computing Class progress codes. |
NA |
0x1000 0x7FFF |
Reserved for subclass use. See the subclass definitions within this specification for value definitions. |
NA |
0x8000 0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
OEM defined. |
6.4.1.3. Error Code Operations¶
All computing unit subclasses share the error codes listed in the table below. See Error Code Definitions in Computing Unit Class for the definitions of these error codes.
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|
EFI_CU_EC_NON_SPECIFIC |
No error details available. |
See subclass. |
EFI_CU_EC_DISABLED |
Instance is disabled. |
See subclass. |
EFI_CU_EC_NOT_SUPPORTED |
Instance is not supported. |
See subclass. |
EFI_CU_EC_NOT_DETECTED |
Instance not detected when it was expected to be present. |
See subclass. |
E FI_CU_EC_NOT_CONFIGURED |
Instance could not be properly or completely initialized or configured. |
See subclass. |
0x0005 0x0FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification for Computing Class error codes. |
NA |
0x1000 0x7FFF |
Subclass defined: See the subclass definitions within this specification. |
NA |
0x8000 0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
OEM defined. |
6.4.1.4. Subclasses¶
6.4.1.4.1. Defined Subclasses¶
The table below lists the subclasses in the Computing Unit class. The following topics describe each subclass in more detail. See Subclass Definitions in Code Definitions: Computing Unit Class for the definitions of these subclasses.
Subclass |
Code Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Unspecified |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_UNSPECIFIED |
The computing unit type is unknown, undefined, or unspecified. |
Host processor |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT _HOST_PROCESSOR |
The computing unit is a full-service central processing unit. |
Firmware processor |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT _FIRMWARE_PROCESSOR |
The computing unit is a limited service processor, typically designed to handle tasks of limited scope. |
I O processor |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT _IO_PROCESSOR |
The computing unit is a processor designed specifically to handle I/O transactions. |
Cache |
EFI _COMPUTING_UNIT_CACHE |
The computing unit is a cache. All types of cache qualify. |
Memory |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MEMORY |
The computing unit is memory. Many types of memory qualify. |
Chipset |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_CHIPSET |
The computing unit is a chipset component. |
0x07 0x7F |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
|
0x80 0xFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
6.4.1.4.2. Unspecified Subclass¶
This subclass can be used for any computing unit type of component that does not belong in one of the other subclasses.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Computing Unit class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000 0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Error |
0x1000 0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.1.4.3. Host Processor Subclass¶
This subclass is used for computing units that provide the system’s main processing power and their associated hardware. These are general-purpose processors capable of a wide range of functionality. The instance number matches the processor handle number that is assigned to the processor by the Multiprocessor (MP) Services Protocol. They often contain multiple levels of embedded cache.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Computing Unit class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_CU_HP_PC_POWER_ON_INIT |
Power-on initialization |
None |
EFI_CU_HP_PC_CACHE_INIT |
Embedded cache initialization including cache controller hardware and cache memory. |
EFI_CACHE_INIT_DATA |
|
Progress (cont.) |
EFI_CU_HP_PC_RAM_INIT |
Embedded RAM initialization |
None |
EFI_CU_HP_PC_MEMORY _CONTROLLER_INIT |
Embedded memory controller initialization |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_PC_IO_INIT |
Embedded I/O complex initialization |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_PC_BSP_SELECT |
BSP selection |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_PC_BSP_RESELECT |
BSP reselection |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_PC_AP_INIT |
AP initialization (this operation is performed by the current BSP) |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_PC_SMM_INIT |
SMM initialization |
None |
|
0x000B-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI _CU_EC_DISABLED |
Instance is disabled. This is a standard error code for this class. |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT _CPU_DISABLED _ERROR_DATA |
EFI_CU_HP_EC _INVALID_TYPE |
Instance is not a valid type. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC _INVALID_SPEED |
Instance is not a valid speed. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC_MISMATCH |
Mismatch detected between two instances. |
EFI_HOST_PROCESSOR _MISMATCH_ERROR_DATA |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC _TIMER_EXPIRED |
A watchdog timer expired. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC_SELF_TEST |
Instance detected an error during BIST. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC_INTERNAL |
Instance detected an IERR. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC_THERMAL |
An over temperature condition was detected with this instance. |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT _THERMAL_ERROR_DATA |
|
Error (cont.) |
EFI_CU_HP_EC _LOW_VOLTAGE |
Voltage for this instance dropped below the low voltage threshold. |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT _VOLTAGE_ERROR_DATA |
EFI_CU_HP_EC_HIGH_VOLTAGE |
Voltage for this instance surpassed the high voltage threshold. |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT _VOLTAGE_ERROR_DATA |
|
EFI _CU_HP_EC_CACHE |
The instance suffered a cache failure. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC _MICROCODE_UPDATE |
Instance microcode update failed. |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT _MICROCODE_UPDATE_ERROR_DATA |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC_CORRECTABLE |
Correctable error detected. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_HP_EC _UNCORRECTABLE |
Uncorrectable ECC error detected. |
None |
|
EF I_CU_HP_EC_NO._MICROCODE_UPDATE |
No matching microcode update is found. |
None |
|
0x100D 0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
See the following topics in Subclass Definitions for definitions of the subclass-specific operations:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
See Extended Error Data in Computing Unit Class for definitions of the extended error data.
6.4.1.4.4. Firmware Processor Subclass¶
This subclass applies to processors other than the Host Processors that provides services to the system.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Computing Unit class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000 0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Error |
EFI_CU_FP_EC_HARD_FAIL |
Firmware processor detected a hardware error during initialization. |
None |
EFI_CU_FP_EC_SOFT_FAIL |
Firmware processor detected an error during initialization. E.g. Firmware processor NVRAM contents are invalid. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_FP_EC_COMM_ERROR |
The host processor encountered an error while communicating with the firmware processor. |
None |
|
0x1004 0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Related Definitions
See the following topics in Computing Unit Class for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
6.4.1.4.5. I/O Processor Subclass¶
This subclass applies to system I/O processors and their associated hardware. These processors are typically designed to offload I/O tasks from the central processors in the system. Examples would include graphics or I20 processors. The subclass is identical to the host processor subclass. See Host Processor Subclass for more information.
See Host Processor Subclass for the definition of this subclass.
6.4.1.4.6. Cache Subclass¶
The cache subclass applies to any external/system level caches. Any cache embedded in a computing unit would not be counted in this subclass, but would be considered a member of that computing unit subclass.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Computing Unit class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_CU_CACHE_PC_PRESENCE_DETECT |
Detecting cache presence. |
None |
EFI_CU_CACHE_PC_CONFIGURATION |
Configuring cache. |
None |
|
0x1002 0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_CU_CACHE_EC_INVALID_TYPE |
Instance is not a valid type. |
None |
EFI_CU_CACHE_EC_INVALID_SPEED |
Instance is not a valid speed. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_CACHE_EC_INVALID_SIZE |
Instance size is invalid. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_CACHE_EC_MISMATCH |
Instance does not match other caches. |
None |
|
0x1004-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Related Definitions
See the following topics in Computing Unit Class for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
6.4.1.4.7. Memory Subclass¶
The memory subclass applies to any external/system level memory and associated hardware. Any memory embedded in a computing unit would not be counted in this subclass, but would be considered a member of that computing unit subclass.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Computing Unit class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
For all operations and errors, the instance number
specifies the DIMM number unless stated otherwise. Some
of the operations may affect multiple memory devices and
multiple memory controllers. The specification provides
mechanisms (EFI_MULTIPLE_MEMORY_DEVICE_OPERATION and
others) to describe such group operations. See
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DIMM_NUMBER in Computing Unit Class for details.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_SPD_READ |
Reading configuration data (e.g. SPD) from memory devices. |
None |
EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC _PRESENCE_DETECT |
Detecting presence of memory devices (e.g. DIMMs). |
None |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_TIMING |
Determining optimum configuration e.g. timing for memory devices. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_CONFIGURING |
Initial configuration of memory device and memory controllers. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_OPTIMIZING |
Programming the memory controller and memory devices with optimized settings. |
None |
|
Progress (cont.) |
EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_INIT |
Memory initialization such as ECC initialization. |
EFI_MEMORY _RANGE _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_TEST |
Performing memory test. |
EFI_MEMORY _RANGE _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
0x1007-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_INVALID_TYPE |
Instance is not a valid type. |
None |
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_INVALID_SPEED |
Instance is not a valid speed. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_CORRECTABLE |
Correctable error detected. |
EFI_MEMORY _EXTENDED _ERROR_DATA |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_UNCORRECTABLE |
Uncorrectable error detected. This included memory miscomparisions during the memory test. |
EFI_MEMORY _EXTENDED _ERROR_DATA |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_SPD_FAIL |
Instance SPD failure detected. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_INVALID_SIZE |
Instance size is invalid. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_MISMATCH |
Mismatch detected between two instances. |
EFI_MEMORY _MODULE _MISMATCH _ERROR_DATA |
|
E FI_CU_MEMORY_EC _S3_RESUME_FAIL |
Resume from S3 failed. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_UPDATE_FAIL |
Flash Memory Update failed. |
None |
|
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_NONE_DETECTED |
Memory was not detected in the system. Instance field is ignored. |
None |
|
Error cont |
EFI_CU_MEMORY _EC_NONE_USEFUL |
No useful memory was detected in the system. E.g., Memory was detected but cannot be used due to errors. Instance field is ignored. |
None |
0x1009-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Related Definitions
See the following topics in Computing Unit Class for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
See Extended Data Formats for definitions of the extended error data listed above.
6.4.1.4.8. Chipset Subclass¶
This subclass can be used for any chipset components and their related hardware.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Computing Unit class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_PEI_CAR_SB_INIT |
South Bridge initialization prior to memory detection |
None |
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_PEI_CAR_NB_INIT |
North Bridge initialization prior to memory detection |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_PEI_MEM_SB_INIT |
South Bridge initialization after memory detection |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_PEI_MEM_NB_INIT |
North Bridge initialization after memory detection |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_HB_INIT |
PCI Host Bridge DXE initialization |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_NB_INIT |
North Bridge DXE initialization |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_NB_SMM_INIT |
North Bridge specific SMM initialization in DXE |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_SB_RT_INIT |
Initialization of the South Bridge specific UEFI Runtime Services |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_SB_INIT |
South Bridge DXE initialization |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_SB_SMM_INIT |
South Bridge specific SMM initialization in DXE |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE _SB_DEVICES_INIT |
Initialization of the South Bridge devices |
None |
|
Progress |
0x100B-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
EFI_CHIPSET_EC_BAD_BATTERY |
Bad battery status has been detected |
None |
EFI_CHIPSET_EC_DXE_NB_ERROR |
North Bridge initialization error in DXE |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_EC_DXE_NB_ERROR |
South Bridge initialization error in DXE |
None |
|
EFI_CHIPSET_EC_INTRUDER_DETECT |
Physical access to inner system components that are not accessible during normal system operation is detected |
None |
|
Error |
0x1004-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2. User-Accessible Peripheral Class¶
The User-Accessible Peripheral class refers to any peripheral with which the user interacts. Subclass elements correspond to general classes of peripherals. See the following for the User-Accessible Peripheral class:
instance number
progress code operations
error code operations
defined subclasses
6.4.2.1. Instance Number¶
The instance number refers to the peripheral’s geographic location in some manner. Instance number of 0 means that instance number information is not available or the provider of the information is not interested in providing the instance number.
6.4.2.2. Progress Code Operations¶
All peripheral subclasses share the operation codes listed in the table below. See Progress Code Definitions for the definitions of these progress codes.
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|
EFI_P_PC_INIT |
General Initialization. No details regarding operation are made available. |
See subclass |
EFI_P_PC_RESET |
Resetting the peripheral. |
See subclass |
EFI_P_PC_DISABLE |
Disabling the peripheral. |
See subclass |
EFI_P_PC _PRESENCE_DETECT |
Detecting the presence. |
See subclass |
EFI_P_PC_ENABLE |
Enabling the peripheral. |
See subclass |
EFI_P_PC_RECONFIG |
Reconfiguration. |
See subclass |
EFI_P_PC_DETECTED |
Peripheral was detected. |
See subclass |
EFI_P_PC_REMOVED |
Peripheral was unplugged, ejected, or otherwise removed from the system. |
See subclass |
0x0007 0x0FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification for Peripheral Class progress codes. |
NA |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for subclass use. See the subclass definitions within this specification for value definitions. |
See subclass |
0x8000-0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
NA |
6.4.2.3. Error Code Operations¶
All peripheral subclasses share the error codes listed in the table below. See User-Accessible Peripherals Class for the definitions of these error codes.
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|
EFI_P_EC_NON_SPECIFIC |
No error details available |
See subclass |
EFI_P_EC_DISABLED |
Instance is disabled |
See subclass |
EFI_P_EC _NOT_SUPPORTED |
Instance is not supported |
See subclass |
EFI_P_EC _NOT_DETECTED |
Instance not detected when it was expected to be present |
See subclass |
EFI_P_EC _NOT_CONFIGURED |
Instance could not be properly or completely initialized or configured |
See subclass |
EFI_P_EC_INTERFACE_ERROR |
An error occurred with the peripheral interface |
See subclass |
EFI_P_EC_CONTROLLER_ERROR |
An error occurred with the peripheral controller |
See subclass |
EFI_P_EC_INPUT_ERROR |
An error occurred getting input from the peripheral |
See subclass |
E FI_P_EC_OUTPUT_ERROR |
An error occurred putting output to the peripheral |
See subclass |
EFI_P_EC_RESOURCE_CONFLICT |
A resource conflict exists with this instance s resource requirements |
See EFI_RESOURCE_ALLO C_FAILURE_ERROR_DATA for all subclasses |
0x0006-0x0FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification for User-Accessible Peripheral class error codes |
NA |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
See the subclass definitions within this specification |
See subclass |
0x8000-0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use |
NA |
6.4.2.4. Subclasses¶
6.4.2.4.1. Defined Subclasses¶
The table below lists the subclasses in the User-Accessible Peripheral class. The following topics describe each subclass in more detail. See Subclass Definitions. for the definitions of these subclasses.
Subclass |
Code Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Unspecified |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_UNSPECIFIED |
The peripheral type is unknown, undefined, or unspecified. |
Keyboard |
E FI_PERIPHERAL_KEYBOARD |
The peripheral referred to is a keyboard. |
Mouse |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_MOUSE |
The peripheral referred to is a mouse. |
Local console |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_LOCAL_CONSOLE |
The peripheral referred to is a console directly attached to the system. |
Remote console |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_REMOTE_CONSOLE |
The peripheral referred to is a console that can be remotely accessed. |
Serial port |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_SERIAL_PORT |
The peripheral referred to is a serial port. |
Parallel port |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_PARALLEL_PORT |
The peripheral referred to is a parallel port. |
Fixed media |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_FIXED_MEDIA |
The peripheral referred to is a fixed media device–e.g., an IDE hard disk drive. |
Removable media |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_REMOVABLE_MEDIA |
The peripheral referred to is a removable media device–e.g., a DVD ROM drive. |
Audio input |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_AUDIO_INPUT |
The peripheral referred to is an audio input device–e.g., a microphone. |
Audio output |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_AUDIO_OUTPUT |
The peripheral referred to is an audio output device–e.g., speakers or headphones. |
LCD device |
EFI _PERIPHERAL_LCD_DEVICE |
The peripheral referred to is an LCD device. |
Network device |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_NETWORK |
The peripheral referred to is a network device–e.g., a network card. |
Docking Station |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_DOCKING |
The peripheral referred to is a docking station. |
Trusted Platform Module |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_TPM |
The peripheral referred to is a Trusted Platform Module |
0x0F-0x7F |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
|
0x80-0xFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
6.4.2.4.2. Unspecified Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any user-accessible peripheral not belonging to any of the other subclasses.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.3. Keyboard Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any keyboard style interfaces. ExtendedData contains the device path to the keyboard device as defined in EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA and the instance is ignored.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_P_KEYBOARD _PC_CLEAR_BUFFER |
Clearing the input keys from keyboard. |
The device path to the keyboard device See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_P_KEYBOARD _PC_SELF_TEST |
Keyboard self test. |
The device path to the keyboard device See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
0x1002-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_P_KEYBOARD _EC_LOCKED |
The keyboard input is locked. |
The device path to the keyboard device See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_P_KEYBOARD _EC_STUCK_KEY |
A stuck key was detected. |
The device path to the keyboard device See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
EFI_P_KEYBOARD _EC_BUFFER_FULL |
Keyboard buffer is full. |
The device path to the keyboard device See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
0x1003-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Related Definitions
See the following topics in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
See Extended Error Data in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for definitions of the extended error data listed above.
6.4.2.4.4. Mouse Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any mouse or pointer
peripherals. ExtendedData contains the device path
to the mouse device as defined in
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA and the instance is
ignored.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_P_MOUSE_PC _SELF_TEST |
Mouse self test |
The device path to the mouse device See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
0x1001-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_P_MOUSE _EC_LOCKED |
The mouse input is locked |
The device path to the mouse device See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
0x1001-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
See the following topics in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
See Extended Error Data in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for definitions of the extended error data listed above.
6.4.2.4.5. Local Console Subclass¶
This subclass applies to all console devices directly
connected to the system. This would include VGA/UGA
devices. ExtendedData contains the device path to the
console device as defined in
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA and the instance is
ignored. LCD devices have their own subclass.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.6. Remote Console Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any console not directly
connected to the system. This would include consoles
displayed via serial or LAN Hconnections.
ExtendedData contains the device path to the console
device as defined in EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA
and the instance is ignored.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.7. Serial Port Subclass¶
This subclass applies to devices attached to a system
serial port, such as a modem. ExtendedData contains
the device path to the device as defined in
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA and the instance is
ignored.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_P_SERIAL_PORT _PC_CLEAR_BUFFER |
Clearing the serial port input buffer |
The device handle See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
0x1001-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
|
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
See the following topics in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
See Extended Error Data in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for definitions of the extended error data listed above.
6.4.2.4.8. Parallel Port Subclass¶
This subclass applies to devices attached to a system
parallel port, such as a printer. ExtendedData
contains the device path to the device as defined in
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA and the instance is
ignored.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.9. Fixed Media Subclass¶
This subclass applies to fixed media peripherals such
as hard drives. These peripherals are capable of
producing the EFI_BLOCK_IO Protocol. ExtendedData
contains the device path to the device as defined in
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA and the instance is
ignored.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.10. Removable Media Subclass¶
This subclass applies to removable media peripherals
such as floppy disk drives or LS-120 drives. These
peripherals are capable of producing the
EFI_BLOCK_IO Protocol. ExtendedData contains the
device path to the device as defined in
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA and the instance is
ignored.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.11. Audio Input Subclass¶
This subclass applies to audio input devices such as microphones.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.12. Audio Output Subclass¶
This subclass applies to audio output devices like speakers or headphones.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.13. LCD Device Subclass¶
This subclass applies to LCD display devices attached to the system.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Errror Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.2.4.14. Network Device Subclass¶
This subclass applies to network adapters attached to the system. These devices are capable of producing standard UEFI networking protocols such as the EFI_SIMPLE_NETWORK Protocol.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the User-Accessible Peripheral class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.3. I/O Bus Class¶
The I/O bus class covers hardware buses irrespective of any software protocols that are used. At a broad level, everything that connects the computing unit to the user peripheral can be covered by this class. Subclass elements correspond to industry-standard hardware buses. See the following for the I/O Bus class:
instance number
progress code operations
error code operations
defined subclasses
6.4.3.1. Instance Number¶
The instance number is ignored and the ExtendedData
describes the device path to the controller or the device
as defined in EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA .
6.4.3.2. Progress Code Operations¶
All I/O bus subclasses share the operation codes listed in the table below. See Progress Code Definitions for the definitions of these progress codes.
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|
EFI_IOB_PC_INIT |
General initialization. No details regarding operation are made available. |
The device path corresponding to the host bus controller (the controller that produces this bus). For the PCI bus, it is the PCI root bridge. The format of the device path extended data is defined in EFI_DEVICE _PATH_EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_IOB_PC_RESET |
Resetting the bus. Generally, this operation resets all the devices on the bus as well. |
The device path corresponding to the host controller (the controller that produces this bus) The format is defined in EFI_DEVICE _PATH_EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_IOB_PC_DISABLE |
Disabling all the devices on the bus prior to enumeration. |
The device path corresponding to the host controller (the controller that produces this bus). The format is defined in EFI_DEVICE _PATH_EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_IOB_PC_DETECT |
Detecting devices on the bus. |
The device path corresponding to the host controller (the controller that produces this bus). The format is defined in EFI_DEVICE _PATH_EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_IOB_PC_ENABLE |
Configuring the bus and enabling device on the bus. |
The device path corresponding to the host controller (the controller that produces this bus). The format is defined in EFI_DEVICE _PATH_EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_IOB_PC_RECONFIG |
Bus reconfiguration including resource re-enumeration. |
The device path corresponding to the host controller the controller that produces this bus The format is defined in EFI_DEVICE _PATH_EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_IOB_PC_HOTPLUG |
A hot-plug event was detected on the bus and the hot-plugged device was initialized. |
The device path corresponding to the host controller (the controller that produces this bus). The format is defined in EFI_DEVICE _PATH_EXTENDED_DATA |
0x0007 0x0FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification for I/O Bus class progress codes. |
NA |
0x1000 0x7FFF |
Reserved for subclass use. See the subclass definitions within this specification for value definitions. |
NA |
0x8000 0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
OEM defined. |
6.4.3.3. Error Code Operations¶
All I/O bus subclasses share the error codes listed in the table below. See Error Code Definitions in Error Code Operations: I/O Bus Class for the definitions of these error codes.
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|
EFI_IOB_EC_NON_SPECIFIC |
No error details available. |
None. |
EFI_IOB_EC_DISABLED |
A device is disabled due to bus-level errors. |
The device path corresponding to the device. See EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_IOB_EC_NOT_SUPPORTED |
A device is nots upported on thisbus. |
The device path corresponding to the device. See EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_IOB_EC_NOT_DETECTED |
Instance not detected when it was expected to be present. |
The device path corresponding to the device. See EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_IOB_EC_NOT_CONFIGURED |
Instance could not be properly or completely initialized/configured. |
The device path corresponding to the device. See EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_IOB_EC_INTERFACE_ERROR |
An error occurred with the bus interface. |
The device path corresponding to the failing device. See EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_IOB_EC_CONTROLLER_ERROR |
An error occurred with the host bus controller (the controller that produces this bus). |
The device path corresponding to the bus controller. See EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_IOB_EC_READ_ERROR |
A bus specific error occurred getting input from a device on the bus. |
The device path corresponding to the failing device or the closest device path. See EFI_DEVICE_PATH_ |
EFI_IOB_EC_WRITE_ERROR |
An error occurred putting output to the bus. |
The device path corresponding to the failing device or the closest device path. See EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_IOB_EC_RESOURCE_CONFLICT |
A resource conflict exists with this instance’s resource requirements. |
See EFI_RESOURCE_ALLOC_FAILURE ERROR_DATA. |
0x000A-0x0FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification for I/O Bus class errorcodes. |
NA |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
See the subclass definitions within this specification. |
NA |
0x8000-0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
NA |
6.4.3.4. Subclasses¶
6.4.3.4.1. Defined Subclasses¶
The table below lists the subclasses in the . The following topics describe each subclass in more detail. See Subclass Definitions for the definitions of these subclasses.
Subclass |
Code Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Unspecified |
EF I_IO_BUS_UNSPECIFIED |
The bus type is unknown undefined or unspecified |
PCI |
EFI_IO_BUS_PCI |
The bus is a PCI bus |
USB |
EFI_IO_BUS_USB |
The bus is a USB bus |
InfiniBand architecture |
EFI_IO_BUS_IBA |
The bus is an IBA bus |
AGP |
EFI_IO_BUS_AGP |
The bus is an AGP bus |
PC card |
EFI_IO_BUS_PC_CARD |
The bus is a PC Card bus |
Low pin count LPC |
EFI_IO_BUS_LPC |
The bus is a LPC bus |
SCSI |
EFI_IO_BUS_SCSI |
The bus is a SCSI bus |
ATA ATAPI SATA |
EFI_IO_BUS_ATA_ATAPI |
The bus is a ATA ATAPI bus |
Fibre Channel |
EFI_IO_BUS_FC |
The bus is an EC bus |
IP network |
E FI_IO_BUS_IP_NETWORK |
The bus is an IP network bus |
SMBus |
EFI_IO_BUS_SMBUS |
The bus is a SMBUS bus |
I2C |
EFI_IO_BUS_I2C |
The bus is an I2C bus |
0x0D 0x7F |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
|
0x80 0xFF |
Reserved for OEM use |
|
6.4.3.4.2. Unspecified Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any I/O bus not belonging to any of the other I/O bus subclasses.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Related Definitions
None.
6.4.3.4.3. PCI Subclass¶
This subclass applies to PCI buses and devices. It also includes different variations of PCI bus including PCI-X and PCI Express.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_IOB_PCI _BUS_ENUM |
Enumerating buses under a root bridge. |
The device path corresponding to the PCI root bridge See EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_IOB_PCI _RES_ALLOC |
Allocating resources to devices under a host bridge. |
The host bridge handle as defined in EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
EFI_IOB_PCI _HPC_INIT |
Initializing a PCI hot-plug controller. |
The device path to the controller as defined in EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
0x1003-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_IOB_PCI _EC_PERR |
Parity error; see PCI Specification. |
The device path to the controller that generated the PERR The data format is defined in EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_IOB_PCI _EC_SERR |
System error; see PCI Specification. |
The device path to the controller that generated the SERR The data format is defined in EFI_DEVICE_PATH _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
0x1002-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
See the following topics in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
See Extended Error Data in I/O Bus Class for definitions of the extended error data listed above.
6.4.3.5. USB Subclass¶
This subclass applies to USB buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.1. InfiniBand* Architecture Subclass¶
This subclass applies to InfiniBand* (IBA) buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.2. AGP Subclass¶
This subclass applies to AGP buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.3. PC Card Subclass¶
This subclass applies to PC Card buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.4. LPC Subclass¶
This subclass applies to LPC buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.5. SCSI Subclass¶
This subclass applies to SCSI buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.6. ATA/ATAPI/SATA Subclass¶
This subclass applies to ATA and ATAPI buses and devices. It also includes Serial ATA (SATA) buses.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART_ENABLE |
SMART is enabled on the storage device |
NA |
EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART_DISABLE |
SMART is disabled on the storage device |
NA |
|
EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART _OVERTHRESHOLD |
SMART records are over threshold on the storage device |
NA |
|
EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART _UNDERTHRESHOLD |
SMART records are under threshold on the storage device |
NA |
|
0x1004-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART _NOTSUPPORTED |
SMART is not supported on the storage device |
NA |
EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART _DISABLED |
SMART is disabled on the storage device |
NA |
|
0x1002-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.7. Fibre Channel (FC) Subclass¶
This subclass applies to Fibre Channel buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.8. IP Network Subclass¶
This subclass applies to IP network buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.9. 3SMBus Subclass¶
This subclass applies to SMBus buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.4.3.5.10. I2C Subclass¶
This subclass applies to I2C buses and devices.
See Subclass Definitions for the definition of this subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the I/O Bus class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.5. Software Classes¶
6.5.1. Host Software Class¶
The Host Software class covers any software-generated codes. Subclass elements correspond to common software types in a PI Architecture system. See the following for the Host Software class:
instance number
progress code operations
error code operations
defined subclasses
6.5.2. Instance Number¶
The instance number is not used for software subclasses unless otherwise stated.
6.5.3. Progress Code Operations¶
All host software subclasses share the operation codes listed in the table below. See Progress Code Definitions in Software Classes for the definitions of these progress codes.
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|
EFI_SW_PC_INIT |
General initialization. No details regarding operation are made available. |
None |
EFI_SW_PC_LOAD |
Loading a software module in the preboot phase by using LoadImage() or an equivalent PEI service. May include a PEIM, DXE drivers, UEFI application, etc. |
Handle identifying the module. There will be an instance of EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL on this handle. See EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_SW_PC _INIT_BEGIN |
Initializing software module by using StartImage() or an equivalent PEI service. |
Handle identifying the module. There will be an instance of EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL on this handle. See EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_SW_PC _INIT_END |
Software module returned control back after initialization. |
Handle identifying the module. There will be an instance of EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL on this handle. See EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_SW_PC _AUTHENTICATE_BEGIN |
Performing authentication (passwords, biometrics, etc.) |
None |
EFI_SW_PC _AUTHENTICATE_END |
Authentication completed |
None |
EFI_SW_PC _INPUT_WAIT |
Waiting for user input |
None |
EFI_SW_PC _USER_SETUP |
Executing user setup |
None |
0x0008-0x0FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification for Host Software class progress codes. |
NA |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for subclass use. See the subclass definitions within this specification for value definitions. |
NA |
0x8000-0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
NA |
6.5.4. Error Code Operations¶
All host software subclasses share the error codes listed in the table below. See Error Code Definitions in Software Classes for the definitions of these progress codes.
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|
EFI_SW_EC_NON_SPECIFIC |
No error details are available. |
None |
EFI_SW_EC_LOAD_ERROR |
The software module load failed. |
Handle identifying the module. There will be an instance of EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL on this handle. See EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_SW_EC_INVALID_PARAMETER |
An invalid parameter was passed to the instance. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_UNSUPPORTED |
An unsupported operation was requested. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_INVALID_BUFFER |
The instance encountered an invalid buffer (too large, small, or nonexistent). |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
Insufficient resources exist. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_ABORTED |
The instance was aborted. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_ILLEGAL_SOFTWARE_STATE |
The instance detected an illegal software state. |
See EFI_DEBUG_ASSERT_DATA |
EFI_SW_EC_ILLEGAL_HARDWARE_STATE |
The instance detected an illegal hardware state. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_START_ERROR |
The software module returned an error when started via StartImage() or equivalent. |
Handle identifying the module. There will be an instance of EFI_LOADED_IMAGE_PROTOCOL on this handle. See EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE_EXTENDED_DATA. |
EFI_SW_EC_BAD_DATE_TIME |
The system date/time is invalid |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_CFG_INVALID |
Invalid configuration settings were detected. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_CFG_CLR_REQUEST |
User requested that configuration defaults be loaded (via a physical jumper, for example). |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_CFG_DEFAULT |
Configuration defaults were loaded. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_PWD_INVALID |
Invalid password settings were detected. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_PWD_CLR_REQUEST |
User requested that the passwords be cleared (via a physical jumper, for example). |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_PWD_CLEARED |
Passwords were cleared. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_EVENT_LOG_FULL |
System event log is full. |
None. |
EFI_SW_EC_WRITE_PROTECTED |
The device cannot be written to. |
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA if device path to the write protected device is available; otherwise, none. |
EFI_SW_EC_FV_CORRUPTED |
Corrupted Firmware Volume is detected. |
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA if device path to the corrupted firmware volume is available; otherwise, none. |
EFI_SW_EC_INCONSISTENT_MEMORY_MAP |
System will reboot due to inconsistent memory maps |
None |
0x0015-0x00FF |
Reserved for future use by this specification for Host Software class error codes. |
None. |
0x0100-0x01FF |
Unexpected EBC exceptions. |
See EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_EXTENDED_DATA. |
0x0200-0x02FF |
Unexpected IA-32 processor exceptions. |
See EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_EXTENDED_DATA. |
0x0300-0x03FF |
Unexpected Itanium(r) processor family exceptions. |
See EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_EXTENDED_DATA. |
0x0400-0x7FFF |
See the subclass definitions within this specification. |
|
0x8000-0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
6.5.5. Subclasses¶
6.5.5.1. Defined Subclasses¶
The table below lists the subclasses in the Host Software class. The following topics describe each subclass in more detail.
See Subclass Definitions for the definitions of these subclasses.
Subclass |
Code Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Unspecified |
EFI_SOFTWARE_UNSPECIFIED |
The software type is unknown, undefined, or unspecified. |
Security SEC |
EFI_SOFTWARE_SEC |
The software is a part of the SEC phase. |
PEI Foundation |
E FI_SOFTWARE_PEI_CORE |
The software is the PEI Foundation module. |
PEI module |
EFI _SOFTWARE_PEI_MODULE |
The software is a PEIM. |
DXE Foundation |
E FI_SOFTWARE_DXE_CORE |
The software is the DXE Foundation module. |
DXE Boot Service driver |
EFI_SOFTWARE_DXE _BS_DRIVER |
The software is a DXE Boot Service driver. Boot service drivers are not available once ExitBootServices() is called. |
DXE Runtime Service driver |
EFI_SOFTWARE_DXE_RT_DRIVER |
The software is a DXE Runtime Service driver. These drivers execute during runtime phase. |
SMM driver |
EFI _SOFTWARE _SMM_DRIVER |
The software is a SMM driver. |
EFI application |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI _APPLICATION |
The software is a UEFI application. |
OS loader |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI _OS_LOADER |
The software is an OS loader. |
Runtime (RT) |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_RT |
The software is a part of the RT phase. |
EBC exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EBC _EXCEPTION |
The status code is directly related to an EBC exception. |
IA-32 exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_IA32 _EXCEPTION |
The status code is directly related to an IA-32 exception. |
Itanium processor family exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_IPF _EXCEPTION |
The status code is directly related to an Itanium processor family exception. |
x64 software exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_X64 _EXCEPTION |
The status code is directly related to anx64 exception. |
ARM software exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_ARM _EXCEPTION |
The status code is directly related to an ARM exception whilst executing in AArch32 state. |
ARM AArch64 exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_AARCH64 _EXCEPTION |
The status code is directly related to an ARM exception whilst executing in AArch64 state. |
RISC-V software exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_RISCV _EXCEPTION |
The status code is directly related to RISC-V exception. |
PEI Services |
EFI_SOFTWARE_PEI _SERVICE |
The status code is directly related to a PEI Services function. |
EFI Boot Services |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_BOOT _SERVICE |
The status code is directly related to a UEFI Boot Services function. |
EFI Runtime Services |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI _RUNTIME_SERVICE |
The status code is directly related to a UEFI Runtime Services function. |
DXE Services |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_DXE_SERVICE |
The status code is directly related to a DXE Services function. |
0x13-0x7F |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
0x80-0xFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
NA |
6.5.5.2. Unspecified Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any software entity not belonging to any of the other software subclasses. It may also be used if the caller is unable to determine the exact subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
None.
6.5.5.3. SEC Subclass¶
This subclass applies to the Security (SEC) phase in software.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass. In most platforms, status code services may be unavailable during the SEC phase.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_SEC_PC_ENTRY_POINT |
Entry point of the phase. |
None |
EFI_SW_SEC_PC _HANDOFF_TO_NEXT |
Handing off to the next phase |
None |
|
0x1002-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
|
Error |
0x1000 0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
6.5.5.4. PEI Foundation Subclass¶
This subclass applies to the PEI Foundation. The PEI Foundation is responsible for starting and ending the PEI phase as well as dispatching Pre-EFI Initialization Modules (PEIMs).
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_PC_ENTRY_POINT |
Entry point of the phase |
None |
EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_PC_HANDOFF _TO_NEXT |
Handing off to the next phase (DXE) |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_PC_RETURN _TO_LAST |
Returning to the last phase |
None |
|
0x1003-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_EC_DXE _CORRUPT |
Unable to hand off to DXE because the DXE Foundation could not be found |
None |
EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_EC_DXEIPL _NOT_FOUND |
DXE IPL PPI could not be found |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_EC_MEMORY _NOT_INSTALLED |
PEIM dispatching is over and InstallPeiMemory() PEI Service has not been called |
None |
|
0x1003-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
6.5.5.5. PEI Module Subclass¶
This subclass applies to Pre-EFI Initialization Modules (PEIMs).
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_PEI_PC_RECOVERY_BEGIN |
Crisis recovery has been initiated. |
NULL |
EFI_SW_PEI_PC_CAPSULE_LOAD |
Found a recovery capsule. About to load the recovery capsule. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_PC_CAPSULE_START |
Loaded the recovery capsule. About to hand off control to the capsule. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_PC_RECOVERY_USER |
Recovery was forced by the user via a jumper, for example. Reported by the PEIM that detects the jumpers and updates the boot mode. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_PC_RECOVERY_AUTO |
Recovery was forced by the software based on some policy. Reported by the PEIM that updates the boot mode to force recovery. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_PC_S3_BOOT_SCRIPT |
S3 boot script execution. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_PC_OS_WAKE |
Calling OS S3 wake up vector. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_PC_S3_STARTED |
Signifies beginning of the EFI_PEI_S3 _RESUME_PPI S3 RestoreConfig() execution. |
NULL |
|
0x1008-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NULL |
|
Error |
EFI _SW_PEI_EC_NO _RECOVERY_CAPSULE |
Unable to continue with the crisis recovery because no recovery capsule was found. |
NULL |
EFI_SW_PEI_EC_INVALID _CAPSULE_DESCRIPTOR |
An invalid or corrupt capsule descriptor was detected. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_RESUME _PPI_NOT_FOUND |
S3 Resume PPI is not found. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_BOOT _SCRIPT_ERROR |
Error during boot script execution. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_OS _WAKE_ERROR |
Error related to the OS wake up vector (no valid vector found or vector returned control back to the firmware) |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3 _RESUME_FAILED |
Unspecified S3 resume failure. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_EC_RECOVERY _PPI_NOT_FOUND |
Recovery failed because Recovery Module PPI is not found. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_EC _RECOVERY_FAILED |
Unspecified Recovery failure. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_RESUME _ERROR |
Error during S3 resume process. |
NULL |
|
EFI_SW_PEI_EC_INVALID _CAPSULE |
Invalid capsule is detected. |
NULL |
|
0x100A-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
6.5.5.6. DXE Foundation Subclass¶
This subclass applies to DXE Foundation software. The DXE Foundation is responsible for providing core services, dispatching DXE drivers, and calling the Boot Device Selection (BDS) phase.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_ENTRY _POINT |
Entry point of the phase. |
None |
EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_HANDOFF _TO_NEXT |
Handing off to the next phase (Runtime). |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_RETURN _TO_LAST |
Returning to the last phase. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_START _DRIVER |
Calling the Start() function of the EFI _DRIVER_BINDING Protocol. |
See EFI_STATUS _CODE_START _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_ARCH _READY |
All architectural protocols are available. |
None |
|
0x1005-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_EC_NO_ARCH |
Driver dispatching is over and some of the architectural protocols are not available. |
None |
0x1001-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
See Extended Error Data in Software Classes for definitions of the extended error data listed above.
6.5.5.7. DXE Boot Service Driver Subclass¶
This subclass applies to DXE boot service drivers. If a driver provides both boot services and runtime services, it is considered a runtime service driver.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_LEGACY _OPROM_INIT |
Initializing a legacy Option ROM (OpROM). |
See EFI_LEGACY_OPROM _EXTENDED_DATA |
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_READY _TO_BOOT_EVENT |
The EFI_EVENT_GROUP _READY_TO_BOOT event was signaled. See the UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC _LEGACY_BOOT_EVENT |
The event with GUID EFI_EVENT_LEGACY _BOOT_GUID was signaled. See the DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_EXIT _BOOT_SERVICES_EVENT |
The EVT_SIGNAL_EXIT _BOOT_SERVICES event was signaled. See the UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_VIRTUAL _ADDRESS_CHANGE_EVENT |
The EVT_SIGNAL_VIRTUAL _ADDRESS_CHANGE event was signaled. See the UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC _VARIABLE_SERVICES_INIT |
Variable Services initialization |
None |
|
EFI _SW_DXE_BS_PC _VARIABLE_RECLAIM |
Variable Services driver is about to start variable store reclaim process (a process of storage optimization by removing stale data). |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC _CONFIG_RESET |
Configuration is about to be reset |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC _CSM_INIT |
Compatibility (legacy BIOS) Support Module initialization. |
None |
|
0x100A-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC _LEGACY_OPROM_NO_SPACE |
Not enough memory available to shadow a legacy option ROM. |
See EFI_LEGACY_OPROM _ EXTENDED_DATA. RomImageBase corresponds to the ROM image in the regular memory as opposed to shadow RAM. |
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC _INVALID_PASSWORD |
Invalid password has been provided. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC _BOOT_OPTION_LOAD_ERROR |
Error during boot option loading (LoadImage returned error). |
E FI_RETURN_STATU S_EXTENDED_DATA |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC _BOOT_OPTION_FAILED |
Error during boot option launch (StartImage returned error). |
EFI_RETURN_STATUS _EXTENDED_DATA |
|
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC_INVALID _IDE_PASSWORD |
Invalid hard driver password has been provided. |
None |
|
Progress |
EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_ATTEMPT _BOOT_ORDER_EVENT |
Attempting boot from options defined in the BootOrder list. |
None |
0x1005-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
Error Code Definitions
See Extended Error Data in Software Classes for definitions of the extended error data listed above.
6.5.5.8. DXE Runtime Service Driver Subclass¶
This subclass applies to DXE runtime service drivers.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
None.
6.5.5.9. SMM Driver Subclass¶
This subclass applies to SMM code.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.5.5.10. EFI Application Subclass¶
This subclass applies to UEFI applications.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.5.5.11. OS Loader Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any OS loader application. Although OS loaders are UEFI applications, they are very special cases and merit a separate subclass.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
None.
6.5.6. Runtime (RT) Subclass¶
This subclass applies to runtime software. Runtime software is made up of the UEFI-aware operating system and the non-UEFI software running under the operating system environment. Other firmware components, such as SAL code or ASL code, are also executing during this phase but cannot call a UEFI runtime service. Hence no codes are reserved for them.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_RT_PC_ENTRY_POINT |
Entry point of the phase. |
None |
EFI_SW_RT_PC_RETURN_TO_LAST |
Returning to the last phase. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RT_PC_HANDOFF_TO_NEXT |
|||
0x1003-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
6.5.6.1. PEI Services Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any PEI Service present in the PEI Services Table.
Progress and Error Codes
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass. These progress codes are reported by the code that provides the specified boot service and not by the module that invokes the given boot service.
Many of the descriptions below refer to the Platform Initialization Pre-EFI Initialization Core Interface Specification, or PEI CIS. Also, see “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_PS_PC_INSTALL_PPI |
Install a PPI. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
EFI_SW_PS_PC_REINSTALL_PPI |
Reinstall a PPI. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_LOCATE_PPI |
Locate an existing. PPI See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_NOTIFY_PPI |
Install a notification callback. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_GET_BOOT_MODE |
Get the current boot mode. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_SET_BOOT_MODE |
Set the current boot mode. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_GET_HOB_LIST |
Get the HOB list. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_CREATE_HOB |
Create a HOB. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
Progress cont |
EFI_SW_PS_PC_FFS_FIND_NEXT_VOLUME |
Find the next FFS formatted firmware volume. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
EFI_SW_PS_PC_FFS_FIND_NEXT_FILE |
Find the next FFS file. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_FFS_FIND_SECTION_DATA |
Find a section in an FFS file. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_INSTALL_PEI_MEMORY |
Install the PEI memory. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_ALLOCATE_PAGES |
Allocate pages from the memory heap. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_ALLOCATE_POOL |
Allocate from the memory heap. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_COPY_MEM |
Copy memory. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_SET_MEM |
Set a memory range to a specific value. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_RESET_SYSTEM |
System reset. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_FFS_FIND_FILE_BY_NAME |
Find a file in a firmware volume by name. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_FFS_GET_FILE_INFO |
Get information about a file in a firmware volume. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_FFS_GET_VOLUME_INFO |
Get information about a firmware volume. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_PS_PC_FFS_REGISTER _FOR_SHADOW |
Register a module to be shadowed after permanent memory is discovered. See the PEI CIS. |
None |
|
0x1017-0x7fff |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
EFI_SW_PS_EC_RESET_NOT_AVAILABLE |
ResetSystem() PEI Service is failed because Reset PPI is not available. |
None |
EFI_SW_PS_EC_MEMORY_INSTALLED _TWICE |
InstallPeiMemory() PEI Service is called more than once. |
None |
|
0x1002 0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
6.5.6.2. Boot Services Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any boot service present in the UEFI Boot Services Table.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass. These progress codes are reported by the code that provides the specified boot service and not by the module that invokes the given boot service.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_BS_PC_RAISE_TPL |
Raise the task priority level service; see UEFI Specification. This code is an invalid operation because the status code driver uses this boot service. The status code driver cannot report its own status codes. |
None |
EFI_SW_BS_PC_RESTORE_TPL |
Restore the task priority level service; see UEFI Specification. This code is an invalid operation because the status code driver uses this boot service. The status code driver cannot report its own status codes. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_ALLOCATE_PAGE |
Allocate page service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_FREE_PAGES |
Free page service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_GET_MEMORY_MAP |
Get memory map service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_ALLOCATE_POOL |
Allocate pool service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_FREE_POOL |
Free pool service see; UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_CREATE_EVENT |
CreateEvent service see; UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_SET_TIMER |
Set timer service see; UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_WAIT_FOR_EVENT |
Wait for event service see; UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
Progress cont |
EFI_SW_BS_PC_SIGNAL_EVENT |
Signal event service; see UEFI Specification. This code is an invalid operation because the status code driver uses this boot service. The status code driver cannot report its own status codes. |
None |
EFI_SW_BS_PC_CLOSE_EVENT |
Close event service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_CHECK_EVENT |
Check event service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_INSTALL _PROTOCOL_INTERFACE |
Install protocol interface service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_REINSTALL _PROTOCOL_INTERFACE |
Reinstall protocol interface service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_UNINSTALL _PROTOCOL_INTERFACE |
Uninstall protocol interface service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_HANDLE _PROTOCOL |
Handle protocol service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_PC _HANDLE_PROTOCOL |
PC handle protocol service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_REGISTER _PROTOCOL_NOTIFY |
Register protocol notify service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_LOCATE _HANDLE |
Locate handle service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_INSTALL _CONFIGURATION_TABLE |
Install configuration table service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_LOAD_IMAGE |
Load image service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_START_IMAGE |
Start image service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EF I_SW_BS_PC_EXIT |
Exit service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_UNLOAD _IMAGE |
Unload image service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_EXIT_BOOT _SERVICES |
Exit boot services service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_GET_NEXT _MONOTONIC_COUNT |
Get next monotonic count service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI _SW_BS_PC_STALL |
Stall service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_SET_WATCHDOG _TIMER |
Set watchdog timer service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_CONNECT _CONTROLLER |
Connect controller service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
Progress cont |
EFI_SW_BS_PC_DISCONNECT _CONTROLLER |
Disconnect controller service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
EFI_SW_BS_PC_OPEN_PROTOCOL |
Open protocol service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_CLOSE_PROTOCOL |
Close protocol service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_OPEN_PROTOCOL _INFORMATION |
Open protocol Information service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_PROTOCOLS _PER_HANDLE |
Protocols per handle service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_LOCATE _HANDLE_BUFFER |
Locate handle buffer service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_LOCATE_PROTOCOL |
Locate protocol service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
E FI_SW_BS_PC_INSTALL_MULTIPLE _PROTOCOL_INTERFACES |
Install multiple protocol interfaces service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_UNINSTALL_MULTIPLE _PROTOCOL_INTERFACES |
Uninstall multiple protocol interfaces service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_CALCULATE _CRC_32 |
Calculate CRC32 service; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_COPY_MEM |
Copy memory; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_SET_MEM |
Set memory to a specific value; see UEFI Specification |
None |
|
EFI_SW_BS_PC_CREATE_EVENT_EX |
Create an event and optionally associate it with an event group. See the UEFI Specification |
None |
|
0x102b-0x7fff |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
|
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
6.5.6.3. Runtime Services Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any runtime service present in the UEFI Runtime Services Table.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that
are defined for the Host Software class, the table below
lists the additional codes for this subclass. For obvious
reasons, the runtime service ReportStatusCode() cannot
report status codes related to the progress of the
ReportStatusCode() function.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_RS_PC_GET_TIME |
Get time service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
EFI_SW_RS_PC_SET_TIME |
Set time service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_GET _WAKEUP_TIME |
Get wakeup time service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_SET _WAKEUP_TIME |
Set wakeup time service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_SET _VIRTUAL_ADDRESS_MAP |
Set virtual address map service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_CONVERT _POINTER |
Convert pointer service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_GET _VARIABLE |
Get variable service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_GET_NEXT _VARIABLE_NAME |
Get next variable name service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_SET _VARIABLE |
Set variable service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_GET_NEXT _HIGH_MONOTONIC_COUNT |
Get next high monotonic count service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_RESET _SYSTEM |
Reset system service; see UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_UPDATE _CAPSULE |
Update a capsule. See the UEFI Specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_QUERY_CAPSULE _CAPABILITIES |
Query firmware support for capsulate capabilities.See the UEFI specification. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_RS_PC_QUERY_VARIABLE _INFO |
Query firmware support for EFI variables. See the UEFI specification. |
None |
|
0x100E |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
6.5.6.4. DXE Services Subclass¶
This subclass applies to any DXE Service that present in the UEFI DXE Services Table.
Progress and Error Code Operations
In addition to the standard progress and error codes that are defined for the Host Software class, the table below lists the additional codes for this subclass.
See “Related Definitions” below for links to the definitions of code listed in this table.
Type of Code |
Operation |
Description |
Extended Data |
|---|---|---|---|
Progress |
EFI_SW_DS_PC_ADD _MEMORY_SPACE |
Add memory to GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
EFI_SW_DS_PC_ALLOCATE _MEMORY_SPACE |
Allocate memory from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_FREE _MEMORY_SPACE |
Free memory from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_REMOVE _MEMORY_SPACE |
Remove memory from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_GET _MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR |
Get memory descriptor from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_SET _MEMORY_SPACE_ATTRIBUTES |
Set attributes of memory in GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_GET_MEMORY _SPACE_MAP |
Get map of memory space from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_ADD _IO_SPACE |
Add I/O to GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_ALLOCATE _IO_SPACE |
Allocate I/O from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_FREE _IO_SPACE |
Free I/O from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_REMOVE_IO _SPACE |
Remove I/O space from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_GET_IO_SPACE _DESCRIPTOR |
Get I/O space descriptor from GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_GET_IO _SPACE_MAP |
Get map of I/O space from the GCD. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_DISPATCH |
Dispatch DXE drivers from a firmware volume. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_SCHEDULE |
Clear the schedule on request flag for a driver. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_TRUST |
Promote a file to trusted state. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
EFI_SW_DS_PC_PROCESS _FIRMWARE_VOLUME |
Dispatch all drivers in a firmware volume. See DXE CIS. |
None |
|
0x1011-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
|
Error |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
NA |
See the following topic in Software Classes for definitions of the subclass-specific operations listed above:
Progress Code Definitions
6.6. Code Definitions¶
This section provides the code definitions for the following data types and structures for status codes:
Data structures and types that are common to all status codes
Progress, error, and debug codes that are common to all classes
Class definitions
Subclass definitions for each status code class
Extended error data
This section defines the data structures that are common to all status codes. For class- and subclass-specific information, see Class Definitions.
6.6.1. Data Structures¶
See the ReportStatusCode() declaration in Volume 2 of this specification for definitions and details on the following basic data structures:
EFI_STATUS_CODE_TYPEand defined severitiesEFI_PROGRESS_CODEEFI_ERROR_CODEEFI_DEBUG_CODEEFI_STATUS_CODE_VALUE
6.6.2. Extended Data Header¶
6.6.2.1. EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA¶
Summary
The definition of the status code extended data header. The
data will follow HeaderSize bytes from the beginning of the
structure and is Size bytes long.
typedef struct {
UINT16 HeaderSize;
UINT16 Size;
EFI_GUID Type;
} EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA;
Parameters
HeaderSizeThe size of the structure. This is specified to enable future expansion.
SizeThe size of the data in bytes. This does not include the size of the header structure.
TypeThe GUID defining the type of the data. The standard GUIDs and their associated data structures are defined in this specification.
Description
The status code information may be accompanied by optional
extended data. The extended data begins with a header. The
header contains a Type field that represents the format of
the extended data following the header. This specification
defines two GUIDs and their meaning. If these GUIDs are used,
the extended data contents must follow this specification.
Extended data formats that are not compliant with this
specification are permitted, but they must use different GUIDs.
The format of the extended data header is defined in Platform
Initialization DXE CIS , but it is duplicated here for
convenience.
6.6.2.2. EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA_TYPE_STRING_GUID¶
Summary
Defines a string type of extended data.
GUID
#define EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA_TYPE_STRING_GUID \
{ 0x92D11080, 0x496F, 0x4D95, 0xBE, 0x7E, 0x03, 0x74, \
0x88, 0x38, 0x2B, 0x0A }
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_STRING_TYPE StringType;
EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING String;
} EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data. D
ataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_DATA) - HeaderSizeandDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA_TYPE_STRING_GUID.
StringTypeSpecifies the format of the data in
String. TypeEFI_STRING_TYPEis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
StringA pointer to the extended data. The data follows the format specified by
StringType. TypeEFI_STRING_TYPEis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
Description
This data type defines a string type of extended data. A string can accompany any status code. The string can provide additional information about the status code. The string can be ASCII, Unicode, or a Human Interface Infrastructure (HII) token/GUID pair.
//**********************************************
// EFI_STRING_TYPE
//**********************************************
typedef enum {
EfiStringAscii,
EfiStringUnicode,
EfiStringToken
} EFI_STRING_TYPE;
EfiStringAsciiA
NULL-terminated ASCII string.EfiStringUnicodeA double
NULL-terminated Unicode string.EfiStringTokenAn
EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_TOKENrepresenting the string. The actual string can be obtained by querying the HII database.
//**********************************************
// EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_TOKEN
//**********************************************
//
// HII string token
//
typedef struct {
EFI_HII_HANDLE Handle;
EFI_STRING_ID Token;
} EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_TOKEN;
HandleThe HII package list which contains the string.
Handleis a dynamic value that may not be the same for different boots. TypeEFI_HII_HANDLEis defined inEFI_HII_DATABASE_PROTOCOL.NewPackageList()in theUEFI Specification.TokenWhen combined with
Handle, the string token can be used to retrieve the string. TypeEFI_STRING_IDis defined inEFI_IFR_OP_HEADERin theUEFI Specification.
//**********************************************
// EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING
//**********************************************
//
// String structure
//
typedef union {
CHAR8 *Ascii;
CHAR16 *Unicode;
EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_TOKEN Hii;
} EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING;
AsciiASCII formatted string.
UnicodeUnicode formatted string.
HiiHII handle/token pair. Type
EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_TOKENis defined above.
6.6.2.3. EFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID¶
Summary
Indicates that the format of the accompanying data depends upon the status code value but follows this specification.
GUID
#define EFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID \
{0x335984bd,0xe805,0x409a,0xb8,0xf8,0xd2,0x7e, \
0xce,0x5f,0xf7,0xa6}
Description
This GUID indicates that the format of the accompanying data
depends upon the status code value but follows this
specification. This specification defines the format of the
extended data for several status code values. For example,
EFI_DEBUG_ASSERT_DATA defines the extended error data for the
error code EFI_SW_EC_ILLEGAL_SOFTWARE_STATE . The agent
reporting this error condition can use this GUID if the
extended data follows the format defined in
EFI_DEBUG_ASSERT_DATA .
If the consumer of the status code detects this GUID, it must look up the status code value to correctly interpret the contents of the extended data.
This specification declares certain ranges of status code values as OEM specific. Because this specification does not define the meaning of status codes in these ranges, the extended data for these cannot use this GUID. The OEM defining the meaning of the status codes is responsible for defining the GUID that is to be used for associated extended data.
6.6.3. Enumeration Schemes¶
6.6.3.1. Operation Code Enumeration Scheme¶
Summary
All operation codes (regardless of class and subclass) use the progress code partitioning scheme listed in the table below.
Operation |
Description |
|---|---|
0x0000-0x0FFF |
These operation codes are common to all the subclasses in a given class. These values are used to represent operations that are common to all subclasses in a given class. For example, all the I/O buses in the I/O Bus subclasses share an operation code that represents the reset operation, which is a common operation for most buses. It is possible that certain operation codes in this range will not be applicable to certain subclasses. It is also possible that the format of the extended data will vary from one subclass to another. If the subclass does not define the format of the extended data extended data is not required. These codes are reserved by this specification. |
0x1000-0x7FFF |
These operation codes are specific to the subclass and represent operations that are specific to the subclass. These codes are reserved by this specification. |
0x8000-0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
Prototype
//
// General partitioning scheme for Progress and Error Codes
// 0x0000-0x0FFF - Shared by all subclasses in a given class
// 0x1000-0x7FFF - Subclass Specific
// 0x8000-0xFFFF - OEM specific
//
#define EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC 0x1000
#define EFI_OEM_SPECIFIC 0x8000
6.6.3.2. Debug Code Enumeration Scheme¶
Summary
All classes share these debug operation codes. It is not currently expected that operation codes have a lot of meaning for debug information. Only one debug code is currently defined by this specification and it is shared by all classes and subclasses.
Debug Code |
Description |
0x0000-0x7FFF |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
0x8000-0xFFFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
Prototype
//
// Debug Code definitions for all classes and subclass
// Only one debug code is defined at this point and should
// be used for anything that gets sent to debug stream.
//
#define EFI_DC_UNSPECIFIED 0x0
6.6.4. Common Extended Data Formats¶
This section specifies formats for the extended data included in a variety of status codes.
6.6.4.1. EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA¶
Summary
Extended data about the device path, which is used for many errors and progress codes to point to the device.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA ``DataHeader`` ;
// EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL ``DevicePath`` ;
} EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA).DataHeader.Sizeshould be the size of variable-lengthDevicePath, andDataHeader.Sizeis zero for a virtual device that does not have a device path.DataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
DevicePathThe device path to the controller or the hardware device. Note that this parameter is a variable-length device path structure and not a pointer to such a structure. This structure is populated only if it is a physical device. For virtual devices, the Size field in
DataHeaderis set to zero and this field is not populated.
Description
The device path is used to point to the physical device in case
there is more than one device belonging to the same subclass.
For example, the system may contain two USB keyboards and one
PS/2* keyboard. The driver that parses the status code can use
the device path extended data to differentiate between the
three. The index field is not useful in this case because there
is no standard numbering convention. Device paths are preferred
over using device handles because device handles for a given
device can change from one boot to another and do not mean
anything beyond Boot Services time. In certain cases, the bus
driver may not create a device handle for a given device if it
detects a critical error. In these cases, the device path
extended data can be used to refer to the device, but there may
not be any device handles with an instance of
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL that matches DevicePath . The
variable device path structure is included in this structure to
make it self sufficient.
6.6.4.2. EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE_EXTENDED_DATA¶
Summary
Extended data about the device handle, which is used for many errors and progress codes to point to the device.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_HANDLE Handle;
} EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE_EXTENDED_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE_EXTENDED_DATA)-HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
HandleThe device handle.
Description
The handle of the device with which the progress or error code is associated. The handle is guaranteed to be accurate only at the time the status code is reported. Handles are dynamic entities between boots, so handles cannot be considered to be valid if the system has reset subsequent to the status code being reported. Handles may be used to determine a wide variety of useful information about the source of the status code.
6.6.4.3. EFI_RESOURCE_ALLOC_FAILURE_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing a PCI resource allocation error.
Prototype
- Note:
The following structure contains variable-length fields and cannot be defined as a C-style structure.
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
UINT32 Bar;
UINT16 DevicePathSize;
UINT16 ReqResSize;
UINT16 AllocResSize;
// EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL DevicePath;
// UINT8 ReqRes[...];
// UINT8 AllocRes[...];
} EFI_RESOURCE_ALLOC_FAILURE_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould be sizeof(EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA), DataHeader.Sizeshould be(DevicePathSize + DevicePathSize + DevicePathSize+sizeof(UINT32) + 3 \* sizeof (UINT16) ),andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
BarThe PCI BAR. Applicable only for PCI devices. Ignored for all other devices.
DevicePathSizeDevicePathSizeshould be zero if it is a virtual device that is not associated with a device path. Otherwise, this parameter is the length of the variable-lengthDevicePath.
ReqResSizeRepresents the size the
ReqResparameter.ReqResSizeshould be zero if the requested resources are not provided as a part of extended data.
AllocResSizeRepresents the size the
AllocResparameter.AllocResSizeshould be zero if the allocated resources are not provided as a part of extended data.
DevicePathThe device path to the controller or the hardware device that did not get the requested resources. Note that this parameter is the variable-length device path structure and not a pointer to this structure.
ReqResThe requested resources in the format of an ACPI 2.0 resource descriptor. This parameter is not a pointer; it is the complete resource descriptor.
AllocResThe allocated resources in the format of an ACPI 2.0 resource descriptor. This parameter is not a pointer; it is the complete resource descriptor.
Description
This extended data conveys details for a PCI resource allocation failure error. See the PCI specification and the ACPI specification for details on PCI resource allocations and the format for resource descriptors. This error does not detail why the resource allocation failed. It may be due to a bad resource request or a lack of available resources to satisfy a valid request. The variable device path structure and the resource structures are included in this structure to make it self sufficient.
6.7. Class Definitions¶
Summary
Classes correspond to broad types of system pieces. These types are chosen to provide a reasonable initial classification of the system entity whose status is represented. There are three classes of hardware and one class for software. These classes are listed in the table below. Each class is made up of several subclasses. See “Types of Status Codes” for descriptions of each of these classes.
Type of Class |
Class Name |
Data Type Name |
|---|---|---|
Hardware |
Computing Unit |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT |
User-Accessible Peripherals |
EFI_PERIPHERAL |
|
I/O Bus |
EFI_IO_BUS |
|
Software |
Host Software |
EFI_SOFTWARE |
Prototype
//
// Class definitions
// Values of 4-127 are reserved for future use by this
// specification.
// Values in the range 128-255 are reserved for OEM use.
//
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT 0x00000000
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL 0x01000000
#define EFI_IO_BUS 0x02000000
#define EFI_SOFTWARE 0x03000000
6.7.1. Computing Unit Class¶
The table below lists the subclasses defined in the Computing Unit class. See the following section for their code definitions.
Subclass |
Code Name |
Unspecified |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_UNSPECIFIED |
Host processor |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_HOST_PROCESSOR |
Firmware processor |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_FIRMWARE_PROCESSOR |
Service processor |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_SERVICE_PROCESSOR |
I/O processor |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_IO_PROCESSOR |
Cache |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_CACHE |
Memory |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MEMORY |
Chipset |
EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_CHIPSET |
6.7.1.1. Subclass Definitions¶
Summary
Definitions for the Computing Unit subclasses. See Subclasses in Computing Unit Class for descriptions of these subclasses.
Prototype
//
// Computing Unit Subclass definitions.
// Values of 8-127 are reserved for future use by this
// specification.
// Values of 128-255 are reserved for OEM use.
//
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_UNSPECIFIED \
(EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_HOST_PROCESSOR \
(EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT | 0x00010000)
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_FIRMWARE_PROCESSOR \
(EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT | 0x00020000)
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_IO_PROCESSOR \
(EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT | 0x00030000)
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_CACHE \
(EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT | 0x00040000)
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MEMORY \
(EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT | 0x00050000)
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_CHIPSET \
(EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT | 0x00060000)
6.7.1.2. Progress Code Definitions¶
Summary
Progress code definitions for the Computing Unit class and all subclasses. See Progress Code Operations in “Computing Unit Class” for descriptions of these progress codes. The following subclasses define additional subclass-specific progress code operations, which are included below:
Host processor
Cache
Memory
Prototype
//
// Computing Unit Class Progress Code definitions.
// These are shared by all subclasses.
//
#define EFI_CU_PC_INIT_BEGIN 0x00000000
#define EFI_CU_PC_INIT_END 0x00000001
//
// Computing Unit Unspecified Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Computing Unit Host Processor Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_POWER_ON_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_CACHE_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_RAM_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_MEMORY_CONTROLLER_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_IO_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_BSP_SELECT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_BSP_RESELECT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006)
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_AP_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000007)
#define EFI_CU_HP_PC_SMM_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000008)
//
// Computing Unit Firmware Processor Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Computing Unit IO Processor Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Computing Unit Cache Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_CU_CACHE_PC_PRESENCE_DETECT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CU_CACHE_PC_CONFIGURATION \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
//
// Computing Unit Memory Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_SPD_READ \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_PRESENCE_DETECT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_TIMING \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_CONFIGURING \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_OPTIMIZING \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_PC_TEST \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006)
//
// Computing Unit Chipset Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_PEI_CAR_SB_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_PEI_CAR_NB_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_PEI_MEM_SB_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_PEI_MEM_NB_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_HB_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_NB_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_NB_SMM_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_SB_RT_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000007)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_SB_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000008)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_SB_SMM_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000009)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_PC_DXE_SB_DEVICES_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x0000000A)
6.7.1.3. Error Code Definitions¶
Summary
Error code definitions for the Computing Unit class and all subclasses. See Error Code Operations in Computing Unit Class for descriptions of these error codes.
The following subclasses define additional subclass-specific error code operations, which are included below:
Host processor
Firmware processor
Cache
Memory
Prototype
//
// Computing Unit Class Error Code definitions.
// These are shared by all subclasses.
//
#define EFI_CU_EC_NON_SPECIFIC 0x00000000
#define EFI_CU_EC_DISABLED 0x00000001
#define EFI_CU_EC_NOT_SUPPORTED 0x00000002
#define EFI_CU_EC_NOT_DETECTED 0x00000003
#define EFI_CU_EC_NOT_CONFIGURED 0x00000004
//
// Computing Unit Unspecified Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Computing Unit Host Processor Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_INVALID_TYPE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_INVALID_SPEED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_MISMATCH \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_TIMER_EXPIRED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_SELF_TEST \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_INTERNAL \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_THERMAL \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_LOW_VOLTAGE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000007)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_HIGH_VOLTAGE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000008)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_CACHE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000009)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_MICROCODE_UPDATE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x0000000A)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_CORRECTABLE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x0000000B)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_UNCORRECTABLE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x0000000C)
#define EFI_CU_HP_EC_NO_MICROCODE_UPDATE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x0000000D)
//
// Computing Unit Firmware Processor Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_CU_FP_EC_HARD_FAIL \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CU_FP_EC_SOFT_FAIL \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_CU_FP_EC_COMM_ERROR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
//
// Computing Unit IO Processor Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Computing Unit Cache Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_CU_CACHE_EC_INVALID_TYPE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CU_CACHE_EC_INVALID_SPEED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_CU_CACHE_EC_INVALID_SIZE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_CU_CACHE_EC_MISMATCH \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
//
// Computing Unit Memory Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_INVALID_TYPE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_INVALID_SPEED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_CORRECTABLE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_UNCORRECTABLE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_SPD_FAIL \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_INVALID_SIZE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_MISMATCH \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_S3_RESUME_FAIL\
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000007)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_UPDATE_FAIL \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000008)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_NONE_DETECTED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000009)
#define EFI_CU_MEMORY_EC_NONE_USEFUL \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x0000000A)
//
// Computing Unit Chipset Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_CHIPSET_EC_BAD_BATTERY \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_EC_DXE_NB_ERROR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_EC_DXE_SB_ERROR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_CHIPSET_EC_INTRUDER_DETECT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
6.7.1.4. Extended Data Formats¶
6.7.1.4.1. Host Processor Subclass¶
6.7.1.5. EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_VOLTAGE_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure provides details about the computing unit voltage error.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_EXP_BASE10_DATA Voltage;
EFI_EXP_BASE10_DATA Threshold;
} EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_VOLTAGE_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_VOLTAGE_ERROR_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
VoltageThe voltage value at the time of the error.
ThresholdThe voltage threshold.
Description
This structure provides the voltage at the time of error. It also provides the threshold value indicating the minimum or maximum voltage that is considered an error. If the voltage is less than the threshold, the error indicates that the voltage fell below the minimum acceptable value. If the voltage is greater than the threshold, the error indicates that the voltage rose above the maximum acceptable value.
6.7.1.6. EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MICROCODE_UPDATE_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure provides details about the microcode update error.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
UINT32 Version;
} EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MICROCODE_UPDATE_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MICROCODE_UPDATE_ERROR_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
VersionThe version of the microcode update from the header.
6.7.1.7. EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_TIMER_EXPIRED_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure provides details about the computing unit timer expiration error.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_EXP_BASE10_DATA TimerLimit;
} EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_TIMER_EXPIRED_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_TIMER_EXPIRED_ERROR_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
TimerLimitThe number of seconds that the computing unit timer was configured to expire.
Description
The timer limit provides the timeout value of the timer prior to expiration.
6.7.1.8. EFI_HOST_PROCESSOR_MISMATCH_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data for processor mismatch errors.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
UINT32 Instance;
UINT16 Attributes;
} EFI_HOST_PROCESSOR_MISMATCH_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI\_ HOST_PROCESSOR_MISMATCH_ERROR_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
InstanceThe unit number of the computing unit that does not match.
AttributesThe attributes describing the failure. See “Related Definitions” below for the type declarations.
Description
This provides information to indicate which processors
mismatch, and how they mismatch. The status code contains the
instance number of the processor that is in error. This
structure’s Instance indicates the second processor that does
not match. This differentiation allows the consumer to
determine which two processors do not match. The Attributes
indicate what mismatch is being reported. Because Attributes
is a bit field, more than one mismatch can be reported with one
error code.
//***********************************************************
// EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_ATTRIBUTES
//***********************************************************
//
// All other attributes are reserved for future use and
// must be initialized to 0.
//
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_SPEED 0x0001
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_FSB_SPEED 0x0002
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_FAMILY 0x0004
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_MODEL 0x0008
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_STEPPING 0x0010
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_CACHE_SIZE 0x0020
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_OEM1 0x1000
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_OEM2 0x2000
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_OEM3 0x4000
#define EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_MISMATCH_OEM4 0x8000
6.7.1.9. EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_THERMAL_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure provides details about the computing unit thermal failure.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_EXP_BASE10_DATA Temperature;
EFI_EXP_BASE10_DATA Threshold;
} EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_THERMAL_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_THERMAL_ERROR_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
TemperatureThe thermal value at the time of the error.
ThresholdThe thermal threshold.
Description
This structure provides the temperature at the time of error. It also provides the threshold value indicating the minimum temperature that is considered an error.
6.7.1.10. EFI_CACHE_INIT_DATA¶
Summary
This structure provides cache initialization data.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
UINT32 Level;
EFI_INIT_CACHE_TYPE Type;
} EFI_CACHE_INIT_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof(EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof(EFI_CACHE_INIT_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
LevelThe cache level. Starts with 1 for level 1 cache.
TypeThe type of cache. Type
EFI_INIT_CACHE_TYPEis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
Description
This structure contains the cache level and type information.
//***********************************************
// EFI_INIT_CACHE_TYPE
//***********************************************
// Valid cache types
typedef enum {
EfiInitCacheDataOnly,
EfiInitCacheInstrOnly,
EfiInitCacheBoth,
EfiInitCacheUnspecified
} EFI_INIT_CACHE_TYPE;
6.7.1.11. EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_CPU_DISABLED_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure provides information about the disabled computing unit.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
UINT32 Cause;
BOOLEAN SoftwareDisabled*;
} EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_CPU_DISABLED_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_COMPUTING_UNIT_CPU_DISABLED_ERROR_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
CauseThe reason for disabling the processor. See “Related Definitions” below for defined values.
SoftwareDisabledTRUEif the processor is disabled via software means such as not listing it in the ACPI tables. Such a processor will respond to Interprocessor Interrupts (IPIs). FALSE if the processor is hardware disabled, which means it is invisible to software and will not respond to IPIs.
Description
This structure provides details as to why and how the computing unit was disabled. The causes should cover the typical reasons a processor would be disabled. How the processor was disabled is important because there are distinct differences between hardware and software disabling.
//************************************************************
// EFI_CPU_STATE_CHANGE_CAUSE
//************************************************************
typedef UINT32 EFI_CPU_STATE_CHANGE_CAUSE;
//
// The reason a processor was disabled
//
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_INTERNAL_ERROR 0x0001
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_THERMAL_ERROR 0x0002
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_SELFTEST_FAILURE 0x0004
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_PREBOOT_TIMEOUT 0x0008
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_FAILED_TO_START 0x0010
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_CONFIG_ERROR 0x0020
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_USER_SELECTION 0x0080
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_BY_ASSOCIATION 0x0100
#define EFI_CPU_CAUSE_UNSPECIFIED 0x8000
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_INTERNAL_ERROR |
The processor was disabled because it signaled an internal error (IERR). |
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_THERMAL_ERROR |
The processor was disabled because of a thermal error. |
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_SELFTEST_FAILURE |
The processor was disabled because it failed BIST. |
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_PREBOOT_TIMEOUT |
The processor started execution, but it timed out during a particular task and was therefore disabled. |
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_FAILED_TO_START |
The processor was disabled because it failed to start execution (FRB-3 timeout). |
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_CONFIG_ERROR |
The processor was disabled due to a configuration error. |
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_USER_SELECTION |
The processor state was changed due to user selection. Applicable to enabling and disabling of processors. |
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_BY_ASSOCIATION |
The processor state was changed due because it shared the state with another processor and the state of the other processor was changed. |
EFI_CPU_CAUSE_UNSPECIFIED |
The CPU state was changed due to unspecified reason. Applicable to enabling and disabling of processors. |
Summary
6.7.1.12. EFI_MEMORY_EXTENDED_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing a memory error.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_GRANULARITY Granularity;
EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_OPERATION Operation;
UINT32 Syndrome;
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS Address;
UINTN Resolution;
} EFI_MEMORY_EXTENDED_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_MEMORY_EXTENDED_ERROR_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
GranularityThe error granularity type. Type
EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_GRANULARITYis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
OperationThe operation that resulted in the error being detected. Type
EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_OPERATIONis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
SyndromeThe error syndrome, vendor-specific ECC syndrome, or CRC data associated with the error. If unknown, should be initialized to 0.
AddressThe physical address of the error. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined inAllocatePages()in the UEFI Specification .
ResolutionThe range, in bytes, within which the error address can be determined.
Description
This structure provides specific details about the memory error that was detected. It provides enough information so that consumers can identify the exact failure and provides enough information to enable corrective action if necessary.
//*********************************************************
// EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_GRANULARITY
//*********************************************************
typedef UINT8 EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_GRANULARITY;
//
// Memory Error Granularities
//
#define EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_OTHER 0x01
#define EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_UNKNOWN 0x02
#define EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_DEVICE 0x03
#define EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_PARTITION 0x04
//*********************************************************
// EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_OPERATION
//*********************************************************
typedef UINT8 EFI_MEMORY_ERROR_OPERATION;
//
// Memory Error Operations
//
#define EFI_MEMORY_OPERATION_OTHER 0x01
#define EFI_MEMORY_OPERATION_UNKNOWN 0x02
#define EFI_MEMORY_OPERATION_READ 0x03
#define EFI_MEMORY_OPERATION_WRITE 0x04
#define EFI_MEMORY_OPERATION_PARTIAL_WRITE 0x05
6.7.1.13. EFI_STATUS_CODE_DIMM_NUMBER¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing a DIMM.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
UINT16 Array;
UINT16 Device;
} EFI_STATUS_CODE_DIMM_NUMBER;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DIMM_NUMBER) - HeaderSize, andDataHeader. Type should beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
ArrayThe memory array number.
DeviceThe device number within that
Array.
Description
This extended data provides some context that consumers can use
to locate a DIMM within the overall memory scheme. The Array
and Device numbers may indicate a specific DIMM, or they may
be populated with the group definitions in “Related
Definitions” below.
//
// Definitions to describe Group Operations
// Many memory init operations are essentially group
// operations.
//
#define EFI_MULTIPLE_MEMORY_DEVICE_OPERATION 0xfffe
#define EFI_ALL_MEMORY_DEVICE_OPERATION 0xffff
#define EFI_MULTIPLE_MEMORY_ARRAY_OPERATION 0xfffe
#define EFI_ALL_MEMORY_ARRAY_OPERATION 0xffff
EFI_MULTIPLE_MEMORY_DEVICE_OPERATION |
A definition to describe that the operation is performed on multiple devices within the array. |
EFI_ALL_MEMORY_DEVICE_OPERATION |
A definition to describe that the operation is performed on all devices within the array. |
EFI _MULTIPLE_MEMORY_ARRAY_OPERATION |
A definition to describe that the operation is performed on multiple arrays. |
EFI_ALL_MEMORY_ARRAY_OPERATION |
A definition to describe that the operation is performed on all the arrays. |
6.7.1.14. EFI_MEMORY_MODULE_MISMATCH_ERROR_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing memory modules that do not match.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DIMM_NUMBER Instance;
} EFI_MEMORY_MODULE_MISMATCH_ERROR_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould be sizeof (EFI_MEMORY_MODULE_MISMATCH_ERROR_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
InstanceThe instance number of the memory module that does not match. See the definition for type
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DIMM_NUMBER.
Description
This extended data may be used to convey the specifics of memory modules that do not match.
6.7.1.15. EFI_MEMORY_RANGE_EXTENDED_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing a memory range.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS Start;
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS Length;
} EFI_MEMORY_RANGE_EXTENDED_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_MEMORY_RANGE_EXTENDED_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
StartThe starting address of the memory range. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined inAllocatePages()in the UEFI Specification .
LengthThe length in bytes of the memory range.
Description
This extended data may be used to convey the specifics of a memory range. Ranges are specified with a start address and a length.
6.7.2. User-Accessible Peripherals Class¶
The table below lists the subclasses defined in the User-Accessible Peripheral class. See the following subsection for their code definitions.
Subclass |
Code Name |
|---|---|
Unspecified |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_UNSPECIFIED |
Keyboard |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_KEYBOARD |
Mouse |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_MOUSE |
Local console |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_LOCAL_CONSOLE |
Remote console |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_REMOTE_CONSOLE |
Serial port |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_SERIAL_PORT |
Parallel port |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_PARALLEL_PORT |
Fixed media |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_FIXED_MEDIA |
Removable media |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_REMOVABLE_MEDIA |
Audio input |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_AUDIO_INPUT |
Audio output |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_AUDIO_OUTPUT |
LCD device |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_LCD_DEVICE |
Network device |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_NETWORK |
Docking Station |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_DOCKING |
Trusted Platform Module |
EFI_PERIPHERAL_TPM |
0x0F-0x7F |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
0x80-0xFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
6.7.2.1. Subclass Definitions¶
Summary
Definitions for the User-Accessible Peripheral subclasses. See Subclasses in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for descriptions of these subclasses.
Prototype
//
// Peripheral Subclass definitions.
// Values of 12-127 are reserved for future use by this
// specification.
// Values of 128-255 are reserved for OEM use.
//
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_UNSPECIFIED \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_KEYBOARD \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00010000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_MOUSE \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00020000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_LOCAL_CONSOLE \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00030000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_REMOTE_CONSOLE \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00040000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_SERIAL_PORT \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00050000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_PARALLEL_PORT \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00060000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_FIXED_MEDIA \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00070000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_REMOVABLE_MEDIA \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00080000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_AUDIO_INPUT \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x00090000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_AUDIO_OUTPUT \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x000A0000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_LCD_DEVICE \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x000B0000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_NETWORK \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x000C0000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_DOCKING \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x000D0000)
#define EFI_PERIPHERAL_TPM \
(EFI_PERIPHERAL | 0x000E0000)
6.7.2.2. Progress Code Definitions¶
Summary
Progress code definitions for the User-Accessible Peripheral class and all subclasses. See Progress Code Operations in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for descriptions of these progress codes.
The following subclasses define additional subclass-specific progress code operations, which are included below:
Keyboard
Mouse
Serial port
Prototype
//
// Peripheral Class Progress Code definitions.
// These are shared by all subclasses.
//
#define EFI_P_PC_INIT 0x00000000
#define EFI_P_PC_RESET 0x00000001
#define EFI_P_PC_DISABLE 0x00000002
#define EFI_P_PC_PRESENCE_DETECT 0x00000003
#define EFI_P_PC_ENABLE 0x00000004
#define EFI_P_PC_RECONFIG 0x00000005
#define EFI_P_PC_DETECTED 0x00000006
#define EFI_P_PC_REMOVED 0x00000007
//
// Peripheral Class Unspecified Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Keyboard Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_P_KEYBOARD_PC_CLEAR_BUFFER \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_P_KEYBOARD_PC_SELF_TEST \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
//
// Peripheral Class Mouse Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_P_MOUSE_PC_SELF_TEST \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
//
// Peripheral Class Local Console Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Remote Console Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Serial Port Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_P_SERIAL_PORT_PC_CLEAR_BUFFER \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
//
// Peripheral Class Parallel Port Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Fixed Media Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Removable Media Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Audio Input Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Audio Output Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class LCD Device Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Network Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
6.7.2.3. Error Code Definitions¶
Summary
Error code definitions for the User-Accessible Peripheral class and all subclasses. See Error Code Operations in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for descriptions of these error codes.
The following subclasses define additional subclass-specific error code operations, which are included below:
Keyboard
Mouse
Prototype
//
// Peripheral Class Error Code definitions.
// These are shared by all subclasses.
//
#define EFI_P_EC_NON_SPECIFIC 0x00000000
#define EFI_P_EC_DISABLED 0x00000001
#define EFI_P_EC_NOT_SUPPORTED 0x00000002
#define EFI_P_EC_NOT_DETECTED 0x00000003
#define EFI_P_EC_NOT_CONFIGURED 0x00000004
#define EFI_P_EC_INTERFACE_ERROR 0x00000005
#define EFI_P_EC_CONTROLLER_ERROR 0x00000006
#define EFI_P_EC_INPUT_ERROR 0x00000007
#define EFI_P_EC_OUTPUT_ERROR 0x00000008
#define EFI_P_EC_RESOURCE_CONFLICT \
0x00000009
//
// Peripheral Class Unspecified Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Keyboard Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_P_KEYBOARD_EC_LOCKED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_P_KEYBOARD_EC_STUCK_KEY \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_P_KEYBOARD_EC_BUFFER_FULL \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
//
// Peripheral Class Mouse Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_P_MOUSE_EC_LOCKED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
//
// Peripheral Class Local Console Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Remote Console Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Serial Port Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Parallel Port Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Fixed Media Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Removable Media Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Audio Input Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Audio Output Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class LCD Device Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Peripheral Class Network Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
6.7.2.4. Extended Data Formats¶
The User-Accessible Peripheral class uses the following extended error data definitions:
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATAEFI_RESOURCE_ALLOC_FAILURE_ERROR_DATA
See Common Extended Data Formats for definitions.
6.7.3. I/O Bus Class¶
The table below lists the subclasses defined in the I/O Bus class. See Subclass Definitions for their code definitions.
Subclass |
Code Name |
Unspecified |
EFI_IO_BUS_UNSPECIFIED |
PCI |
EFI_IO_BUS_PCI |
USB |
EFI_IO_BUS_USB |
InfiniBand* architecture |
EFI_IO_BUS_IBA |
AGP |
EFI_IO_BUS_AGP |
PC card |
EFI_IO_BUS_PC_CARD |
Low pin count (LPC) |
EFI_IO_BUS_LPC |
SCSI |
EFI_IO_BUS_SCSI |
ATA/ATAPI/SATA |
EFI_IO_BUS_ATA_ATAPI |
Fibre Channel |
EFI_IO_BUS_FC |
IP network |
EFI_IO_BUS_IP_NETWORK |
SMBus |
EFI_IO_BUS_SMBUS |
I2C |
EFI_IO_BUS_I2C |
0x0D-0x7F |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
0x80-0xFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
6.7.3.1. Subclass Definitions¶
Summary
Definitions for the I/O Bus subclasses. See Subclasses in I/O Bus Class for descriptions of these subclasses.
Prototype
//
// IO Bus Subclass definitions.
// Values of 14-127 are reserved for future use by this
// specification.
// Values of 128-255 are reserved for OEM use.
//
#define EFI_IO_BUS_UNSPECIFIED \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_PCI \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00010000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_USB \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00020000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_IBA \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00030000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_AGP \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00040000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_PC_CARD \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00050000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_LPC \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00060000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_SCSI \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00070000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_ATA_ATAPI \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00080000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_FC \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x00090000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_IP_NETWORK \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x000A0000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_SMBUS \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x000B0000)
#define EFI_IO_BUS_I2C \
(EFI_IO_BUS | 0x000C0000)
6.7.3.2. Progress Code Definitions¶
Summary
Progress code definitions for the I/O Bus class and all subclasses. See Progress Code Operations in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for descriptions of these progress codes.
The following subclasses define additional subclass-specific progress code operations, which are included below:
PCI
Prototype
//
// IO Bus Class Progress Code definitions.
// These are shared by all subclasses.
//
typedef struct _EFI_SIO_PROTOCOL EFI_SIO_PROTOCOL;
#define EFI_IOB_PC_INIT 0x00000000
#define EFI_IOB_PC_RESET 0x00000001
#define EFI_IOB_PC_DISABLE 0x00000002
#define EFI_IOB_PC_DETECT 0x00000003
#define EFI_IOB_PC_ENABLE 0x00000004
#define EFI_IOB_PC_RECONFIG 0x00000005
#define EFI_IOB_PC_HOTPLUG 0x00000006
//
// IO Bus Class Unspecified Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class PCI Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_IOB_PCI_BUS_ENUM \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_IOB_PCI_RES_ALLOC \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#defineEFI_IOB_PCI_HPC_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
//
// IO Bus Class USB Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class IBA Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class AGP Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class PC Card Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class LPC Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class SCSI Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class ATA/ATAPI Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART_ENABLE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART_DISABLE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART_OVERTHRESHOLD \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART_UNDERTHRESHOLD \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
//
// IO Bus Class FC Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class IP Network Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class SMBUS Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class I2C Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
6.7.3.3. Error Code Definitions¶
Summary
Error code definitions for the I/O Bus class and all subclasses. See Error Code Operations in User-Accessible Peripherals Class for descriptions of these error codes.
The following subclasses define additional subclass-specific error code operations, which are included below:
PCI
Prototype
// IO Bus Class Error Code definitions.
// These are shared by all subclasses.
//
#define EFI_IOB_EC_NON_SPECIFIC 0x00000000
#define EFI_IOB_EC_DISABLED 0x00000001
#define EFI_IOB_EC_NOT_SUPPORTED 0x00000002
#define EFI_IOB_EC_NOT_DETECTED 0x00000003
#define EFI_IOB_EC_NOT_CONFIGURED 0x00000004
#define EFI_IOB_EC_INTERFACE_ERROR 0x00000005
#define EFI_IOB_EC_CONTROLLER_ERROR 0x00000006
#define EFI_IOB_EC_READ_ERROR 0x00000007
#define EFI_IOB_EC_WRITE_ERROR 0x00000008
#define EFI_IOB_EC_RESOURCE_CONFLICT 0x00000009
//
// IO Bus Class Unspecified Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class PCI Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_IOB_PCI_EC_PERR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_IOB_PCI_EC_SERR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
//
// IO Bus Class USB Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class IBA Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class AGP Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class PC Card Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class LPC Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class SCSI Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class ATA/ATAPI Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART_NOTSUPPORTED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_IOB_ATA_BUS_SMART_DISABLED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
//
// IO Bus Class FC Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class IP Network Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class SMBUS Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// IO Bus Class I2C Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
6.7.3.4. Extended Data Formats¶
The I/O Bus class uses the following extended data definitions:
EFI_DEVICE_PATH_EXTENDED_DATAEFI_DEVICE_HANDLE_EXTENDED_DATAEFI_RESOURCE_ALLOC_FAILURE_ERROR_DATA
See Common Extended Data Formats for definitions.
6.7.4. Software Classes¶
The table below lists the subclasses defined in the Host Software class. See Subclass Definitions for their code definitions.
Subclass |
Code Name |
|---|---|
Unspecified |
EFI_SOFTWARE_UNSPECIFIED |
Security (SEC) |
EFI_SOFTWARE_SEC |
PEI Foundation |
EFI_SOFTWARE_PEI_CORE |
PEI module |
EFI_SOFTWARE_PEI_MODULE |
DXE Foundation |
EFI_SOFTWARE_DXE_CORE |
DXE Boot Service driver |
EFI_SOFTWARE_DXE_BS_DRIVER |
DXE Runtime Service driver |
EFI_SOFTWARE_DXE_RT_DRIVER |
SMM driver |
EFI_SOFTWARE_SMM_DRIVER |
EFI application |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_APPLICATION |
OS loader |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_OS_LOADER |
Runtime (RT) |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_RT |
EBC exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EBC_EXCEPTION |
IA 32 exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_IA32_EXCEPTION |
Itanium processor family exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_IPF_EXCEPTION |
PEI Services |
EFI_SOFTWARE_PEI_SERVICE |
EFI Boot Service |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_BOOT_SERVICE |
EFI Runtime Service |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICE |
DXE Service |
EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_DXE_SERVICE |
0x13 0x7F |
Reserved for future use by this specification. |
0x80 0xFF |
Reserved for OEM use. |
x64 software exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_X64_EXCEPTION |
ARM AArch32 software exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_ARM_EXCEPTION |
ARM AArch64 software exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_AARCH64_EXCEPTION |
RISC V software exception |
EFI_SOFTWARE_RISCV_EXCEPTION |
6.7.4.1. Subclass Definitions¶
Summary
Definitions for the Host Software subclasses. See Subclasses in Host Software Class for descriptions of these subclasses.
Prototype
//
// Software Subclass definitions.
// Values of 14-127 are reserved for future use by this
// specification.
// Values of 128-255 are reserved for OEM use.
//
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_UNSPECIFIED \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_SEC \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00010000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_PEI_CORE \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00020000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_PEI_MODULE \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00030000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_DXE_CORE \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00040000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_DXE_BS_DRIVER \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00050000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_DXE_RT_DRIVER \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00060000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_SMM_DRIVER \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00070000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_APPLICATION \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00080000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_OS_LOADER\
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00090000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_RT \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x000A0000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_AL \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x000B0000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_EBC_EXCEPTION \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x000C0000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_IA32_EXCEPTION \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x000D0000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_IPF_EXCEPTION \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x000E0000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_PEI_SERVICE \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x000F0000
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_BOOT_SERVICE \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00100000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICE \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00110000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_EFI_DXE_SERVICE \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00120000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_X64_EXCEPTION \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00130000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_ARM_EXCEPTION \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00140000)
#define EFI_SOFTWARE_AARCH64_EXCEPTION \
(EFI_SOFTWARE | 0x00150000)
6.7.4.2. Progress Code Definitions¶
Summary
Progress code definitions for the Host Software class and all subclasses. See Table 6.45 for descriptions of these progress codes.
The following subclasses define additional subclass-specific progress code operations, which are included below:
SEC
PEI Foundation
PEI Module
DXE Foundation
DXE Boot Service Driver
Runtime (RT)
PEI Services
Boot Services
Runtime Services
DXE Services
Prototype
//
// Software Class Progress Code definitions.
// These are shared by all subclasses.
//
#define EFI_SW_PC_INIT \
0x00000000
#define EFI_SW_PC_LOAD \
0x00000001
#define EFI_SW_PC_INIT_BEGIN \
0x00000002
#define EFI_SW_PC_INIT_END \
0x00000003
#define EFI_SW_PC_AUTHENTICATE_BEGIN \
0x00000004
#define EFI_SW_PC_AUTHENTICATE_END \
0x00000005
#define EFI_SW_PC_INPUT_WAIT \
0x00000006
#define EFI_SW_PC_USER_SETUP \
0x00000007
//
// Software Class Unspecified Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Software Class SEC Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_SEC_PC_ENTRY_POINT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_SEC_PC_HANDOFF_TO_NEXT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
//
// Software Class PEI Foundation Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_PC_ENTRY_POINT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_PC_HANDOFF_TO_NEXT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_PC_RETURN_TO_LAST \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
//
// Software Class PEI Module Subclass Progress Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_PEI_PC_RECOVERY_BEGIN \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_PC_CAPSULE_LOAD \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_PC_CAPSULE_START \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_PC_RECOVERY_USER \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_PC_RECOVERY_AUTO \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_PC_S3_BOOT_SCRIPT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_PC_OS_WAKE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006
#define EFI_SW_PEI_PC_S3_STARTED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000007)
//
// Software Class DXE Foundation Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_ENTRY_POINT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_HANDOFF_TO_NEXT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_RETURN_TO_LAST \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_START_DRIVER \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_PC_ARCH_READY \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
//
// Software Class DXE BS Driver Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_LEGACY_OPROM_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_READY_TO_BOOT_EVENT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_LEGACY_BOOT_EVENT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_EXIT_BOOT_SERVICES_EVENT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_VIRTUAL_ADDRESS_CHANGE_EVENT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_VARIABLE_SERVICES_INIT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_VARIABLE_RECLAIM \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006)
6.7.4.3. Error Code Definitions¶
Summary
Error code definitions for the Host Software class and all subclasses. See Error Code Operations in Host Software Class for descriptions of these error codes.
The following subclasses define additional subclass-specific error code operations, which are included below:
PEI Foundation
PEIM
DxeBootServiceDriver
EFI Byte Code (EBC) exception
IA-32 exception
Itanium(r) processor family exception
ARM AArch32 and AArch64 exceptions
Prototype
//
// Software Class Error Code definitions.
// These are shared by all subclasses.
//
#define EFI_SW_EC_NON_SPECIFIC 0x00000000
#define EFI_SW_EC_LOAD_ERROR 0x00000001
#define EFI_SW_EC_INVALID_PARAMETER 0x00000002
#define EFI_SW_EC_UNSUPPORTED 0x00000003
#define EFI_SW_EC_INVALID_BUFFER 0x00000004
#define EFI_SW_EC_OUT_OF_RESOURCES 0x00000005
#define EFI_SW_EC_ABORTED 0x00000006
#define EFI_SW_EC_ILLEGAL_SOFTWARE_STATE 0x00000007
#define EFI_SW_EC_ILLEGAL_HARDWARE_STATE 0x00000008
#define EFI_SW_EC_START_ERROR 0x00000009
#define EFI_SW_EC_BAD_DATE_TIME 0x0000000A
#define EFI_SW_EC_CFG_INVALID 0x0000000B
#define EFI_SW_EC_CFG_CLR_REQUEST 0x0000000C
#define EFI_SW_EC_CFG_DEFAULT 0x0000000D
#define EFI_SW_EC_PWD_INVALID 0x0000000E
#define EFI_SW_EC_PWD_CLR_REQUEST 0x0000000F
#define EFI_SW_EC_PWD_CLEARED 0x00000010
#define EFI_SW_EC_EVENT_LOG_FULL 0x00000011
#define EFI_SW_EC_WRITE_PROTECTED 0x00000012
#define EFI_SW_EC_FV_CORRUPTED 0x00000013
#define EFI_SW_EC_INCONSISTENT_MEMORY_MAP 0x00000014
//
// Software Class Unspecified Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Software Class SEC Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Software Class PEI Foundation Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_EC_DXE_CORRUPT \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_EC_DXEIPL_NOT_FOUND \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_CORE_EC_MEMORY_NOT_INSTALLED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
//
// Software Class PEI Module Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_NO_RECOVERY_CAPSULE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_INVALID_CAPSULE_DESCRIPTOR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_RESUME_PPI_NOT_FOUND \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_BOOT_SCRIPT_ERROR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_OS_WAKE_ERROR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_RESUME_FAILED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_RECOVERY_PPI_NOT_FOUND \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_RECOVERY_FAILED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000007)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_S3_RESUME_ERROR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000008)
#define EFI_SW_PEI_EC_INVALID_CAPSULE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000009)
//
// Software Class DXE Foundation Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_DXE_CORE_EC_NO_ARCH \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
//
// Software Class DXE Boot Service Driver Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC_LEGACY_OPROM_NO_SPACE\
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC_INVALID_PASSWORD \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC_BOOT_OPTION_LOAD_ERROR \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000002)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC_BOOT_OPTION_FAILED \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_EC_INVALID_IDE_PASSWORD \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
//
// Software Class DXE Runtime Service Driver Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Software Class SMM Driver Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Software Class EFI Application Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Software Class EFI OS Loader Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Software Class EFI RT Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
//
// Software Class EBC Exception Subclass Error Code definitions.
// These exceptions are derived from the debug protocol
// definitions in the EFI specification.
//
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_UNDEFINED \
0x00000000
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_DIVIDE_ERROR \
EXCEPT_EBC_DIVIDE_ERROR
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_DEBUG \
EXCEPT_EBC_DEBUG
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_DEBUG \
EXCEPT_EBC_DEBUG
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_BREAKPOINT \
EXCEPT_EBC_BREAKPOINT
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_OVERFLOW \
EXCEPT_EBC_OVERFLOW
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_INVALID_OPCODE \
EXCEPT_EBC_INVALID_OPCODE
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_STACK_FAULT \
EXCEPT_EBC_STACK_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_ALIGNMENT_CHECK \
EXCEPT_EBC_ALIGNMENT_CHECK
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_INSTRUCTION_ENCODING \
EXCEPT_EBC_INSTRUCTION_ENCODING
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_BAD_BREAK \
EXCEPT_EBC_BAD_BREAK
#define EFI_SW_EC_EBC_STEP EXCEPT_EBC_STEP
//
// Software Class IA32 Exception Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
// These exceptions are derived from the debug protocol
// definitions in the EFI specification.
//
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_DIVIDE_ERROR \
EXCEPT_IA32_DIVIDE_ERROR
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_DEBUG \
EXCEPT_IA32_DEBUG
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_NMI \
EXCEPT_IA32_NMI
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_BREAKPOINT \
EXCEPT_IA32_BREAKPOINT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_OVERFLOW \
EXCEPT_IA32_OVERFLOW
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_BOUND \
EXCEPT_IA32_BOUND
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_INVALID_OPCODE \
EXCEPT_IA32_INVALID_OPCODE
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_DOUBLE_FAULT \
EXCEPT_IA32_DOUBLE_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_INVALID_TSS \
EXCEPT_IA32_INVALID_TSS
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_SEG_NOT_PRESENT \
EXCEPT_IA32_SEG_NOT_PRESENT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_STACK_FAULT \
EXCEPT_IA32_STACK_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_GP_FAULT \
EXCEPT_IA32_GP_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_PAGE_FAULT \
EXCEPT_IA32_PAGE_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_FP_ERROR \
EXCEPT_IA32_FP_ERROR
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_ALIGNMENT_CHECK \
EXCEPT_IA32_ALIGNMENT_CHECK
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_MACHINE_CHECK \
EXCEPT_IA32_MACHINE_CHECK
#define EFI_SW_EC_IA32_SIMD EXCEPT_IA32_SIMD
//
// Software Class IPF Exception Subclass Error Code definitions.
// These exceptions are derived from the debug protocol
// definitions in the EFI specification.
//
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_ALT_DTLB \
EXCEPT_IPF_ALT_DTLB
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_DNESTED_TLB \
EXCEPT_IPF_DNESTED_TLB
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_BREAKPOINT \
EXCEPT_IPF_BREAKPOINT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPT \
EXCEPT_IPF_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_GEN_EXCEPT \
EXCEPT_IPF_GEN_EXCEPT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_NAT_CONSUMPTION \
EXCEPT_IPF_NAT_CONSUMPTION
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_DEBUG_EXCEPT \
EXCEPT_IPF_DEBUG_EXCEPT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_UNALIGNED_ACCESS \
EXCEPT_IPF_UNALIGNED_ACCESS
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_FP_FAULT \
EXCEPT_IPF_FP_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_FP_TRAP \
EXCEPT_IPF_FP_TRAP
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_TAKEN_BRANCH \
EXCEPT_IPF_TAKEN_BRANCH
#define EFI_SW_EC_IPF_SINGLE_STEP \
EXCEPT_IPF_SINGLE_STEP
//
// Software Class PEI Service Subclass Error Code definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_PS_EC_RESET_NOT_AVAILABLE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_PS_EC_MEMORY_INSTALLED_TWICE \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
//
// Software Class EFI Boot Service Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
//
//
// Software Class EFI Runtime Service Subclass Error Code \
// definitions.
//
//
// Software Class EFI DXE Service Subclass Error Code \
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_BEGIN_CONNECTING_DRIVERS \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_BS_PC_VERIFYING_PASSWORD \
(EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000006)
//
// Software Class DXE RT Driver Subclass Progress Code
// definitions.
//
#define EFI_SW_DXE_RT_PC_S0 (EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000000)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_RT_PC_S1 (EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000001)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_RT_PC_S2 (EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC |
0x00000002)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_RT_PC_S3 (EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000003)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_RT_PC_S4 (EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000004)
#define EFI_SW_DXE_RT_PC_S5 (EFI_SUBCLASS_SPECIFIC | 0x00000005)
//
// Software Class X64 Exception Subclass Error Code definitions.
// These exceptions are derived from the debug protocol
// definitions in the EFI
// specification.
//
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_DIVIDE_ERROR EXCEPT_X64_DIVIDE_ERROR
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_DEBUG EXCEPT_X64_DEBUG
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_NMI EXCEPT_X64_NMI
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_BREAKPOINT EXCEPT_X64_BREAKPOINT
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_OVERFLOW EXCEPT_X64_OVERFLOW
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_BOUND EXCEPT_X64_BOUND
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_INVALID_OPCODE \
EXCEPT_X64_INVALID_OPCODE
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_DOUBLE_FAULT EXCEPT_X64_DOUBLE_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_INVALID_TSS EXCEPT_X64_INVALID_TSS
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_SEG_NOT_PRESENT \
EXCEPT_X64_SEG_NOT_PRESENT
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_STACK_FAULT EXCEPT_X64_STACK_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_GP_FAULT EXCEPT_X64_GP_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_PAGE_FAULT EXCEPT_X64_PAGE_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_FP_ERROR EXCEPT_X64_FP_ERROR
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_ALIGNMENT_CHECK \
EXCEPT_X64_ALIGNMENT_CHECK
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_MACHINE_CHECK EXCEPT_X64_MACHINE_CHECK
#define EFI_SW_EC_X64_SIMD EXCEPT_X64_SIMD
//
// Software Class ARM Exception Subclass Error Code definitions.
// These exceptions are derived from the debug protocol
// definitions in the EFI
// specification.
//
#define EFI_SW_EC_ARM_RESET EXCEPT_ARM_RESET
#define EFI_SW_EC_ARM_UNDEFINED_INSTRUCTION \
EXCEPT_ARM_UNDEFINED_INSTRUCTION
#define EFI_SW_EC_ARM_SOFTWARE_INTERRUPT \
EXCEPT_ARM_SOFTWARE_INTERRUPT
#define EFI_SW_EC_ARM_PREFETCH_ABORT \
EXCEPT_ARM_PREFETCH_ABORT
#define EFI_SW_EC_ARM_DATA_ABORT EXCEPT_ARM_DATA_ABORT
#define EFI_SW_EC_ARM_RESERVED EXCEPT_ARM_RESERVED
#define EFI_SW_EC_ARM_IRQ EXCEPT_ARM_IRQ
#define EFI_SW_EC_ARM_FIQ EXCEPT_ARM_FIQ
#define EFI_SW_EC_AARCH64_SYNCHRONOUS_EXCEPTIONS \
EXCEPT_AARCH64_SYNCHRONOUS_EXCEPTIONS
#define EFI_SW_EC_AARCH64_IRQ EXCEPT_AARCH64_IRQ
#define EFI_SW_EC_AARCH64_FIQ EXCEPT_AARCH64_FIQ
#define EFI_SW_EC_AARCH64_SERROR EXCEPT_AARCH64_SERROR
//
// Software Class RISC-V Exception Subclass Error Code
// definitions.
// These exceptions are derived from the debug protocol
// definitions in the EFI specification.
//
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_INST_MISALIGNED
EXCEPT_RISCV_INST_MISALIGNED
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_INST_ACCESS_FAULT
EXCEPT_RISCV_INST_ACCESS_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_ILLEGAL_INST
EXCEPT_RISCV_ILLEGAL_INST
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_BREAKPOINT EXCEPT_RISCV_BREAKPOINT
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_LOAD_ADDRESS_MISALIGNED \
EXCEPT_RISCV_LOAD_ADDRESS_MISALIGNED
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_LOAD_ACCESS_FAULT
EXCEPT_RISCV_LOAD_ACCESS_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_STORE_AMO_ADDRESS_MISALIGNED \
EXCEPT_RISCV_STORE_AMO_ADDRESS_MISALIGNED
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_STORE_AMO_ACCESS_FAULT \
EXCEPT_RISCV_STORE_AMO_ACCESS_FAULT
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_ENV_CALL_FROM_UMODE
EXCEPT_RISCV_ENV_CALL_FROM_UMODE
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_ENV_CALL_FROM_SMODE
EXCEPT_RISCV_ENV_CALL_FROM_SMODE
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_ENV_CALL_FROM_HMOD
EXCEPT_RISCV_ENV_CALL_FROM_HMODE
#define EFI_SW_EC_RISCV_ENV_CALL_FROM_MMODE
EXCEPT_RISCV_ENV_CALL_FROM_MMODE
6.7.4.4. Extended Data Formats¶
In addition to the other class-specific error definitions in this subsection, the Host Software class uses the following extended error data definition:
EFI_DEVICE_HANDLE_EXTENDED_DATA
See Common Extended Data Formats for its definition.
6.7.4.5. EFI_DEBUG_ASSERT_DATA¶
Summary
This structure provides the assert information that is typically associated with a debug assertion failing.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA *DataHeader;
UINT32 LineNumber;
UINT32 FileNameSize;
EFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_DATA *FileName;
} EFI_DEBUG_ASSERT_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_DEBUG_ASSERT_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
LineNumberThe line number of the source file where the fault was generated.
FileNameSizeThe size in bytes of
FileName.
FileNameA pointer to a
NULL-terminated ASCII or Unicode string that represents the file name of the source file where the fault was generated. TypeEFI_STATUS_CODE_STRING_DATAis defined in Extended Data Header.
Description
The data indicates the location of the assertion that failed in the source code. This information includes the file name and line number that are necessary to find the failing assertion in source code.
6.7.4.6. EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_EXTENDED_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing a processor exception error.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_SYSTEM_CONTEXT Context;
} EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_EXTENDED_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_EXTENDED_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
ContextThe system context. Type
EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_SYSTEM_CONTEXTis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
Description
This extended data allows the processor context that is present at the time of the exception to be reported with the exception. The format and contents of the context data varies depending on the processor architecture.
//********************************************************
// EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_SYSTEM_CONTEXT
//********************************************************
typedef union {
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_EBC SystemContextEbc;
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_IA32 SystemContextIa32;
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_IPF SystemContextIpf;
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_X64 SystemContextX64;
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_ARM SystemContextArm;
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_RISCV32 SystemContextRiscV32;
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_RISCV64 SystemContextRiscV64;
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_RISCV128 SystemContextRiscv128;
} EFI_STATUS_CODE_EXCEP_SYSTEM_CONTEXT;
SystemContextEbcThe context of the EBC virtual machine when the exception was generated. Type
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_EBCis defined inEFI_DEBUG_SUPPORT_PROTOCOLin the UEFI Specification .
SystemContextIa32The context of the IA-32 processor when the exception was generated. Type
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_IA32is defined in theEFI_DEBUG_SUPPORT_PROTOCOLin the UEFI Specification.
SystemContextIpfThe context of the Itanium(r) processor when the exception was generated. Type
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_IPFis defined in theEFI_DEBUG_SUPPORT_PROTOCOLin the UEFI Specification .
SystemContextX64The context of the X64 processor when the exception was generated. Type
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_X64is defined in theEFI_DEBUG_SUPPORT_PROTOCOLin the UEFI Specification .
SystemContextArmThe context of the ARM processor when the exception was generated. Type
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_ARMis defined in theEFI_DEBUG_SUPPORT_PROTOCOLin the UEFI Specification .
SystemContextRiscV32The context of the RISC-V RV32 processor when the exception was generated. Type
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_RISCV32is defined in theEFI_DEBUG_SUPPORT_PROTOCOLin the UEFI Specification.
SystemContextRiscV64The context of the RISC-V RV64 processor when the exception was generated. Type
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_RISCV64is defined in theEFI_DEBUG_SUPPORT_PROTOCOLin the UEFI Specification.
SystemContextRiscV128The context of the RISC-V RV128 processor when the exception was generated. Type
EFI_SYSTEM_CONTEXT_RISCV128is defined in theEFI_DEBUG_SUPPORT_PROTOCOLin the UEFI Specification.
6.7.4.7. EFI_STATUS_CODE_START_EXTENDED_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing a call to a driver binding protocol start function.
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_HANDLE ControllerHandle;
EFI_HANDLE DriverBindingHandle;
UINT16 DevicePathSize;
// EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL RemainingDevicePath;
} EFI_STATUS_CODE_START_EXTENDED_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data.
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof (EFI_STATUS_CODE_START_EXTENDED_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
ControllerHandleThe controller handle.
DriverBindingHandleThe driver binding handle.
DevicePathSizeThe size of the
RemainingDevicePath. It is zero if theStart()function is called withRemainingDevicePath= NULL. The UEFI Specification allows that theStart()function of bus drivers can be called in this way.
RemainingDevicePathMatches the
RemainingDevicePathparameter being passed to theStart()function. Note that this parameter is the variable-length device path and not a pointer to the device path.
Description
This extended data records information about a Start()
function call. Start() is a member of the UEFI Driver Binding
Protocol.
6.7.4.8. EFI_LEGACY_OPROM_EXTENDED_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing a legacy option ROM (OpROM).
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_HANDLE DeviceHandle;
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS RomImageBase;
} EFI_LEGACY_OPROM_EXTENDED_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data:
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof(EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof(EFI_LEGACY_OPROM_EXTENDED_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
DeviceHandleThe handle corresponding to the device that this legacy option ROM is being invoked.
RomImageBaseThe base address of the shadowed legacy ROM image. May or may not point to the shadow RAM area. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined inAllocatePages()in theUEFI Specification.
Description
The device handle and ROM image base can be used by consumers to determine which option ROM failed. Due to the black-box nature of legacy option ROMs, the amount of information that can be obtained may be limited.
6.7.4.9. EFI_RETURN_STATUS_EXTENDED_DATA¶
Summary
This structure defines extended data describing an EFI_STATUS
return value that stands for a failed function call (such as a
UEFI boot service).
Prototype
typedef struct {
EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA DataHeader;
EFI_STATUS ReturnStatus;
} EFI_RETURN_STATUS_EXTENDED_DATA;
Parameters
DataHeaderThe data header identifying the data:
DataHeader.HeaderSizeshould besizeof(EFI_STATUS_CODE_DATA),DataHeader.Sizeshould besizeof(EFI_RETURN_STATUS_EXTENDED_DATA) -HeaderSize, andDataHeader.Typeshould beEFI_STATUS_CODE_SPECIFIC_DATA_GUID.
ReturnStatusThe
EFI_STATUSreturn value of the service or function whose failure triggered the reporting of the status code (generally an error code or a debug code).
Description
The extended data records the return value of a service or function call whose failure justifies reporting a status code (generally an error code or debug code).