7. Services - DXE Services¶
7.1. Introduction¶
This chapter describes the services in the DXE Services Table. These services include the following:
Global Coherency Domain (GCD) Services
Dispatcher Services
The GCD Services are used to manage the system memory, memory-mapped I/O, and I/O resources present in a platform. The Dispatcher Services are used to invoke the DXE Dispatcher and modify the state of a DXE driver that is being tracked by the DXE Dispatcher.
7.2. Global Coherency Domain Services¶
7.2.1. Global Coherency Domain (GCD) Services Overview¶
The Global Coherency Domain (GCD) Services are used to manage the memory and I/O resources visible to the boot processor. These resources are managed in two different maps:
GCD memory space map
GCD I/O space map
If memory or I/O resources are added, removed, allocated, or freed, then the GCD memory space map and GCD I/O space map are updated. GCD Services are also provided to retrieve the contents of these two resource maps.
The GCD Services can be broken up into two groups. The first manages the memory resources visible to the boot processor, and the second manages the I/O resources visible to the boot processor. Not all processor types support I/O resources, so the management of I/O resources may not be required. However, since system memory resources and memory-mapped I/O resources are required to execute the DXE environment, the management of memory resources is always required.
7.2.2. GCD Memory Resources¶
The Global Coherency Domain (GCD) Services used to manage memory resources include the following:
AddMemorySpace()AllocateMemorySpace()FreeMemorySpace()RemoveMemorySpace()SetMemorySpaceAttributes()SetMemorySpaceCapabilities()
The GCD Services used to retrieve the GCD memory space map include the following:
GetMemorySpaceDescriptor()GetMemorySpaceMap()
The GCD memory space map is initialized from the HOB list that
is passed to the entry point of the DXE Foundation. One HOB
type describes the number of address lines that are used to
access memory resources. This information is used to initialize
the state of the GCD memory space map. Any memory regions
outside this initial region are not available to any of the GCD
Services that are used to manage memory resources. The GCD
memory space map is designed to describe the memory address
space with as many as 64 address lines. Each region in the GCD
memory space map can begin and end on a byte boundary. There
are additional HOB types that describe the location of system
memory, the location memory mapped I/O, the location of
firmware devices, the location of firmware volumes, the
location of reserved regions, and the location of system memory
regions that were allocated prior to the execution of the DXE
Foundation. The DXE Foundation must parse the contents of the
HOB list to guarantee that memory regions reserved prior to the
execution of the DXE Foundation are honored. As a result, the
GCD memory space map must reflect the memory regions described
in the HOB list. The GCD memory space map provides the DXE
Foundation with the information required to initialize the
memory services such as AllocatePages() , FreePages() ,
AllocatePool() , FreePool() , and GetMemoryMap() . See
the UEFI 2.0 specification for definitions of these services.
A memory region described by the GCD memory space map can be in one of several different states:
Nonexistent memory
System memory
Memory-mapped I/O
Reserved memory
These memory regions can be allocated and freed by DXE drivers executing in the DXE environment. In addition, a DXE driver can attempt to adjust the caching attributes of a memory region. GCD Memory State Transitions shows the possible state transitions for each byte of memory in the GCD memory space map. The transitions are labeled with the GCD Service that can move the byte from one state to another. The GCD services are required to merge similar memory regions that are adjacent to each other into a single memory descriptor, which reduces the number of entries in the GCD memory space map.
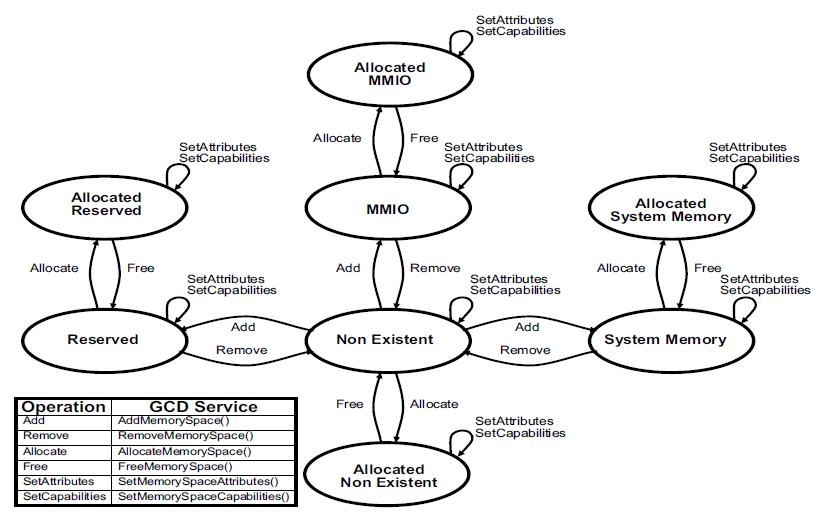
Fig. 7.2 GCD Memory State Transitions¶
7.2.3. GCD I/O Resources¶
The Global Coherency Domain (GCD) Services used to manage I/O resources include the following:
AddIoSpace()AllocateIoSpace()FreeIoSpace()RemoveIoSpace()
The GCD Services used to retrieve the GCD I/O space map include the following:
GetIoSpaceDescriptor()GetIoSpaceMap()
The GCD I/O space map is initialized from the HOB list that is passed to the entry point of the DXE Foundation. One HOB type describes the number of address lines that are used to access I/O resources. This information is used to initialize the state of the GCD I/O space map. Any I/O regions outside this initial region are not available to any of the GCD Services that are used to manage I/O resources. The GCD I/O space map is designed to describe the I/O address space with as many as 64 address lines. Each region in the GCD I/O space map can being and end on a byte boundary.
An I/O region described by the GCD I/O space map can be in several different states. These include nonexistent I/O, I/O, and reserved I/O. These I/O regions can be allocated and freed by DXE drivers executing in the DXE environment. GCD I/O State Transitions shows the possible state transitions for each byte of I/O in the GCD I/O space map. The transitions are labeled with the GCD Service that can move the byte from one state to another. The GCD Services are required to merge similar I/O regions that are adjacent to each other into a single I/O descriptor, which reduces the number of entries in the GCD I/O space map.
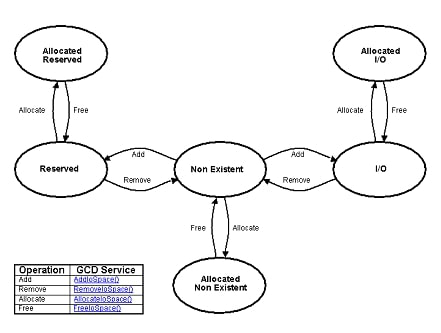
Fig. 7.3 GCD I/O State Transitions¶
7.2.4. Global Coherency Domain Services¶
The functions that make up Global Coherency Domain (GCD) Services are used during preboot to add, remove, allocate, free, and provide maps of the system memory, memory-mapped I/O, and I/O resources in a platform. These services, used in conjunction with the Memory Allocation Services, provide the ability to manage all the memory and I/O resources in a platform. Global Coherency Domain Boot Type Services lists the Global Coherency Domain Services.
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
AddMemorySpace |
This service adds reserved memory system memory or memory mapped I O resources to the global coherency domain of the processor |
AllocateMemorySpace |
This service allocates nonexistent memory reserved memory system memory or memory mapped I O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor |
FreeMemorySpace |
This service frees nonexistent memory reserved memory system memory or memory mapped I O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor |
RemoveMemorySpace |
This service removes reserved memory system memory or memory mapped I O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor |
GetM emorySpaceDescriptor |
This service retrieves the descriptor for a memory region containing a specified address |
SetM emorySpaceAttributes |
This service modifies the attributes for a memory region in the global coherency domain of the processor |
SetMem orySpaceCapabilities |
This service modifies the capabilities for a memory region in the global coherency domain of the processor |
GetMemorySpaceMap |
Returns a map of the memory resources in the global coherency domain of the processor |
AddIoSpace |
This service adds reserved I O or I O resources to the global coherency domain of the processor |
AllocateIoSpace |
This service allocates nonexistent I O reserved I O or I O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor |
FreeIoSpace |
This service frees nonexistent I O reserved I O or I O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor |
RemoveIoSpace |
This service removes reserved I O or I O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor |
GetIoSpaceDescriptor |
This service retrieves the descriptor for an I O region containing a specified address |
GetIoSpaceMap |
Returns a map of the I O resources in the global coherency domain of the processor |
7.2.4.1. AddMemorySpace()¶
Summary
This service adds reserved memory, system memory, or memory-mapped I/O resources to the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_ADD_MEMORY_SPACE) (
IN EFI_GCD_MEMORY_TYPE GcdMemoryType,
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
IN UINT64 Length,
IN UINT64 Capabilities
);
Parameters
GcdMemoryTypeThe type of memory resource being added. Type
EFI_GCD_MEMORY_TYPEis defined in “Related Definitions” below. The only types allowed areEfiGcdMemoryTypeReserved,EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystemMemory,EfiGcdMemoryTypePersistent,EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliable,EfiGcdMemoryTypeUnaccepted, andEfiGcdMemoryTypeMemoryMappedIo.
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of the memory resource being added. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthThe size, in bytes, of the memory resource that is being added.
CapabilitiesThe bit mask of attributes that the memory resource region supports. The bit mask of available attributes is defined in the
GetMemoryMap()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Description
The AddMemorySpace() function converts unallocated
non-existent memory ranges to a range of reserved memory, a
range of system memory, or a range of memory mapped I/O.
BaseAddress and Length specify the memory range, and
GcdMemoryType specifies the memory type. The bit mask of
all supported attributes for the memory range being added is
specified by Capabilities . If the memory range is
successfully added, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If the memory range specified by BaseAddress and Length
is of type EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystemMemory or
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliable , then the memory range may
be automatically allocated for use by the UEFI memory
services. If the addition of the memory range specified by
BaseAddress and Length results in a GCD memory space map
containing one or more 4 KiB regions of unallocated
EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystemMemory or
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliable aligned on 4 KiB boundaries,
then those regions will always be converted to ranges of
allocated EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystemMemory or
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliable respectively. This extra
conversion will never be performed for fragments of memory
that do not meet the above criteria.
If the GCD memory space map contains adjacent memory regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent memory regions must be merged into a single memory descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If GcdMemoryType is not EfiGcdMemoryTypeReserved , EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystemMemory , EfiGcdMemoryTypeMemoryMappedIo , EfiGcdMemoryPersistent , EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliable , or EfiGcdMemoryTypeUnaccepted then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If the processor does not support one or more bytes of the
memory range specified by BaseAddress and Length , then
EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned.
If any portion of the memory range specified by
BaseAddress and Length is not of type
EfiGcdMemoryTypeNonExistent , then EFI_ACCESS_DENIED is
returned.
If any portion of the memory range specified by
BaseAddress and Length was allocated in a prior call to
AllocateMemorySpace() , then EFI_ACCESS_DENIED is
returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to add
the memory resource to the global coherency domain of the
processor, then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
//*******************************************************
// EFI_GCD_MEMORY_TYPE
//*******************************************************
typedef enum {
EfiGcdMemoryTypeNonExistent,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeReserved,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystemMemory,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMemoryMappedIo,
EfiGcdMemoryTypePersistent,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliable,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeUnaccepted,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMaximum
} EFI_GCD_MEMORY_TYPE;
EfiGcdMemoryTypeNonExistentA memory region that is visible to the boot processor. However, there are no system components that are currently decoding this memory region.
EfiGcdMemoryTypeReservedA memory region that is visible to the boot processor. This memory region is being decoded by a system component, but the memory region is not considered to be either system memory or memory-mapped I/O.
EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystemMemoryA memory region that is visible to the boot processor. A memory controller is currently decoding this memory region and the memory controller is producing a tested system memory region that is available to the memory services.
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMemoryMappedIoA memory region that is visible to the boot processor. This memory region is currently being decoded by a component as memory-mapped I/O that can be used to access I/O devices in the platform.
EfiGcdMemoryTypePersistentA memory region that is visible to the boot processor. This memory supports byte-addressable non-volatility.
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliableA memory region that provides higher reliability relative to other memory in the system. If all memory has the same reliability, then this bit is not used.
EfiGcdMemoryTypeUnacceptedA memory region that is unaccepted. This region must be accepted before it can be converted to system memory.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The memory resource was added to the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to add the memory resource to the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The processor does not support one or more bytes of the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
One or more bytes of the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
One or more bytes of the memory resource range specified by |
7.2.4.2. AllocateMemorySpace()¶
Summary
This service allocates nonexistent memory, reserved memory, system memory, or memory-mapped I/O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI \*EFI_ALLOCATE_MEMORY_SPACE) (
IN EFI_GCD_ALLOCATE_TYPE GcdAllocateType,
IN EFI_GCD_MEMORY_TYPE GcdMemoryType,
IN UINTN Alignment,
IN UINT64 Length,
IN OUT EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS *BaseAddress,
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_HANDLE DeviceHandle OPTIONAL
);
Parameters
GcdAllocateTypeThe type of allocation to perform. Type
EFI_GCD_ALLOCATE_TYPEis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
GcdMemoryTypeThe type of memory resource being allocated. Type
EFI_GCD_MEMORY_TYPEis defined inAddMemorySpace(). The only types allowed areEfiGcdMemoryTypeNonExistent,EfiGcdMemoryTypeReserved,EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystemMemory,EfiGcdMemoryTypePersistent, EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliableandEfiGcdMemoryTypeMemoryMappedIo.
AlignmentThe log base 2 of the boundary that
BaseAddressmust be aligned on output. For example, a value of 0 means thatBaseAddresscan be aligned on any byte boundary, and a value of 12 means thatBaseAddressmust be aligned on a 4 KiB boundary.
LengthThe size in bytes of the memory resource range that is being allocated.
BaseAddressA pointer to a physical address. On input, the way in which the address is used depends on the value of
Type. See “Description” below for more information. On output the address is set to the base of the memory resource range that was allocated. TypeEFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
ImageHandleThe image handle of the agent that is allocating the memory resource. Type
EFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
DeviceHandleThe device handle for which the memory resource is being allocated. If the memory resource is not being allocated for a device that has an associated device handle, then this parameter is optional and may be
NULL. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Description
The AllocateMemorySpace() function searches for a memory
range of type GcdMemoryType and converts the discovered
memory range from the unallocated state to the allocated
state. The parameters GcdAllocateType , Alignment ,
Length , and BaseAddress specify the manner in which the
GCD memory space map is searched. If a memory range is found
that meets the search criteria, then the base address of the
memory range is returned in BaseAddress , and
EFI_SUCCESS is returned. ImageHandle and DeviceHandle
are used to convert the memory range from the unallocated
state to the allocated state. ImageHandle identifies the
image that is calling AllocateMemorySpace() , and
DeviceHandle identifies the device that ImageHandle is
managing that requires the memory range. DeviceHandle is
optional, because the device that ImageHandle is managing
might not have an associated device handle. If a memory
range meeting the search criteria cannot be found, then
EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned.
If GcdAllocateType is EfiGcdAllocateAnySearchBottomUp ,
then the GCD memory space map is searched from the lowest
address up to the highest address looking for unallocated
memory ranges of Length bytes beginning on a boundary
specified by Alignment that matches GcdMemoryType .
If GcdAllocateType is EfiGcdAllocateAnySearchTopDown ,
then the GCD memory space map is searched from the highest
address down to the lowest address looking for unallocated
memory ranges of Length bytes beginning on a boundary
specified by Alignment that matches GcdMemoryType .
If GcdAllocateType is
EfiGcdAllocateMaxAddressSearchBottomUp , then the GCD
memory space map is searched from the lowest address up to
BaseAddress looking for unallocated memory ranges of
Length bytes beginning on a boundary specified by
Alignment that matches GcdMemoryType .
If GcdAllocateType is
EfiGcdAllocateMaxAddressSearchTopDown , then the GCD
memory space map is searched from BaseAddress down to the
lowest address looking for unallocated memory ranges of
Length bytes beginning on a boundary specified by
Alignment that matches GcdMemoryType .
If GcdAllocateType is EfiGcdAllocateAddress , then the
GCD memory space map is checked to see if the memory range
starting at BaseAddress for Length bytes is of type
GcdMemoryType , unallocated, and begins on a the boundary
specified by Alignment .
If the GCD memory space map contains adjacent memory regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent memory regions must be merged into a single memory descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If BaseAddress is NULL , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If ImageHandle is NULL , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If GcdMemoryType is not EfiGcdMemoryTypeNonExistent ,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeReserved , EfiGcdMemoryTypeSystem Memory
, EfiGcdMemoryTypePersistent ,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMemoryMappedIo ,
EfiGcdMemoryTypeMoreReliable , then
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If GcdAlocateType is less than zero, or GcdAllocateType
is greater than or equal to EfiGcdMaxAllocateType then
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to
allocate the memory range, then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is
returned.
//*******************************************************
// EFI_GCD_ALLOCATE_TYPE
//*******************************************************
typedef enum {
EfiGcdAllocateAnySearchBottomUp,
EfiGcdAllocateMaxAddressSearchBottomUp,
EfiGcdAllocateAddress,
EfiGcdAllocateAnySearchTopDown,
EfiGcdAllocateMaxAddressSearchTopDown,
EfiGcdMaxAllocateType
} EFI_GCD_ALLOCATE_TYPE;
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The memory resource was allocated from the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to allocate the memory resource from the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The memory resource request could not be satisfied |
7.2.4.3. FreeMemorySpace()¶
Summary
This service frees nonexistent memory, reserved memory, system memory, or memory-mapped I/O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_FREE_MEMORY_SPACE) (
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
IN UINT64 Length
);
Parameters
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of the memory resource being freed. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthThe size in bytes of the memory resource range that is being freed.
Description
The FreeMemorySpace() function converts the memory range
specified by BaseAddress and Length from the allocated
state to the unallocated state. If this conversion is
successful, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If the GCD memory space map contains adjacent memory regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent memory regions must be merged into a single memory descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If the processor does not support one or more bytes of the
memory range specified by BaseAddress and Length , then
EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned.
If one or more bytes of the memory range specified by
BaseAddress and Length were not allocated on previous
calls to AllocateMemorySpace() , then EFI_NOT_FOUND is
returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to free
the memory range, then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The memory resource was freed from the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The processor does not support one or more bytes of the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The memory resource range specified by |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to free the memory resource from the global coherency domain of the processor |
7.2.4.4. RemoveMemorySpace()¶
Summary
This service removes reserved memory, system memory, or memory-mapped I/O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_REMOVE_MEMORY_SPACE) (
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
IN UINT64 Length
);
Parameters
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of the memory resource being removed. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthThe size in bytes of the memory resource that is being removed.
Description
The RemoveMemorySpace() function converts the memory range
specified by BaseAddress and Length to the memory type
EfiGcdMemoryTypeNonExistent . If this conversion is
successful, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If the GCD memory space map contains adjacent memory regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent memory regions must be merged into a single memory descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If the processor does not support one or more bytes of the
memory range specified by BaseAddress and Length , then
EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned.
If one or more bytes of the memory range specified by
BaseAddress and Length were not added to the GCD memory
space map with previous calls to AddMemorySpace() , then
EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned.
If one or more bytes of the memory range specified by
BaseAddress and Length were allocated from the GCD
memory space map with previous calls to
AllocateMemorySpace() , then EFI_ACCESS_DENIED is
returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to remove
the memory range, then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The memory resource was removed from the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The processor does not support one or more bytes of the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
One or more bytes of the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
One or more bytes of the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to remove the memory resource from the global coherency domain of the processor |
7.2.4.5. GetMemorySpaceDescriptor()¶
Summary
This service retrieves the descriptor for a memory region containing a specified address.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_GET_MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR) (
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
OUT EFI_GCD_MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR *Descriptor
);
Parameters
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of a memory region. Type EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS is defined in the AllocatePages() function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
DescriptorA pointer to a caller allocated descriptor. On return, the descriptor describes the memory region containing
BaseAddress. TypeEFI_GCD_MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTORis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
Description
The GetMemorySpaceDescriptor() function retrieves the
descriptor for the memory region that contains the address
specified by BaseAddress . If a memory region containing
BaseAddress is found, then the descriptor for that memory
region is returned in the caller allocated structure
Descriptor , and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If Descriptor is NULL , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If a memory region containing BaseAddress is not present
in the GCD memory space map, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is
returned.
//*******************************************************
// EFI_GCD_MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR
//*******************************************************
typedef struct {
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress;
UINT64 Length;
UINT64 Capabilities;
UINT64 Attributes;
EFI_GCD_MEMORY_TYPE GcdMemoryType;
EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle;
EFI_HANDLE DeviceHandle;
} EFI_GCD_MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR;
Parameters
BaseAddressThe physical address of the first byte in the memory region. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthThe number of bytes in the memory region.
CapabilitiesThe bit mask of attributes that the memory region is capable of supporting. The bit mask of available attributes is defined in the
GetMemoryMap()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
AttributesThe bit mask of attributes that the memory region is currently using. The bit mask of available attributes is defined in
GetMemoryMap().
GcdMemoryTypeType of the memory region. Type
EFI_GCD_MEMORY_TYPEis defined in theAddMemorySpace()function description.
ImageHandleThe image handle of the agent that allocated the memory resource described by
PhysicalStartandNumberOfBytes. If this field isNULL, then the memory resource is not currently allocated. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
DeviceHandleThe device handle for which the memory resource has been allocated. If
ImageHandleisNULL, then the memory resource is not currently allocated. If this field isNULL, then the memory resource is not associated with a device that is described by a device handle. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The descriptor for the memory resource region containing |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
A memory resource range containing |
EFI_NOT_AVAILABLE_YET |
The attributes cannot be set because CPU architectural protocol is not available yet |
7.2.4.6. SetMemorySpaceAttributes()¶
Summary
This service modifies the attributes for a memory region in the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_SET_MEMORY_SPACE_ATTRIBUTES) (
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
IN UINT64 Length,
IN UINT64 Attributes
);
Parameters
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of a memory region. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthThe size in bytes of the memory region.
AttributesThe bit mask of attributes to set for the memory region. The bit mask of available attributes is defined in the
GetMemoryMap()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Description
The SetMemorySpaceAttributes() function modifies the
attributes for the memory region specified by BaseAddress
and Length from their current attributes to the attributes
specified by Attributes . If this modification of
attributes succeeds, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If the GCD memory space map contains adjacent memory regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent memory regions must be merged into a single memory descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If the processor does not support one or more bytes of the
memory range specified by BaseAddress and Length , then
EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned.
If the attributes specified by Attributes are not
supported for the memory region specified by BaseAddress
and Length , then EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned. The
Attributes bit mask must be a proper subset of the
capabilities bit mask for the specified memory region. The
capabilities bit mask is specified when a memory region is
added with AddMemorySpace() and can be retrieved with
GetMemorySpaceDescriptor() or GetMemorySpaceMap().
If the attributes for one or more bytes of the memory range
specified by BaseAddress and Length cannot be modified
because the current system policy does not allow them to be
modified, then EFI_ACCESS_DENIED is returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to modify
the attributes of the memory range, then
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The attributes were set for the memory region |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The processor does not support one or more bytes of the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The bit mask of attributes is not support for the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
The attributes for the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to modify the attributes of the memory resource range |
7.2.4.7. SetMemorySpaceCapabilities()¶
Summary
This service modifies the capabilities for a memory region in the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_SET_MEMORY_SPACE_CAPABILITIES) (
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
IN UINT64 Length,
IN UINT64 Capabilities*
);
Parameters
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of a memory region. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI Specification.
LengthThe size in bytes of the memory region.
CapabilitiesThe bit mask of capabilities that the memory region supports. The bit mask of available attributes is defined in the
GetMemoryMap()function description in the UEFI specification.
Description
The SetMemorySpaceCapabilities() function modifies the
capabilities for the memory region specified by
BaseAddress and Length from their current capabilities
to the capabilities specified by Capabilities . If this
modification of capabilities succeeds, then EFI_SUCCESS is
returned.
If the value for Capabilities does not include the current
operating memory region attributes (having previously been
set by calling SetMemorySpaceAttributes ) then
EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If the capabilities for one or more bytes of the memory
range specified by BaseAddress and Length cannot be
modified because the current system policy does not allow
them to be modified, then EFI_ACCESS_DENIED is returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to modify
the capabilities of the memory range, then
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The capabilities were set for the memory region |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The capabilities specified by |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
The capabilities for the memory resource range specified by |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to modify the capabilities of the memory resource range |
7.2.4.8. GetMemorySpaceMap()¶
Summary
Returns a map of the memory resources in the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_GET_MEMORY_SPACE_MAP) (
OUT UINTN *NumberOfDescriptors,
OUT EFI_GCD_MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR **MemorySpaceMap
);
Parameters
NumberOfDescriptorsA pointer to number of descriptors returned in the
MemorySpaceMapbuffer. This parameter is ignored on input, and is set to the number of descriptors in theMemorySpaceMapbuffer on output.
MemorySpaceMapA pointer to the array of
EFI_GCD_MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTORs. TypeEFI_GCD_MEMORY_SPACE_DESCRIPTORis defined inGetMemorySpaceDescriptor(). This buffer is allocated withAllocatePool(), so it is the caller’s responsibility to free this buffer with a call toFreePool(). The number of descriptors inMemorySpaceMapis returned inNumberOfDescriptors. See the UEFI 2.0 specification for definitions ofAllocatePool()andFreePool().
Description
The GetMemorySpaceMap() function retrieves the entire GCD
memory space map. If there are no errors retrieving the GCD
memory space map, then the number of descriptors in the GCD
memory space map is returned in NumberOfDescriptors , the
array of descriptors from the GCD memory space map is
allocated with AllocatePool() , the descriptors are
transferred into MemorySpaceMap , and EFI_SUCCESS is
returned.
If NumberOfDescriptors is NULL , then
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If MemorySpaceMap is NULL , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER
is returned.
If there are not enough resources to allocate
MemorySpaceMap , then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The memory space map was returned in the |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough resources to allocate |
7.2.4.9. AddIoSpace()¶
Summary
This service adds reserved I/O, or I/O resources to the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_ADD_IO_SPACE) (
IN EFI_GCD_IO_TYPE GcdIoType,
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
IN UINT64 Length
);
Parameters
GcdIoTypeThe type of I/O resource being added. Type
EFI_GCD_IO_TYPEis defined in “Related Definitions” below. The only types allowed areEfiGcdIoTypeReservedandEfiGcdIoTypeIo.
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of the I/O resource being added. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthThe size in bytes of the I/O resource that is being added.
Description
The AddIoSpace() function converts unallocated
non-existent I/O ranges to a range of reserved I/O, or a
range of I/O. BaseAddress and Length specify the I/O
range, and GcdIoType specifies the I/O type. If the I/O
range is successfully added, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If the GCD I/O space map contains adjacent I/O regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent I/O regions must be merged into a single I/O descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If GcdIoType is not EfiGcdIoTypeReserved or
EfiGcdIoTypeIo , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If the processor does not support one or more bytes of the
I/O range specified by BaseAddress and Length , then
EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned.
If any portion of the I/O range specified by BaseAddress
and Length is not of type EfiGcdIoTypeNonExistent , then
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED is returned.
If any portion of the I/O range specified by BaseAddress
and Length was allocated in a prior call to
AllocateIoSpace() , then EFI_ACCESS_DENIED is returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to add
the I/O resource to the global coherency domain of the
processor, then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
//*******************************************************
// EFI_GCD_IO_TYPE
//*******************************************************
typedef enum {
EfiGcdIoTypeNonExistent,
EfiGcdIoTypeReserved,
EfiGcdIoTypeIo,
EfiGcdIoTypeMaximum
} EFI_GCD_IO_TYPE;
EfiGcdIoTypeNonExistentAn I/O region that is visible to the boot processor. However, there are no system components that are currently decoding this I/O region.
EfiGcdIoTypeReservedAn I/O region that is visible to the boot processor. This I/O region is currently being decoded by a system component, but the I/O region cannot be used to access I/O devices.
EfiGcdIoTypeIoAn I/O region that is visible to the boot processor. This I/O region is currently being decoded by a system component that is producing I/O ports that can be used to access I/O devices.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The I O resource was added to the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to add the I O resource to the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The processor does not support one or more bytes of the I O resource range specified by |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
One or more bytes of the I O resource range specified by |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
One or more bytes of the I O resource range specified by |
7.2.4.10. AllocateIoSpace()¶
Summary
This service allocates nonexistent I/O, reserved I/O, or I/O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_ALLOCATE_IO_SPACE) (
IN EFI_GCD_ALLOCATE_TYPE AllocateType,
IN EFI_GCD_IO_TYPE GcdIoType,
IN UINTN Alignment,
IN UINT64 Length,
IN OUT EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS *BaseAddress,
IN EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle,
IN EFI_HANDLE DeviceHandle OPTIONAL
);
Parameters
GcdAllocateTypeThe type of allocation to perform. Type
EFI_GCD_ALLOCATE_TYPEis defined inAllocateMemorySpace().
GcdIoTypeThe type of I/O resource being allocated. Type
EFI_GCD_IO_TYPEis defined inAddIoSpace(). The only types allowed areEfiGcdIoTypeNonExistent,EfiGcdIoTypeReserved, andEfiGcdIoTypeIo.
AlignmentThe log base 2 of the boundary that
BaseAddressmust be aligned on output. For example, a value of 0 means thatBaseAddresscan be aligned on any byte boundary, and a value of 12 means thatBaseAddressmust be aligned on a 4 KiB boundary.
LengthThe size in bytes of the I/O resource range that is being allocated.
BaseAddressA pointer to a physical address. On input, the way in which the address is used depends on the value of
Type. See “Description” below for more information. On output the address is set to the base of the I/O resource range that was allocated. TypeEFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined inAllocatePages()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
ImageHandleThe image handle of the agent that is allocating the I/O resource. Type
EFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the v.
DeviceHandleThe device handle for which the I/O resource is being allocated. If the I/O resource is not being allocated for a device that has an associated device handle, then this parameter is optional and may be
NULL. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Description
The AllocateIoSpace() function searches for an I/O range
of type GcdIoType and converts the discovered I/O range
from the unallocated state to the allocated state. The
parameters GcdAllocateType , Alignment , Length , and
BaseAddress specify the manner in which the GCD I/O space
map is searched. If an I/O range is found that meets the
search criteria, then the base address of the I/O range is
returned in BaseAddress , and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
ImageHandle and DeviceHandle are used to convert the I/O
range from the unallocated state to the allocated state.
ImageHandle identifies the image that is calling
AllocateIoSpace() , and DeviceHandle identifies the
device that ImageHandle is managing that requires the I/O
range. DeviceHandle is optional, because the device that
ImageHandle is managing might not have an associated
device handle. If an I/O range meeting the search criteria
cannot be found, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned.
If GcdAllocateType is EfiGcdAllocateAnySearchBottomUp ,
then the GCD I/O space map is searched from the lowest
address up to the highest address looking for unallocated
I/O ranges of Length bytes beginning on a boundary
specified by Alignment that matches GcdIoType .
If GcdAllocateType is EfiGcdAllocateAnySearchTopDown ,
then the GCD I/O space map is searched from the highest
address down to the lowest address looking for unallocated
I/O ranges of Length bytes beginning on a boundary
specified by Alignment that matches GcdIoType .
If GcdAllocateType is
EfiGcdAllocateMaxAddressSearchBottomUp , then the GCD I/O
space map is searched from the lowest address up to
BaseAddress looking for unallocated I/O ranges of Length
bytes beginning on a boundary specified by Alignment that
matches GcdIoType .
If GcdAllocateType is
EfiGcdAllocateMaxAddressSearchTopDown , then the GCD I/O
space map is searched from BaseAddress down to the lowest
address looking for unallocated I/O ranges of Length bytes
beginning on a boundary specified by Alignment that
matches GcdIoType .
If GcdAllocateType is EfiGcdAllocateAddress , then the
GCD I/O space map is checked to see if the I/O range
starting at BaseAddress for Length bytes is of type
GcdIoType , unallocated, and begins on a the boundary
specified by Alignment .
If the GCD I/O space map contains adjacent I/O regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent I/O regions must be merged into a single I/O descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If BaseAddress is NULL , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If ImageHandle is NULL , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If GcdIoType is not EfiGcdIoTypeNonExistent ,
EfiGcdIoTypeReserved , or EfiGcdIoTypeIo , then
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If GcdAlocateType is less than zero, or GcdAllocateType
is greater than or equal to EfiGcdMaxAllocateType then
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to
allocate the I/O range, then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is
returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The I O resource was allocated from the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to allocate the I/O resource from the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The I/O resource request could not be satisfied |
7.2.4.11. FreeIoSpace()¶
Summary
This service frees nonexistent I/O, reserved I/O, or I/O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_FREE_IO_SPACE) (
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
IN UINT64 Length
);
Parameters
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of the I/O resource being freed. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthThe size in bytes of the I/O resource range that is being freed.
Description
The FreeIoSpace() function converts the I/O range
specified by BaseAddress and Length from the allocated
state to the unallocated state. If this conversion is
successful, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If the GCD I/O space map contains adjacent I/O regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent I/O regions must be merged into a single I/O descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If the processor does not support one or more bytes of the
I/O range specified by BaseAddress and Length , then
EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned.
If one or more bytes of the I/O range specified by
BaseAddress and Length were not allocated on previous
calls to AllocateIoSpace() , then EFI_NOT_FOUND is
returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to free
the I/O range, then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The I/O resource was freed from the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The processor does not support one or more bytes of the I/O resource range specified by |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The I/O resource range specified by |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to free the I/O resource from the global coherency domain of the processor |
7.2.4.12. RemoveIoSpace()¶
Summary
This service removes reserved I/O, or I/O resources from the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_REMOVE_IO_SPACE) (
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
IN UINT64 Length
);
Parameters
BaseAddressA pointer to a physical address that is the start address of the I/O resource being removed. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined inAllocatePages()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthThe size in bytes of the I/O resource that is being removed.
Description
The RemoveIoSpace() function converts the I/O range
specified by BaseAddress and Length to the I/O type
EfiGcdIoTypeNonExistent . If this conversion is
successful, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If the GCD I/O space map contains adjacent I/O regions that only differ in their base address and length fields, then those adjacent I/O regions must be merged into a single I/O descriptor.
If Length is zero, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If the processor does not support one or more bytes of the
I/O range specified by BaseAddress and Length , then
EFI_UNSUPPORTED is returned.
If one or more bytes of the I/O range specified by
BaseAddress and Length were not added to the GCD I/O
space map with previous calls to AddIoSpace() , then
EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned.
If one or more bytes of the I/O range specified by
BaseAddress and Length were allocated from the GCD I/O
space map with previous calls to AllocateIoSpace() , then
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED is returned.
If there are not enough system resources available to remove
the I/O range, then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The I/O resource was removed from the global coherency domain of the processor |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The processor does not support one or more bytes of the I/O resource range specified by |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
One or more bytes of the I/O resource range specified by |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
One or more bytes of the I/O resource range specified by |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources to remove the I/O resource from the global coherency domain of the processor |
7.2.4.13. GetIoSpaceDescriptor()¶
Summary
This service retrieves the descriptor for an I/O region containing a specified address.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_GET_IO_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR) (
IN EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress,
OUT EFI_GCD_IO_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR *Descriptor
);
Parameters
BaseAddressThe physical address that is the start address of an I/O region. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined inAllocatePages()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
DescriptorA pointer to a caller allocated descriptor. On return, the descriptor describes the I/O region containing
BaseAddress. TypeEFI_GCD_IO_SPACE_DESCRIPTORis defined in “Related Definitions” below.
Description
The GetIoSpaceDescriptor() function retrieves the
descriptor for the I/O region that contains the address
specified by BaseAddress . If an I/O region containing
BaseAddress is found, then the descriptor for that I/O
region is returned in the caller allocated structure
Descriptor , and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If Descriptor is NULL , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If an I/O region containing BaseAddress is not present in
the GCD I/O space map, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned.
//*******************************************************
// EFI_GCD_IO_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR
//*******************************************************
typedef struct {
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESS BaseAddress;
UINT64 Length;
EFI_GCD_IO_TYPE GcdIoType;
EFI_HANDLE ImageHandle;
EFI_HANDLE DeviceHandle;
} EFI_GCD_IO_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR;
Parameters
BaseAddressPhysical address of the first byte in the I/O region. Type
EFI_PHYSICAL_ADDRESSis defined in theAllocatePages()function description in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
LengthNumber of bytes in the I/O region.
GcdIoTypeType of the I/O region. Type
EFI_GCD_IO_TYPEis defined in theAddIoSpace()function description.
ImageHandleThe image handle of the agent that allocated the I/O resource described by
PhysicalStartandNumberOfBytes. If this field isNULL, then the I/O resource is not currently allocated. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
DeviceHandleThe device handle for which the I/O resource has been allocated. If
ImageHandleisNULL, then the I/O resource is not currently allocated. If this field isNULL, then the I/O resource is not associated with a device that is described by a device handle. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The descriptor for the I/O resource region containing |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
An I/O resource range containing |
7.2.4.14. GetIoSpaceMap()¶
Summary
Returns a map of the I/O resources in the global coherency domain of the processor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_GET_IO_SPACE_MAP) (
OUT UINTN *NumberOfDescriptors,
OUT EFI_GCD_IO_SPACE_DESCRIPTOR **IoSpaceMap
);
Parameters
NumberOfDescriptorsA pointer to number of descriptors returned in the
IoSpaceMapbuffer. This parameter is ignored on input, and is set to the number of descriptors in theIoSpaceMapbuffer on output.
IoSpaceMapA pointer to the array of
EFI_GCD_IO_SPACE_DESCRIPTORs. TypeEFI_GCD_IO_SPACE_DESCRIPTORis defined inGetIoSpaceDescriptor(). This buffer is allocated withAllocatePool(), so it is the caller’s responsibility to free this buffer with a call toFreePool(). The number of descriptors inIoSpaceMapis returned inNumberOfDescriptors.
Description
The GetIoSpaceMap() function retrieves the entire GCD I/O
space map. If there are no errors retrieving the GCD I/O
space map, then the number of descriptors in the GCD I/O
space map is returned in NumberOfDescriptors , the array
of descriptors from the GCD I/O space map is allocated with
AllocatePool() , the descriptors are transferred into
IoSpaceMap , and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
If NumberOfDescriptors is NULL , then
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If IoSpaceMap is NULL , then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is
returned.
If there are not enough resources to allocate IoSpaceMap ,
then EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The I/O space map was returned in the |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
|
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough resources to allocate |
7.3. Dispatcher Services¶
The functions that make up the Dispatcher Services are used during preboot to schedule drivers for execution. A driver may optionally have the Schedule On Request (SOR) flag set in the driver’s dependency expression. Drivers with this bit set will not be loaded and invoked until they are explicitly requested to do so. Files loaded from firmware volumes may be placed in the untrusted state by the Security Architectural Protocol. The services in this section provide this ability to clear the SOR flag in a DXE driver’s dependency expression and the ability to promote a file from a firmware volume from the untrusted to the trusted state. Dispatcher Boot Type Services lists the Dispatcher Services.
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
Dispatch |
Loads and executed DXE drivers from firmware volumes |
Schedule |
Clears the Schedule on Request SOR flag for a component that is stored in a firmware volume |
Trust |
Changes the state of a file stored in a firmware volume from the untrusted state to the trusted state |
ProcessFirmwareVolume |
Creates a firmware volume handle for a firmware volume that is present in system memory |
7.3.1. Dispatch()¶
Summary
Loads and executes DXE drivers from firmware volumes.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_DISPATCH) (
VOID
);
Description
The Dispatch() function searches for DXE drivers in firmware
volumes that have been installed since the last time the
Dispatch() service was called. It then evaluates the
dependency expressions of all the DXE drivers and loads and
executes those DXE drivers whose dependency expression evaluate
to TRUE . This service must interact with the Security
Architectural Protocol to authenticate DXE drivers before they
are executed. This process is continued until no more DXE
drivers can be executed. If one or more DXE drivers are
executed, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned. If no DXE drivers are
executed, EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned.
If an attempt is made to invoke the DXE Dispatcher recursively,
then no action is performed by the Dispatch() service, and
EFI_ALREADY_STARTED is returned. In this case, because the
DXE Dispatcher is already running, it is not necessary to
invoke it again. All the DXE drivers that can be dispatched
will be dispatched.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
One or more DXE driver were dispatched |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
No DXE drivers were dispatched |
EFI_ALREADY_STARTED |
An attempt is being made to start the DXE Dispatcher recursively Thus no action was taken |
7.3.2. Schedule()¶
Summary
Clears the Schedule on Request (SOR) flag for a component that is stored in a firmware volume.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_SCHEDULE) (
IN EFI_HANDLE FirmwareVolumeHandle,
IN CONST EFI_GUID *FileName
);
Parameters
FirmwareVolumeHandleThe handle of the firmware volume that contains the file specified by
FileName. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
FileNameA pointer to the name of the file in a firmware volume. This is the file that should have its SOR bit cleared. Type
EFI_GUIDis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Description
The Schedule() function searches the dispatcher queues for
the driver specified by FirmwareVolumeHandle and
FileName . If this driver cannot be found, then
EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned. If the driver is found, and its
Schedule On Request (SOR) flag is not set in its dependency
expression, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned. If the driver
is found, and its SOR bit is set in its dependency
expression, then the SOR flag is cleared, and EFI_SUCCESS
is returned. After the SOR flag is cleared, the driver will
be dispatched if the remaining portions of its dependency
expression are satisfied. This service does not
automatically invoke the DXE Dispatcher. Instead, the
Dispatch() service must be used to invoke the DXE
Dispatcher.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The DXE driver was found and its SOR bit was cleared |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The DXE driver does not exist or the DXE driver exists and its SOR bit is not set |
7.3.3. Trust()¶
Summary
Promotes a file stored in a firmware volume from the untrusted to the trusted state. Only the Security Architectural Protocol can place a file in the untrusted state. A platform specific component may choose to use this service to promote a previously untrusted file to the trusted state.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_TRUST) (
IN EFI_HANDLE FirmwareVolumeHandle,
IN CONST EFI_GUID *FileName
);
Parameters
FirmwareVolumeHandleThe handle of the firmware volume that contains the file specified by
FileName. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
FileNameA pointer to the name of the file in a firmware volume. This is the file that should be promoted from the untrusted state to the trusted state. Type
EFI_GUIDis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Description
The Trust() function promotes the file specified by
FirmwareVolumeHandle and FileName from the untrusted
state to the trusted state. If this file is not found in the
queue of untrusted files, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned.
If the driver is found, and its state is changed to trusted
and EFI_SUCCESS is returned. This service does not
automatically invoke the DXE Dispatcher. Instead, the
Dispatch() service must be used to invoke the DXE
Dispatcher.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The file was found in the untrusted state and it was promoted to the trusted state |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The file was not found in the untrusted state |
ProcessFirmwareVolume()
Summary
Creates a firmware volume handle for a firmware volume that is present in system memory.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_PROCESS_FIRMWARE_VOLUME) (
IN CONST VOID *FirmwareVolumeHeader,
IN UINTN Size,
OUT EFI_HANDLE *FirmwareVolumeHandle
);
Parameters
FirmwareVolumeHeaderA pointer to the header of the firmware volume.
SizeThe size, in bytes, of the firmware volume.
FirmwareVolumeHandleOn output, a pointer to the created handle. This service will install the
EFI_FIRMWARE_VOLUME2_PROTOCOLandEFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOLfor the of the firmware volume that is described byFirmwareVolumeHeaderandSize. TypeEFI_HANDLEis defined inInstallProtocolInterface()in the UEFI 2.0 specification.
Description
The ProcessFirmwareVolume() function examines the contents
of the buffer specified by FirmwareVolumeHeader and Size
. If the buffer contains a valid firmware volume, then a new
handle is created, and the EFI_FIRMWARE_VOLUME2_PROTOCOL
and a memory-mapped EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL are installed
onto the new handle. The new handle is returned in
FirmwareVolumeHandle .
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The |
EFI_VOLUME_CORRUPTED |
The firmware volume described by |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough system resources available to produce the |