17. Protocols — USB Support¶
17.1. USB2 Host Controller Protocol¶
USB2 Host Controller Protocol and USB Host Controller Protocol Overview describe the USB2 Host Controller Protocol. This protocol provides an I/O abstraction for a USB2 Host Controller. The USB2 Host Controller is a hardware component that interfaces to a Universal Serial Bus (USB). It moves data between system memory and devices on the USB by processing data structures and generating transactions on the USB. This protocol is used by a USB Bus Driver to perform all data transaction over the Universal Serial Bus. It also provides services to manage the USB root hub that is integrated into the USB Host Controller. USB device drivers do not use this protocol directly. Instead, they use the I/O abstraction produced by the USB Bus Driver. This protocol should only be used by drivers that require direct access to the USB bus.
17.1.1. USB Host Controller Protocol Overview¶
The USB Host Controller Protocol is used by code, typically USB bus drivers, running in the EFI boot services environment, to perform data transactions over a USB bus. In addition, it provides an abstraction for the root hub of the USB bus.
The interfaces provided in the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL are used to manage data transactions on a USB bus. It also provides control methods for the USB root hub. The EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is designed to support both USB 1.1 and USB 2.0 - compliant host controllers.
The EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL abstracts basic functionality that is designed to operate with the EHCI, UHCI and OHCI standards. By using this protocol, a single USB bus driver can be implemented without knowing if the underlying USB host controller conforms to the XHCI, EHCI, OHCI or the UHCI standards.
Each instance of the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL corresponds to a USB host controller in a platform. The protocol is attached to the device handle of a USB host controller that is created by a device driver for the USB host controller’s parent bus type. For example, a USB host controller that is implemented as a PCI device would require a PCI device driver to produce an instance of the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.
17.1.2. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL¶
Summary
Provides basic USB host controller management, basic data transactions over USB bus, and USB root hub access.
GUID
#define EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_GUID \
{0x3e745226,0x9818,0x45b6,\
{0xa2,0xac,0xd7,0xcd,0x0e,0x8b,0xa2,0xbc}}
Protocol Interface Structure
typedef struct _EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL {
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_GET_CAPABILITY GetCapability;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_RESET Reset;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_GET_STATE GetState;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_SET_STATE SetState;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_CONTROL_TRANSFER ControlTransfer;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_BULK_TRANSFER BulkTransfer;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_ASYNC_INTERRUPT_TRANSFER AsyncInterruptTransfer;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_ASYNC_INTERRUPT_TRANSFER SyncInterruptTransfer;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_ISOCHRONOUS_TRANSFER IsochronousTransfer;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_ASYNC_ISOCHRONOUS_TRANSFER AsyncIsochronousTransfer;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_GET_ROOTHUB_PORT_STATUS GetRootHubPortStatus;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_SET_ROOTHUB_PORT_FEATURE SetRootHubPortFeature;
EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_CLEAR_ROOTHUB_PORT_FEATURE ClearRootHubPortFeature
UINT16 MajorRevision;
UINT16 MinorRevision;
} EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL;
Parameters
- GetCapability
Retrieves the capabilities of the USB host controller. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetCapability() function description.
- Reset
Software reset of USB. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.Reset() function description.
- GetState
Retrieves the current state of the USB host controller. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetState() function description.
- SetState
Sets the USB host controller to a specific state. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.SetState() function description.
- ControlTransfer
Submits a control transfer to a target USB device. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.ControlTransfer() function description.
- BulkTransfer
Submits a bulk transfer to a bulk endpoint of a USB device. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.BulkTransfer() function description.
- AsyncInterruptTransfer
Submits an asynchronous interrupt transfer to an interrupt endpoint of a USB device. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.AsyncInterruptTransfer() function description.
- SyncInterruptTransfer
Submits a synchronous interrupt transfer to an interrupt endpoint of a USB device. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.SyncInterruptTransfer() function description.
- IsochronousTransfer
Submits isochronous transfer to an isochronous endpoint of a USB device. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.IsochronousTransfer() function description.
- AsyncIsochronousTransfer
Submits nonblocking USB isochronous transfer. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.AsyncIsochronousTransfer() function description.
- GetRootHubPortStatus
Retrieves the status of the specified root hub port. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetRootHubPortStatus() function description.
- SetRootHubPortFeature
Sets the feature for the specified root hub port. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.SetRootHubPortFeature() function description.
- ClearRootHubPortFeature
Clears the feature for the specified root hub port. See the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.ClearRootHubPortFeature() function description.
- MajorRevision
The major revision number of the USB host controller. The revision information indicates the release of the Universal Serial Bus Specification with which the host controller is compliant.
- MinorRevision
The minor revision number of the USB host controller. The revision information indicates the release of the Universal Serial Bus Specification with which the host controller is compliant.
Description
The EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL provides USB host controller management, basic data transactions over a USB bus, and USB root hub access. A device driver that wishes to manage a USB bus in a system retrieves the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance that is associated with the USB bus to be managed. A device handle for a USB host controller will minimally contain an EFI Device Path Protocol instance, and an EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance.
17.1.3. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetCapability()¶
Summary
Retrieves the Host Controller capabilities.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_GET_CAPABILITY) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT UINT8 *MaxSpeed,
OUT UINT8 *PortNumber,
OUT UINT8 *Is64BitCapable
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- MaxSpeed
Host controller data transfer speed; see Related Definitions below for a list of supported transfer speed values.
- PortNumber
Number of the root hub ports.
- Is64BitCapable
TRUE if controller supports 64-bit memory addressing, FALSE otherwise.
Related Definitions
#define EFI_USB_SPEED_FULL 0x0000
#define EFI_USB_SPEED_LOW 0x0001
#define EFI_USB_SPEED_HIGH 0x0002
#define EFI_USB_SPEED_SUPER 0x0003
EFI_USB_SPEED_LOW |
Low speed USB device; data bandwidth is up to 1.5 Mb/s. Supported by USB 1.1 OHCI and UHCI host controllers. |
EFI_USB_SPEED_FULL |
Full speed USB device; data bandwidth is up to 12 Mb/s. Supported by USB 1.1 OHCI and UHCI host controllers. |
EFI_USB_SPEED_HIGH |
High speed USB device; data bandwidth is up to 480 Mb/s. Supported by USB 2.0 EHCI host controllers. |
EFI_USB_SPEED_SUPER |
Super speed USB device; data bandwidth is up to 4.8Gbs. Supported by USB 3.0 XHCI host controllers. |
Description
This function is used to retrieve the host controller capabilities. MaxSpeed indicates the maximum data transfer speed the controller is capable of; this information is needed for the subsequent transfers. PortNumber is the number of root hub ports, it is required by the USB bus driver to perform bus enumeration. Is64BitCapable indicates that controller is capable of 64-bit memory access so that the host controller software can use memory blocks above 4 GiB for the data transfers.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The host controller capabilities were retrieved successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
MaxSpeed or PortNumber or Is64BitCapable is NULL. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
An error was encountered while attempting to retrieve the capabilities. |
17.1.4. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.Reset()¶
Summary
Provides software reset for the USB host controller.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_RESET) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT16 Attributes
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- Attributes
A bit mask of the reset operation to perform. See Related Definitions below for a list of the supported bit mask values.
Related Definitions
#define EFI_USB_HC_RESET_GLOBAL 0x0001
#define EFI_USB_HC_RESET_HOST_CONTROLLER 0x0002
#define EFI_USB_HC_RESET_GLOBAL_WITH_DEBUG 0x0004
#define EFI_USB_HC_RESET_HOST_WITH_DEBUG 0x0008
- EFI_USB_HC_RESET_GLOBAL
If this bit is set, a global reset signal will be sent to the USB bus. This resets all of the USB bus logic, including the USB host controller hardware and all the devices attached on the USB bus.
- EFI_USB_HC_RESET_HOST_CONTROLLER
If this bit is set, the USB host controller hardware will be reset. No reset signal will be sent to the USB bus.
- EFI_USB_HC_RESET_GLOBAL_WITH_DEBUG
If this bit is set, then a global reset signal will be sent to the USB bus. This resets all of the USB bus logic, including the USB host controller and all of the devices attached on the USB bus. If this is an XHCI or EHCI controller and the debug port has been configured, then this will still reset the host controller.
- EFI_USB_HC_RESET_HOST_WITH_DEBUG
If this bit is set, the USB host controller hardware will be reset. If this is an XHCI or EHCI controller and the debug port has been configured, then this will still reset the host controller.
Description
This function provides a software mechanism to reset a USB host controller. The type of reset is specified by the Attributes parameter. If the type of reset specified by Attributes is not valid, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the reset operation is completed, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned. If the type of reset specified by Attributes is not currently supported by the host controller hardware, EFI_UNSUPPORTD is returned. If a device error occurs during the reset operation, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned.
Note: For XHCI or EHCI controllers, the EFI_USB_HC_RESET_GLOBAL and EFI_USB_HC_RESET_HOST_CONTROLLER types of reset do not actually reset the bus if the debug port has been configured. In these cases, the function will return EFI_ACCESS_DENIED.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The reset operation succeeded. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Attributes is not valid. |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The type of reset specified by Attributes is not currently supported by the host controller hardware. |
EFI_ACCESS_DENIED |
Reset operation is rejected due to the debug port being configured and active; only EFI_USB_HC_RESET_GLOBAL_WITH_DEBUG or EFI_USB_HC_RESET_HOST_WITH_DEBUG reset Attributes can be used to perform reset operation for this host controller. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
An error was encountered while attempting to perform the reset operation. |
17.1.5. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetState()¶
Summary
Retrieves current state of the USB host controller.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_GET_STATE) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT EFI_USB_HC_STATE *State
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- State
A pointer to the EFI_USB_HC_STATE data structure that indicates current state of the USB host controller. Type EFI_USB_HC_STATE is defined in Related Definitions.
Related Definitions
typedef enum {
EfiUsbHcStateHalt,
EfiUsbHcStateOperational,
EfiUsbHcStateSuspend,
EfiUsbHcStateMaximum
} EFI_USB_HC_STATE;
- EfiUsbHcStateHalt
The host controller is in halt state. No USB transactions can occur while in this state. The host controller can enter this state for three reasons:
After host controller hardware reset.
Explicitly set by software.
Triggered by a fatal error such as consistency check failure.
- EfiUsbHcStateOperational
The host controller is in an operational state. When in this state, the host controller can execute bus traffic. This state must be explicitly set to enable the USB bus traffic.
- EfiUsbHcStateSuspend
The host controller is in the suspend state. No USB transactions can occur while in this state. The host controller enters this state for the following reasons:
Explicitly set by software.
Triggered when there is no bus traffic for 3 microseconds.
Description
This function is used to retrieve the USB host controller’s current state. The USB Host Controller Protocol publishes three states for USB host controller, as defined in Related Definitions below. If State is NULL, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If a device error occurs while attempting to retrieve the USB host controllers current state, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned. Otherwise, the USB host controller’s current state is returned in State, and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The state information of the host controller was returned in State. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
State is NULL. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
An error was encountered while attempting to retrieve the host controller’s current state. |
17.1.6. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.SetState()¶
Summary
Sets the USB host controller to a specific state.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_SET_STATE) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_USB_HC_STATE State
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- State
Indicates the state of the host controller that will be set. See the definition and description of the type EFI_USB_HC_STATE in the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetState() function description.
Description
This function is used to explicitly set a USB host controller’s state. There are three states defined for the USB host controller. These are the halt state, the operational state and the suspend state. The Figure below, Software Triggered State Transitions of a USB Host Controller, illustrates the possible state transitions:
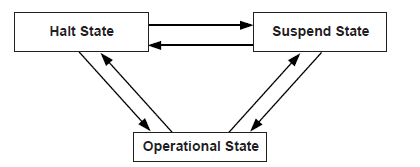
Fig. 17.1 Software Triggered State Transitions of a USB Host Controller¶
If the state specified by State is not valid, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If a device error occurs while attempting to place the USB host controller into the state specified by State, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned. If the USB host controller is successfully placed in the state specified by State, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The USB host controller was successfully placed in the state specified by State. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
State is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
Failed to set the state specified by State due to device error. |
17.1.7. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.ControlTransfer()¶
Summary
Submits control transfer to a target USB device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_CONTROL_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceAddress,
IN UINT8 DeviceSpeed,
IN UINTN MaximumPacketLength,
IN EFI_USB_DEVICE_REQUEST *Request,
IN EFI_USB_DATA_DIRECTION TransferDirection,
IN OUT VOID *Data OPTIONAL,
IN OUT UINTN *DataLength OPTIONAL,
IN UINTN TimeOut,
IN EFI_USB2_HC_TRANSACTION_TRANSLATOR *Translator,
OUT UINT32 *TransferResult
);
Related Definitions
typedef struct {
UINT8 TranslatorHubAddress,
UINT8 TranslatorPortNumber
} EFI_USB2_HC_TRANSACTION_TRANSLATOR;
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- DeviceAddress
Represents the address of the target device on the USB, which is assigned during USB enumeration.
- DeviceSpeed
Indicates device speed. See Related Definitions in GetCapability() for a list of the supported values.
- MaximumPacketLength
Indicates the maximum packet size that the default control transfer endpoint is capable of sending or receiving.
- Request
A pointer to the USB device request that will be sent to the USB device. Refer to UsbControlTransfer() (USB I/O Protocol) for the definition of this function type.
- TransferDirection
Specifies the data direction for the transfer. There are three values available, EfiUsbDataIn, EfiUsbDataOut and EfiUsbNoData. Refer to UsbControlTransfer() (USB I/O Protocol) for the definition of this function type.
- Data
A pointer to the buffer of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
On input, indicates the size, in bytes, of the data buffer specified by Data. On output, indicates the amount of data actually transferred.
- Translator
A pointer to the transaction translator data. See “Description” for the detailed information of this data structure.
- TimeOut
Indicates the maximum time, in milliseconds, which the transfer is allowed to complete.
- TransferResult
A pointer to the detailed result information generated by this control transfer. Refer to UsbControlTransfer() (USB I/O Protocol) for transfer result types ( EFI_USB_ERR_x ).
Description
This function is used to submit a control transfer to a target USB device specified by DeviceAddress. Control transfers are intended to support configuration/command/status type communication flows between host and USB device.
There are three control transfer types according to the data phase. If the TransferDirection parameter is EfiUsbNoData, Data is NULL, and DataLength is 0, then no data phase is present in the control transfer. If the TransferDirection parameter is EfiUsbDataOut, then Data specifies the data to be transmitted to the device, and DataLength specifies the number of bytes to transfer to the device. In this case, there is an OUT DATA stage followed by a SETUP stage. If the TransferDirection parameter is EfiUsbDataIn, then Data specifies the data to be received from the device, and DataLength specifies the number of bytes to receive from the device. In this case there is an IN DATA stage followed by a SETUP stage.
Translator is necessary to perform split transactions on low-speed or full-speed devices connected to a high-speed hub. Such transaction require the device connection information: device address and the port number of the hub that device is connected to. This information is passed through the fields of EFI_USB2_HC_TRANSACTION_TRANSLATOR structure. See Related Definitions for the structure field names. Translator is passed as NULL for the USB1.1 host controllers transfers or when the transfer is requested for high-speed device connected to USB2.0 controller.
If the control transfer has completed successfully, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned. If the transfer cannot be completed within the timeout specified by TimeOut, then EFI_TIMEOUT is returned. If an error other than timeout occurs during the USB transfer, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned and the detailed error code will be returned in the TransferResult parameter.
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned if one of the following conditions is satisfied:
TransferDirection is invalid.
TransferDirection, Data, and DataLength do not match one of the three control transfer types described above.
Request pointer is NULL.
MaximumPacketLength is not valid. If DeviceSpeed is EFI_USB_SPEED_LOW, then MaximumPacketLength must be 8. If DeviceSpeed is EFI_USB_SPEED_FULL or EFI_USB_SPEED_HIGH, then MaximumPacketLength must be 8, 16, 32, or 64. If DeviceSpeed is EFI_USB_SPEED_SUPER, then MaximumPacketLength must be 512.
TransferResult pointer is NULL.
Translator is NULL while the requested transfer requires split transaction. The conditions of the split transactions are described above in “Description” section.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The control transfer was completed successfully. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The control transfer could not be completed due to a lack of resources. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Some parameters are invalid. The possible invalid parameters are described in “Description” above. |
EFI_TIMEOUT |
The control transfer failed due to timeout. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The control transfer failed due to host controller or device error. Caller should check TransferResult for detailed error information. |
17.1.8. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.BulkTransfer()¶
Summary
Submits bulk transfer to a bulk endpoint of a USB device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_BULK_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceAddress,
IN UINT8 EndPointAddress,
IN UINT8 DeviceSpeed,
IN UINTN MaximumPacketLength,
IN UINT8 DataBuffersNumber,
IN OUT VOID *Data[EFI_USB_MAX_BULK_BUFFER_NUM],
IN OUT UINTN *DataLength,
IN OUT UINT8 *DataToggle,
IN UINTN TimeOut,
IN EFI_USB2_HC_TRANSACTION_TRANSLATOR *Translator,
OUT UINT32 *TransferResult
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- DeviceAddress
Represents the address of the target device on the USB, which is assigned during USB enumeration.
- EndPointAddress
The combination of an endpoint number and an endpoint direction of the target USB device. Each endpoint address supports data transfer in one direction except the control endpoint (whose default endpoint address is 0). It is the caller’s responsibility to make sure that the EndPointAddress represents a bulk endpoint.
- DeviceSpeed
Indicates device speed. The supported values are EFI_USB_SPEED_FULL,EFI_USB_SPEED_HIGH or EFI_USB_SPEED_SUPER..
- MaximumPacketLength
Indicates the maximum packet size the target endpoint is capable of sending or receiving.
- DataBuffersNumber
Number of data buffers prepared for the transfer.
- Data
Array of pointers to the buffers of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
When input, indicates the size, in bytes, of the data buffers specified by Data. When output, indicates the actually transferred data size.
- DataToggle
A pointer to the data toggle value. On input, it indicates the initial data toggle value the bulk transfer should adopt; on output, it is updated to indicate the data toggle value of the subsequent bulk transfer.
- Translator
A pointer to the transaction translator data. See ControlTransfer() “Description” for the detailed information of this data structure.
- TimeOut
Indicates the maximum time, in milliseconds, which the transfer is allowed to complete.
- TransferResult
A pointer to the detailed result information of the bulk transfer. Refer to UsbControlTransfer() in USB I/O Protocol for transfer result types ( EFI_USB_ERR_x ).
Description
This function is used to submit bulk transfer to a target endpoint of a USB device. The target endpoint is specified by DeviceAddress and EndpointAddress. Bulk transfers are designed to support devices that need to communicate relatively large amounts of data at highly variable times where the transfer can use any available bandwidth. Bulk transfers can be used only by full-speed and high-speed devices.
High-speed bulk transfers can be performed using multiple data buffers. The number of buffers that are actually prepared for the transfer is specified by DataBuffersNumber. For full-speed bulk transfers this value is ignored.
Data represents a list of pointers to the data buffers. For full-speed bulk transfers only the data pointed by Data[0] shall be used. For high-speed transfers depending on DataLength there several data buffers can be used. The total number of buffers must not exceed EFI_USB_MAX_BULK_BUFFER_NUM. See Related Definitions for the EFI_USB_MAX_BULK_BUFFER_NUM value.
The data transfer direction is determined by the endpoint direction that is encoded in the EndPointAddress parameter. Refer to USB Specification, Revision 2.0 on the Endpoint Address encoding.
The DataToggle parameter is used to track target endpoint’s data sequence toggle bits. The USB provides a mechanism to guarantee data packet synchronization between data transmitter and receiver across multiple transactions. The data packet synchronization is achieved with the data sequence toggle bits and the DATA0/DATA1 PIDs. A bulk endpoint’s toggle sequence is initialized to DATA0 when the endpoint experiences a configuration event. It toggles between DATA0 and DATA1 in each successive data transfer. It is host’s responsibility to track the bulk endpoint’s data toggle sequence and set the correct value for each data packet. The input DataToggle value points to the data toggle value for the first data packet of this bulk transfer; the output DataToggle value points to the data toggle value for the last successfully transferred data packet of this bulk transfer. The caller should record the data toggle value for use in subsequent bulk transfers to the same endpoint.
If the bulk transfer is successful, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned. If USB transfer cannot be completed within the timeout specified by Timeout, then EFI_TIMEOUT is returned. If an error other than timeout occurs during the USB transfer, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned and the detailed status code is returned in TransferResult.
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned if one of the following conditions is satisfied:
Data is NULL.
DataLength is 0.
DeviceSpeed is not valid; the legal values are EFI_USB_SPEED_FULL, EFI_USB_SPEED_HIGH, or EFI_USB_SPEED_SUPER.
MaximumPacketLength is not valid. The legal value of this parameter is 64 or less for full-speed, 512 or less for high-speed, and 1024 or less for super-speed transactions.
DataToggle points to a value other than 0 and 1.
TransferResult is NULL.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The bulk transfer was completed successfully. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The bulk transfer could not be submitted due to lack of resource. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Some parameters are invalid. The possible invalid parameters are described in “Description” above. |
EFI_TIMEOUT |
The bulk transfer failed due to timeout. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The bulk transfer failed due to host controller or device error. Caller should check TransferResult for detailed error information. |
17.1.9. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.AsyncInterruptTransfer()¶
Summary
Submits an asynchronous interrupt transfer to an interrupt endpoint of a USB device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_ASYNC_INTERRUPT_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceAddress,
IN UINT8 EndPointAddress,
IN UINT8 DeviceSpeed,
IN UINTN MaximumPacketLength,
IN BOOLEAN IsNewTransfer,
IN OUT UINT8 *DataToggle,
IN UINTN PollingInterval OPTIONAL,
IN UINTN DataLength OPTIONAL,
IN EFI_USB2_HC_TRANSACTION_TRANSLATOR *Translator OPTIONAL,
IN EFI_ASYNC_USB_TRANSFER_CALLBACK CallBackFunction OPTIONAL,
IN VOID *Context OPTIONAL
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- DeviceAddress
Represents the address of the target device on the USB, which is assigned during USB enumeration.
- EndPointAddress
The combination of an endpoint number and an endpoint direction of the target USB device. Each endpoint address supports data transfer in one direction except the control endpoint (whose default endpoint address is zero). It is the caller’s responsibility to make sure that the EndPointAddress represents an interrupt endpoint.
- DeviceSpeed
Indicates device speed. See Related Definitions in EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.ControlTransfer() for a list of the supported values.
- MaximumPacketLength
Indicates the maximum packet size the target endpoint is capable of sending or receiving.
- IsNewTransfer
If TRUE, an asynchronous interrupt pipe is built between the host and the target interrupt endpoint. If FALSE, the specified asynchronous interrupt pipe is canceled. If TRUE, and an interrupt transfer exists for the target end point, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
- DataToggle
A pointer to the data toggle value. On input, it is valid when IsNewTransfer is TRUE, and it indicates the initial data toggle value the asynchronous interrupt transfer should adopt. On output, it is valid when IsNewTransfer is FALSE, and it is updated to indicate the data toggle value of the subsequent asynchronous interrupt transfer.
- PollingInterval
Indicates the interval, in milliseconds, that the asynchronous interrupt transfer is polled. This parameter is required when IsNewTransfer is TRUE.
- DataLength
Indicates the length of data to be received at the rate specified by PollingInterval from the target asynchronous interrupt endpoint. This parameter is only required when IsNewTransfer is TRUE.
- Translator
A pointer to the transaction translator data.
- CallBackFunction
The Callback function. This function is called at the rate specified by PollingInterval. This parameter is only required when IsNewTransfer is TRUE. Refer to UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer() in USB I/O Protocol for the definition of this function type.
- Context
The context that is passed to the CallBackFunction. This is an optional parameter and may be NULL.
Description
This function is used to submit asynchronous interrupt transfer to a target endpoint of a USB device. The target endpoint is specified by DeviceAddress and EndpointAddress. In the USB Specification, Revision 2.0, interrupt transfer is one of the four USB transfer types. In the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL, interrupt transfer is divided further into synchronous interrupt transfer and asynchronous interrupt transfer.
An asynchronous interrupt transfer is typically used to query a device’s status at a fixed rate. For example, keyboard, mouse, and hub devices use this type of transfer to query their interrupt endpoints at a fixed rate. The asynchronous interrupt transfer is intended to support the interrupt transfer type of “submit once, execute periodically.” Unless an explicit request is made, the asynchronous transfer will never retire.
If IsNewTransfer is TRUE, then an interrupt transfer is started at a fixed rate. The rate is specified by PollingInterval, the size of the receive buffer is specified by DataLength, and the callback function is specified by CallBackFunction. Context specifies an optional context that is passed to the CallBackFunction each time it is called. The CallBackFunction is intended to provide a means for the host to periodically process interrupt transfer data.
If IsNewTransfer is TRUE, and an interrupt transfer exists for the target end point, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If IsNewTransfer is FALSE, then the interrupt transfer is canceled.
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned if one of the following conditions is satisfied:
Data transfer direction indicated by EndPointAddress is other than EfiUsbDataIn.
IsNewTransfer is TRUE and DataLength is 0.
IsNewTransfer is TRUE and DataToggle points to a value other than 0 and 1.
IsNewTransfer is TRUE and PollingInterval is not in the range 1..255.
IsNewTransfer requested where an interrupt transfer exists for the target end point.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The asynchronous interrupt transfer request has been successfully submitted or canceled. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Some parameters are invalid. The possible invalid parameters are described in “Description” above. When an interrupt transfer exists for the target end point and a new transfer is requested, EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The request could not be completed due to a lack of resources. |
17.1.10. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.SyncInterruptTransfer()¶
Summary
Submits synchronous interrupt transfer to an interrupt endpoint of a USB device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_SYNC_INTERRUPT_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceAddress,
IN UINT8 EndPointAddress,
IN UINT8 DeviceSpeed,
IN UINTN MaximumPacketLength,
IN OUT VOID *Data,
IN OUT UINTN *DataLength,
IN OUT UINT8 *DataToggle,
IN UINTN TimeOut,
IN EFI_USB2_HC_TRANSACTION_TRANSLATOR *Translator
OUT UINT32 *TransferResult
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- DeviceAddress
Represents the address of the target device on the USB, which is assigned during USB enumeration.
- EndPointAddress
The combination of an endpoint number and an endpoint direction of the target USB device. Each endpoint address supports data transfer in one direction except the control endpoint (whose default endpoint address is zero). It is the caller’s responsibility to make sure that the EndPointAddress represents an interrupt endpoint.
- DeviceSpeed
Indicates device speed. See Related Definitions in EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.ControlTransfer() for a list of the supported values.
- MaximumPacketLength
Indicates the maximum packet size the target endpoint is capable of sending or receiving.
- Data
A pointer to the buffer of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
On input, the size, in bytes, of the data buffer specified by Data. On output, the number of bytes transferred.
- DataToggle
A pointer to the data toggle value. On input, it indicates the initial data toggle value the synchronous interrupt transfer should adopt; on output, it is updated to indicate the data toggle value of the subsequent synchronous interrupt transfer.
- TimeOut
Indicates the maximum time, in milliseconds, which the transfer is allowed to complete.
- Translator
A pointer to the transaction translator data.
- TransferResult
A pointer to the detailed result information from the synchronous interrupt transfer. Refer to UsbControlTransfer() in USB I/O Protocol for transfer result types (EFI_USB_ERR_x).
Description
This function is used to submit a synchronous interrupt transfer to a target endpoint of a USB device. The target endpoint is specified by DeviceAddress and EndpointAddress. In the USB Specification, Revision2.0, interrupt transfer is one of the four USB transfer types. In the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL , interrupt transfer is divided further into synchronous interrupt transfer and asynchronous interrupt transfer.
The synchronous interrupt transfer is designed to retrieve small amounts of data from a USB device through an interrupt endpoint. A synchronous interrupt transfer is only executed once for each request. This is the most significant difference from the asynchronous interrupt transfer.
If the synchronous interrupt transfer is successful, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned. If the USB transfer cannot be completed within the timeout specified by Timeout, then EFI_TIMEOUT is returned. If an error other than timeout occurs during the USB transfer, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned and the detailed status code is returned in TransferResult.
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned if one of the following conditions is satisfied:
Data is NULL.
DataLength is 0.
MaximumPacketLength is not valid. The legal value of this parameter should be 3072 or less for high-speed device, 64 or less for a full-speed device; for a slow device, it is limited to 8 or less. For the full-speed device, it should be 8, 16, 32, or 64; for the slow device, it is limited to 8.
DataToggle points to a value other than 0 and 1.
TransferResult is NULL.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The synchronous interrupt transfer was completed successfully. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The synchronous interrupt transfer could not be submitted due to lack of resource. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Some parameters are invalid. The possible invalid parameters are described in “Description” above. |
EFI_TIMEOUT |
The synchronous interrupt transfer failed due to timeout. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The synchronous interrupt transfer failed due to host controller or device error. Caller should check TransferResult for detailed error information. |
17.1.11. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.IsochronousTransfer()¶
Summary
Submits isochronous transfer to an isochronous endpoint of a USB device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_ISOCHRONOUS_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceAddress,
IN UINT8 EndPointAddress,
IN UINT8 DeviceSpeed,
IN UINTN MaximumPacketLength,
IN UINT8 DataBuffersNumber,
IN OUT VOID *Data[EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM],
IN UINTN DataLength,
IN EFI_USB2_HC_TRANSACTION_TRANSLATOR *Translator,
OUT UINT32 *TransferResult
);
Related Definitions
#define EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM 7
#define EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM1 2
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- DeviceAddress
Represents the address of the target device on the USB, which is assigned during USB enumeration.
- EndPointAddress
The combination of an endpoint number and an endpoint direction of the target USB device. Each endpoint address supports data transfer in one direction except the control endpoint (whose default endpoint address is 0). It is the caller’s responsibility to make sure that the EndPointAddress represents an isochronous endpoint.
- DeviceSpeed
Indicates device speed. The supported values are EFI_USB_SPEED_FULL, EFI_USB_SPEED_HIGH, or EFI_USB_SPEED_SUPER.
- MaximumPacketLength
Indicates the maximum packet size the target endpoint is capable of sending or receiving. For isochronous endpoints, this value is used to reserve the bus time in the schedule, required for the per-frame data payloads. The pipe may, on an ongoing basis, actually use less bandwidth than that reserved.
- DataBuffersNumber
Number of data buffers prepared for the transfer.
- Data
Array of pointers to the buffers of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
Specifies the length, in bytes, of the data to be sent to or received from the USB device.
- Translator
A pointer to the transaction translator data. See ControlTransfer() “Description” for the detailed information of this data structure.
- TransferResult
A pointer to the detail result information of the isochronous transfer. Refer to UsbControlTransfer() in USB I/O Protocol for transfer result types (EFI_USB_ERR_x).
Description
This function is used to submit isochronous transfer to a target endpoint of a USB device. The target endpoint is specified by DeviceAddress and EndpointAddress. Isochronous transfers are used when working with isochronous date. It provides periodic, continuous communication between the host and a device. Isochronous transfers can be used only by full-speed, high-speed, and super-speed devices.
High-speed isochronous transfers can be performed using multiple data buffers. The number of buffers that are actually prepared for the transfer is specified by DataBuffersNumber. For full-speed isochronous transfers this value is ignored.
Data represents a list of pointers to the data buffers. For full-speed isochronous transfers only the data pointed by Data[0] shall be used. For high-speed isochronous transfers and for the split transactions depending on DataLength there several data buffers can be used. For the high-speed isochronous transfers the total number of buffers must not exceed EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM. For split transactions performed on full-speed device by high-speed host controller the total number of buffers is limited to EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM1 See Related Definitions for the EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM and EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM1 values.
If the isochronous transfer is successful, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned. The isochronous transfer is designed to be completed within one USB frame time, if it cannot be completed, EFI_TIMEOUT is returned. If an error other than timeout occurs during the USB transfer, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned and the detailed status code will be returned in TransferResult.
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned if one of the following conditions is satisfied:
Data is NULL.
DataLength is 0.
DeviceSpeed is not one of the supported values listed above.
MaximumPacketLength is invalid. MaximumPacketLength must be 1023 or less for full-speed devices, and 1024 or less for high-speed and super-speed devices.
TransferResult is NULL.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The isochronous transfer was completed successfully. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The isochronous transfer could not be submitted due to lack of resource. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Some parameters are invalid. The possible invalid parameters are described in “Description” above. |
EFI_TIMEOUT |
The isochronous transfer cannot be completed within the one USB frame time. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The isochronous transfer failed due to host controller or device error. Caller should check TransferResult for detailed error information. |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The implementation doesn’t support an Isochronous transfer function. |
17.1.12. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.AsyncIsochronousTransfer()¶
Summary
Submits nonblocking isochronous transfer to an isochronous endpoint of a USB device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_ASYNC_ISOCHRONOUS_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceAddress,
IN UINT8 EndPointAddress,
IN UINT8 DeviceSpeed,
IN UINTN MaximumPacketLength,
IN UINT8 DataBuffersNumber,
IN OUT VOID *Data[EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM],
IN UINTN DataLength,
IN EFI_USB2_HC_TRANSACTION_TRANSLATOR *Translator,
IN EFI_ASYNC_USB_TRANSFER_CALLBACK IsochronousCallBack,
IN VOID *Context OPTIONAL
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- DeviceAddress
Represents the address of the target device on the USB, which is assigned during USB enumeration.
- EndPointAddress
The combination of an endpoint number and an endpoint direction of the target USB device. Each endpoint address supports data transfer in one direction except the control endpoint (whose default endpoint address is zero). It is the caller’s responsibility to make sure that the EndPointAddress represents an isochronous endpoint.
- DeviceSpeed
Indicates device speed. The supported values are EFI_USB_SPEED_FULL, EFI_USB_SPEED_HIGH, or EFI_USB_SPEED_SUPER.
- MaximumPacketLength
Indicates the maximum packet size the target endpoint is capable of sending or receiving. For isochronous endpoints, this value is used to reserve the bus time in the schedule, required for the per-frame data payloads. The pipe may, on an ongoing basis, actually use less bandwidth than that reserved.
- DataBuffersNumber
Number of data buffers prepared for the transfer.
- Data
Array of pointers to the buffers of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
Specifies the length, in bytes, of the data to be sent to or received from the USB device.
- Translator
A pointer to the transaction translator data. See ControlTransfer() “Description” for the detailed information of this data structure.
- IsochronousCallback
The Callback function. This function is called if the requested isochronous transfer is completed. Refer to UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer() in USB I/O Protocol for the definition of this function type.
- Context
Data passed to the IsochronousCallback function. This is an optional parameter and may be NULL.
Description
This is an asynchronous type of USB isochronous transfer. If the caller submits a USB isochronous transfer request through this function, this function will return immediately. When the isochronous transfer completes, the IsochronousCallback function will be triggered, the caller can know the transfer results. If the transfer is successful, the caller can get the data received or sent in this callback function.
The target endpoint is specified by DeviceAddress and EndpointAddress. Isochronous transfers are used when working with isochronous date. It provides periodic, continuous communication between the host and a device. Isochronous transfers can be used only by full-speed, high-speed, and super-speed devices.
High-speed isochronous transfers can be performed using multiple data buffers. The number of buffers that are actually prepared for the transfer is specified by DataBuffersNumber. For full-speed isochronous transfers this value is ignored.
Data represents a list of pointers to the data buffers. For full-speed isochronous transfers only the data pointed by Data[0] shall be used. For high-speed isochronous transfers and for the split transactions depending on DataLength there several data buffers can be used. For the high-speed isochronous transfers the total number of buffers must not exceed EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM. For split transactions performed on full-speed device by high-speed host controller the total number of buffers is limited to EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM1 See Related Definitions in IsochronousTransfer() section for the EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM and EFI_USB_MAX_ISO_BUFFER_NUM1 values.
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned if one of the following conditions is satisfied:
Data is NULL.
DataLength is 0.
DeviceSpeed is not one of the supported values listed above.
MaximumPacketLength is invalid. MaximumPacketLength must be 1023 or less for full-speed devices and 1024 or less for high-speed and super-speed devices.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The asynchronous isochronous transfer was completed successfully. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The asynchronous isochronous transfer could not be submitted due to lack of resource. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Some parameters are invalid. The possible invalid parameters are described in “Description” above. |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The implementation doesn’t support Isochronous transfer function |
17.1.13. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetRootHubPortStatus()¶
Summary
Retrieves the current status of a USB root hub port.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_GET_ROOTHUB_PORT_STATUS) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 PortNumber,
OUT EFI_USB_PORT_STATUS *PortStatus
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- PortNumber
Specifies the root hub port from which the status is to be retrieved. This value is zero based. For example, if a root hub has two ports, then the first port is numbered 0, and the second port is numbered 1.
- PortStatus
A pointer to the current port status bits and port status change bits. The type EFI_USB_PORT_STATUS is defined in Related Definitions below.
Related Definitions
typedef struct {
UINT16 PortStatus;
UINT16 PortChangeStatus;
} EFI_USB_PORT_STATUS;
//**************************************************
// EFI_USB_PORT_STATUS.PortStatus bit definition
//**************************************************
#define USB_PORT_STAT_CONNECTION 0x0001
#define USB_PORT_STAT_ENABLE 0x0002
#define USB_PORT_STAT_SUSPEND 0x0004
#define USB_PORT_STAT_OVERCURRENT 0x0008
#define USB_PORT_STAT_RESET 0x0010
#define USB_PORT_STAT_POWER 0x0100
#define USB_PORT_STAT_LOW_SPEED 0x0200
#define USB_PORT_STAT_HIGH_SPEED 0x0400
#define USB_PORT_STAT_SUPER_SPEED 0x0800
#define USB_PORT_STAT_OWNER 0x2000
//**************************************************
// EFI_USB_PORT_STATUS.PortChangeStatus bit definition
//**************************************************
#define USB_PORT_STAT_C_CONNECTION 0x0001
#define USB_PORT_STAT_C_ENABLE 0x0002
#define USB_PORT_STAT_C_SUSPEND 0x0004
#define USB_PORT_STAT_C_OVERCURRENT 0x0008
#define USB_PORT_STAT_C_RESET 0x0010
- PortStatus
Contains current port status bitmap. The root hub port status bitmap is unified with the USB hub port status bitmap. See Table below, USB Hub Port Status Bitmap, for a reference, which is borrowed from Chapter 11, Hub Specification, of USB Specification, Revision 1.1.
- PortChangeStatus
Contains current port status change bitmap. The root hub port change status bitmap is unified with the USB hub port status bitmap. See Table below, Hub Port Change Status Bitmap for a reference, which is borrowed from Chapter 11, Hub Specification, of USB Specification, Revision 1.1.
Bit |
Description |
0 |
Current Connect Status: (USB_PORT_STAT_CONNECTION) This field reflects whether or not a device is currently connected to this port.
0 = No device is present
1 = A device is present on this port
|
1 |
Port Enable / Disabled: (USB_PORT_STAT_ENABLE) Ports can be enabled by software only. Ports can be disabled by either a fault condition (disconnect event or other fault condition) or by software.
0 = Port is disabled
1 = Port is enabled
|
2 |
Suspend: (USB_PORT_STAT_SUSPEND) This field indicates whether or not the device on this port is suspended.
0 = Not suspended
1 = Suspended
|
3 |
Over-current Indicator: (USB_PORT_STAT_OVERCURRENT) This field is used to indicate that the current drain on the port exceeds the specified maximum.
0 = All no over-current condition exists on this port
1 = An over-current condition exists on this port
|
4 |
Reset: (USB_PORT_STAT_RESET) Indicates whether port is in reset state.
0 = Port is not in reset state
1 = Port is in reset state
|
5-7 |
Reserved These bits return 0 when read. |
8 |
Port Power: (USB_PORT_STAT_POWER) This field reflects a port’s logical, power control state.
0 = This port is in the Powered-off state
1 = This port is not in the Powered-off state
|
9 |
Low Speed Device Attached: (USB_PORT_STAT_LOW_SPEED) This is relevant only if a device is attached.
0 = Full-speed device attached to this port
1 = Low-speed device attached to this port
|
10 |
High Speed Device Attached: (USB_PORT_STAT_HIGH_SPEED) This field indicates whether the connected device is high-speed device
0 = High-speed device is not attached to this port
1 = High-speed device attached to this port NOTE: this bit has precedence over Bit 9; if set, bit 9 must be ignored.
|
11 |
Super Speed Device Attached: (USB_PORT_STAT_SUPER_SPEED) This field indicates whether the connected device is a super-speed device.
0 = Super-speed device is not attached to this port.
1 = Super-speed device is attached to this port. NOTE: This bit bas precedence over Bit 9 and Bit 10; if set bits 9,10 must be ignored.
|
12 |
Reserved.
Bit returns 0 when read.
|
13 |
The host controller owns the specified port.
0 = Controller does not own the port.
1 = Controller owns the port
|
14-15 |
Reserved
These bits return 0 when read.
|
Bit |
Description |
0 |
Connect Status Change: (USB_PORT_STAT_C_CONNECTION) Indicates a change has occurred in the port’s Current Connect Status.
0 = No change has occurred to Current Connect status
1 = Current Connect status has changed
|
1 |
Port Enable /Disable Change: (USB_PORT_STAT_C _ENABLE)
0 = No change
1 = Port enabled/disabled status has changed
|
2 |
Suspend Change: (USB_PORT_STAT_C _SUSPEND) This field indicates a change in the host-visible suspend state of the attached device.
0 = No change
1 = Resume complete
|
3 |
Over-Current Indicator Change: (USB_PORT_STAT_C_OVERCURRENT)
0 = No change has occurred to Over-Current Indicator
1 = Over-Current Indicator has changed
|
4 |
Reset Change: (USB_PORT_STAT_C_RESET) This field is set when reset processing on this port is complete.
0 = No change
1 = Reset complete
|
5-15 |
Reserved.
These bits return 0 when read.
|
Description
This function is used to retrieve the status of the root hub port specified by PortNumber.
EFI_USB_PORT_STATUS found in Related Definitions EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetRootHubPortStatus() describes the port status of a specified USB port. This data structure is designed to be common to both a USB root hub port and a USB hub port.
The number of root hub ports attached to the USB host controller can be determined with the function EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetRootHubPortStatus(). If PortNumber is greater than or equal to the number of ports returned by GetRootHubPortNumber(), then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. Otherwise, the status of the USB root hub port is returned in PortStatus, and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The status of the USB root hub port specified by PortNumber was returned in PortStatus. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
PortNumber is invalid. |
17.1.14. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.SetRootHubPortFeature()¶
Summary
Sets a feature for the specified root hub port.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_SET_ROOTHUB_PORT_FEATURE) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 PortNumber,
IN EFI_USB_PORT_FEATURE PortFeature
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol .
- PortNumber
Specifies the root hub port whose feature is requested to be set. This value is zero based. For example, if a root hub has two ports, then the first port is number 0, and the second port is numbered 1.
- PortFeature
Indicates the feature selector associated with the feature set request. The port feature indicator is defined in Related Definitions and The Table below, USB Port Features.
Related Definitions
typedef enum {
EfiUsbPortEnable = 1,
EfiUsbPortSuspend = 2,
EfiUsbPortReset = 4,
EfiUsbPortPower = 8,
EfiUsbPortOwner = 13,
EfiUsbPortConnectChange = 16,
EfiUsbPortEnableChange = 17,
EfiUsbPortSuspendChange = 18,
EfiUsbPortOverCurrentChange = 19,
EfiUsbPortResetChange = 20
} EFI_USB_PORT_FEATURE;
The feature values specified in the enumeration variable have special meaning. Each value indicates its bit index in the port status and status change bitmaps, if combines these two bitmaps into a 32-bit bitmap. The meaning of each port feature is listed in Table below, USB Port Features.
Port Feature |
For SetRootHubPortFeature |
For Cl earRootHubPortFeature |
EfiUsbPortEnable |
Enable the given port of the root hub. |
Disable the given port of the root hub. |
EfiUsbPortSuspend |
Put the given port into suspend state. |
Restore the given port from the previous suspend state. |
EfiUsbPortReset |
Reset the given port of the root hub. |
Clear the RESET signal for the given port of the root hub. |
EfiUsbPortPower |
Power the given port. |
Shutdown the power from the given port. |
EfiUsbPortOwner |
N/A. |
Releases the port ownership of this port to companion host controller. |
Ef iUsbPortConnectChange |
N/A. |
Clear USB_P ORT_STAT_C_CONNECTION bit of the given port of the root hub. |
E fiUsbPortEnableChange |
N/A. |
Clear U SB_PORT_STAT_C_ENABLE bit of the given port of the root hub. |
Ef iUsbPortSuspendChange |
N/A. |
Clear US B_PORT_STAT_C_SUSPEND bit of the given port of the root hub. |
EfiUsb PortOverCurrentChange |
N/A. |
Clear USB_PO RT_STAT_C_OVERCURRENT bit of the given port of the root hub. |
EfiUsbPortResetChange |
N/A. |
Clear USB_PORT_STAT_C_RESET bit of the given port of the root hub. |
Description
This function sets the feature specified by PortFeature for the USB root hub port specified by PortNumber. Setting a feature enables that feature or starts a process associated with that feature. For the meanings about the defined features, refer to Table USB Hub Port Status Bitmap and Table Hub Port Change Status Bitmap.
The number of root hub ports attached to the USB host controller can be determined with the function EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetRootHubPortStatus(). If PortNumber is greater than or equal to the number of ports returned by GetRootHubPortNumber(), then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If PortFeature is not EfiUsbPortEnable, EfiUsbPortSuspend, EfiUsbPortReset nor EfiUsbPortPower, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The feature specified by PortFeature was set for the USB root hub port specified by PortNumber. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
PortNumber is invalid or PortFeature is invalid for this function. |
17.1.15. EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.ClearRootHubPortFeature()¶
Summary
Clears a feature for the specified root hub port.
Prototype
typede
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL_CLEAR_ROOTHUB_PORT_FEATURE) (
IN EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL *This
IN UINT8 PortNumber,
IN EFI_USB_PORT_FEATURE PortFeature
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL instance, which is defined in USB2 Host Controller Protocol.
- PortNumber
Specifies the root hub port whose feature is requested to be cleared. This value is zero-based. For example, if a root hub has two ports, then the first port is number 0, and the second port is numbered 1.
- PortFeature
Indicates the feature selector associated with the feature clear request. The port feature indicator EFI_USB_PORT_FEATURE is defined in Section 17.1.14 in the “Related Definitions” section, and in Table 17.3.
Description
This function clears the feature specified by PortFeature for the USB root hub port specified by PortNumber. Clearing a feature disables that feature or stops a process associated with that feature. For the meanings about the defined features, refer to Table USB Hub Port Status Bitmap and Table Hub Port Change Status Bitmap.
The number of root hub ports attached to the USB host controller can be determined with the function EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.GetRootHubPortStatus(). If PortNumber is greater than or equal to the number of ports returned by GetRootHubPortNumber(), then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If PortFeature is not EfiUsbPortEnable, EfiUsbPortSuspend, EfiUsbPortPower, EfiUsbPortConnectChange, EfiUsbPortResetChange, EfiUsbPortEnableChange, EfiUsbPortSuspendChange, or EfiUsbPortOverCurrentChange, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The feature specified by PortFeature was cleared for the USB root hub port specified by PortNumber. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
PortNumber is invalid or PortFeature is invalid. |
17.2. USB Driver Model¶
17.2.1. Scope¶
Section USB Driver Model describes the USB Driver Model. This includes the behavior of USB Bus Drivers, the behavior of a USB Device Drivers, and a detailed description of the EFI USB I/O Protocol. This document provides enough material to implement a USB Bus Driver, and the tools required to design and implement USB Device Drivers. It does not provide any information on specific USB devices.
The material contained in this section is designed to extend this specification and the UEFI Driver Model in a way that supports USB device drivers and USB bus drivers. These extensions are provided in the form of USB specific protocols. This document provides the information required to implement a USB Bus Driver in system firmware. The document also contains the information required by driver writers to design and implement USB Device Drivers that a platform may need to boot a UEFI-compliant OS.
The USB Driver Model described here is intended to be a foundation on which a USB Bus Driver and a wide variety of USB Device Drivers can be created. USB Driver Model Overview
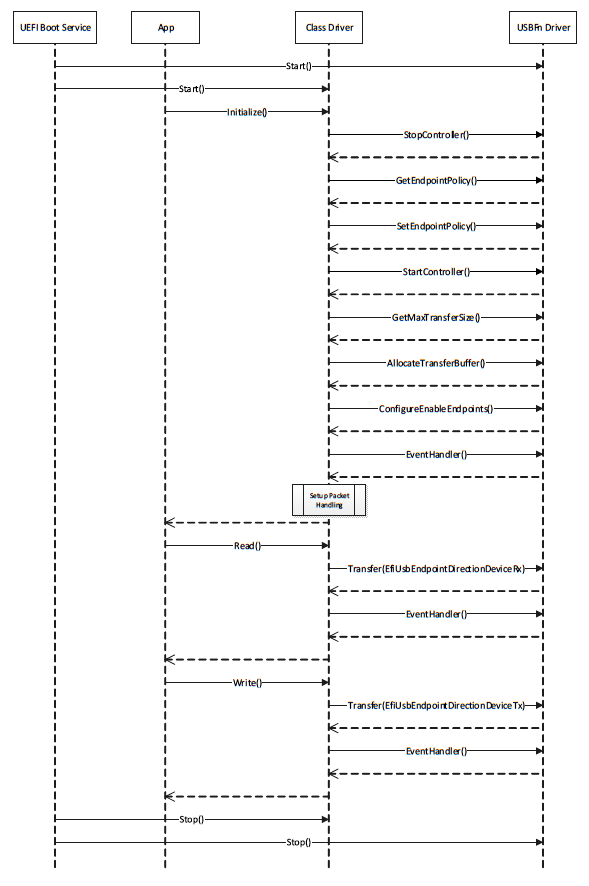
The USB Driver Stack includes the USB Bus Driver, USB Host Controller Driver, and individual USB device drivers.
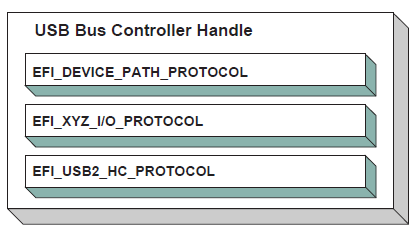
Fig. 17.2 USB Bus Controller Handle¶
In the USB Bus Driver Design, the USB Bus Controller is managed by two drivers. One is USB Host Controller Driver, which consumes its parent bus EFI_XYZ_IO_PROTOCOL, and produces EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL, and attaches it to the Bus Controller Handle. The other one is USB Bus Driver, which consumes EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL, and performs bus enumeration. Figure USB Bus Controller Handle shows protocols that are attached to the USB Bus Controller Handle. Detailed descriptions are presented in the following sections.
17.2.2. USB Bus Driver¶
USB Bus Driver performs periodic Enumeration on the USB Bus. In USB bus enumeration, when a new USB controller is found, the bus driver does some standard configuration for that new controller, and creates a device handle for it. The EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL and EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL are attached to the device handle so that the USB controller can be accessed. The USB Bus Driver is also responsible for connecting USB device drivers to USB controllers. When a USB device is detached from a USB bus, the USB bus driver will stop that USB controller, and uninstall the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL and the EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL from that handle. A detailed description is given in USB Hot-Plug Event.
17.2.2.1. USB Bus Driver Entry Point¶
Like all other device drivers, the entry point for a USB Bus Driver attaches the EFI Driver Binding Protocol to image handle of the USB Bus Driver.
17.2.2.2. Driver Binding Protocol for USB Bus Drivers¶
Supported() tests to see if the USB Bus Driver can manage a device handle. A USB Bus Driver can only manage a device handle that contains EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.
The general idea is that the USB Bus Driver is a generic driver. Since there are several types of USB Host Controllers, an EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is used to abstract the host controller interface. Actually, a USB Bus Driver only requires an EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL.
The Start() function tells the USB Bus Driver to start managing the USB Bus. In this function, the USB Bus Driver creates a device handle for the root hub, and creates a timer to monitor root hub connection changes.
The Stop() function tells the USB Bus Driver to stop managing a USB Host Bus Controller. The Stop() function simply deconfigures the devices attached to the root hub. The deconfiguration is a recursive process. If the device to be deconfigured is a USB hub, then all USB devices attached to its downstream ports will be deconfigured first, then itself. If all of the child devices handles have been destroyed then the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL is closed. Finally, the Stop() unction will then place the USB Host Bus Controller in a quiescent state.
17.2.2.3. USB Hot-Plug Event¶
Hot-Plug is one of the most important features provided by USB. A USB bus driver implements this feature through two methods. There are two types of hubs defined in the USB specification. One is the USB root hub, which is implemented in the USB Host controller. A timer event is created for the root hub. The other one is a USB Hub. An event is created for each hub that is correctly configured. All these events are associated with the same trigger which is USB bus numerator.
When USB bus enumeration is triggered, the USB Bus Driver checks the source of the event. This is required because the root hub differs from standard USB hub in checking the hub status. The status of a root hub is retrieved through the EFI_USB2_HC_PROTOCOL, and that status of a standard USB hub is retrieved through a USB control transfer. A detailed description of the enumeration process is presented in the next section.
17.2.2.4. USB Bus Enumeration¶
When the periodic timer or the hubs notify event is signaled, the USB Bus Driver will perform bus numeration.
Determine if the event is from the roothub or a standard USB hub.
Determine the port on which the connection change event occurred.
Determine if it is a connection change or a disconnection change.
If a connect change is detected, then a new device has been attached. Perform the following:
a – Reset and enable that port.
b – Configure the new device.
c – Parse the device configuration descriptors; get all of its interface descriptors (i.e., all USB controllers), and configure each interface.
d – Create a new handle for each interface (USB Controller) within the USB device. Attach the EFI Device Path Protocol, and EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL to each handle.
e – Connect the USB Controller to a USB device driver with the Boot Service EFI_BOOT_SERVICES.ConnectController() if applicable.
f – If the USB Controller is a USB hub, create a Hub notify event which is associated with the USB Bus Enumerator, and submit an Asynchronous Interrupt Transfer Request (USB I/O Protocol).
If a disconnect change, then a device has been detached from the USB Bus. Perform the following:
a – If the device is not a USB Hub, then find and deconfigure the USB Controllers within the device. Then, stop each USB controller with EFI_BOOT_SERVICES.DisconnectController(), and uninstall the EFI_DEVICE_PATH_PROTOCOL and the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL from the controller’s handle. If the EFI_BOOT_SERVICES.DisconnectController() call fails this process must be retried on a subsequent timer tick.
b – If the USB controller is USB hub controller, first find and deconfigure all its downstream USB devices (this is a recursive process, since there may be additional USB hub controllers on the downstream ports), then deconfigure USB hub controller itself.
17.2.3. USB Device Driver¶
A USB Device Driver manages a USB Controller and produces a device abstraction for use by a preboot application.
17.2.3.1. USB Device Driver Entry Point¶
Like all other device drivers, the entry point for a USB Device Driver attaches EFI Driver Binding Protocol to image handle of the USB Device Driver.
17.2.3.2. Driver Binding Protocol for USB DeviceDrivers¶
The Supported() tests to see if the USB Device Driver can manage a device handle. This function checks to see if a controller can be managed by the USB Device Driver. This is done by opening the See EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL bus abstraction on the USB Controller handle, and using the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL services to determine if this USB Controller matches the profile that the USB Device Driver is capable of managing.
The Start() function tells the USB Device Driver to start managing a USB Controller. It opens the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance from the handle for the USB Controller. This protocol instance is used to perform USB packet transmission over the USB bus. For example, if the USB controller is USB keyboard, then the USB keyboard driver would produce and install the EFI_SIMPLE_TEXT_INPUT_PROTOCOL to the USB controller handle.
The Stop() function tells the USB Device Driver to stop managing a USB Controller. It removes the I/O abstraction protocol instance previously installed in Start() from the USB controller handle. It then closes the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.
17.2.4. USB I/O Protocol¶
This section provides a detailed description of the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL. This protocol is used by code, typically drivers, running in the EFI boot services environment to access USB devices like USB keyboards, mice and mass storage devices. In particular, functions for managing devices on USB buses are defined here.
The interfaces provided in the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL are for performing basic operations to access USB devices. Typically, USB devices are accessed through the four different transfers types:
- Controller Transfer
Typically used to configure the USB device into an operation mode.
- Interrupt Transfer
Typically used to get periodic small amount of data, like USB keyboard and mouse.
- Bulk Transfer
Typically used to transfer large amounts of data like reading blocks from USB mass storage devices.
- Isochronous Transfer
Typically used to transfer data at a fixed rate like voice data.
This protocol also provides mechanisms to manage and configure USB devices and controllers.
17.2.5. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL¶
Summary
Provides services to manage and communicate with USB devices.
GUID
#define EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL_GUID \
{0x2B2F68D6,0x0CD2,0x44cf,\
{0x8E,0x8B,0xBB,0xA2,0x0B,0x1B,0x5B,0x75}}
Protocol Interface Structure
typedef struct _EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL {
EFI_USB_IO_CONTROL_TRANSFER UsbControlTransfer;
EFI_USB_IO_BULK_TRANSFER UsbBulkTransfer;
EFI_USB_IO_ASYNC_INTERRUPT_TRANSFER UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer;
EFI_USB_IO_SYNC_INTERRPUT_TRANSFER UsbSyncInterruptTransfer
EFI_USB_IO_ISOCHRONOUS_TRANSFER UsbIsochronousTransfer;
EFI_USB_IO_ASYNC_ISOCHRONOUS_TRANSFER UsbAsyncIsochronousTransfer;
EFI_USB_IO_GET_DEVICE_DESCRIPTOR UsbGetDeviceDescriptor;
EFI_USB_IO_GET_CONFIG_DESCRIPTOR UsbGetConfigDescriptor;
EFI_USB_IO_GET_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR UsbGetInterfaceDescriptor;
EFI_USB_IO_GET_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR UsbGetEndpointDescriptor;
EFI_USB_IO_GET_STRING_DESCRIPTOR UsbGetStringDescriptor;
EFI_USB_IO_GET_SUPPORTED_LANGUAGES UsbGetSupportedLanguages;
EFI_USB_IO_PORT_RESET UsbPortReset;
} EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL;
Parameters
- UsbControlTransfer
Accesses the USB Device through USB Control Transfer Pipe. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbControlTransfer() function description.
- UsbBulkTransfer
Accesses the USB Device through USB Bulk Transfer Pipe. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbBulkTransfer() function description.
- UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer
Non-block USB interrupt transfer. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer() function description.
- UsbSyncInterruptTransfer
Accesses the USB Device through USB Synchronous Interrupt Transfer Pipe. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbSyncInterruptTransfer() function description.
- UsbIsochronousTransfer
Accesses the USB Device through USB Isochronous Transfer Pipe. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbIsochronousTransfer() function description.
- UsbAsyncIsochronousTransfer
Nonblock USB isochronous transfer. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbAsyncIsochronousTransfer() function description.
- UsbGetDeviceDescriptor
Retrieves the device descriptor of a USB device. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetDeviceDescriptor() function description.
- UsbGetConfigDescriptor
Retrieves the activated configuration descriptor of a USB device. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetConfigDescriptor() function description.
- UsbGetInterfaceDescriptor
- Retrieves the interface descriptor of a USB Controller. See theEFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetInterfaceDescriptor() function description.
- UsbGetEndpointDescriptor
- Retrieves the endpoint descriptor of a USB Controller. See theEFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetEndpointDescriptor() function description.
- UsbGetStringDescriptor
Retrieves the string descriptor inside a USB Device. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetStringDescriptor() function description.
- UsbGetSupportedLanguages
Retrieves the array of languages that the USB device supports. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetSupportedLanguages() function description.
- UsbPortReset
Resets and reconfigures the USB controller. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbPortReset() function description.
Description
The EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL provides four basic transfers types described in the USB 1.1 Specification. These include control transfer, interrupt transfer, bulk transfer and isochronous transfer. The EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL also provides some basic USB device/controller management and configuration interfaces. A USB device driver uses the services of this protocol to manage USB devices.
17.2.6. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbControlTransfer()¶
Summary
This function is used to manage a USB device with a control transfer pipe. A control transfer is typically used to perform device initialization and configuration.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_CONTROL_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_USB_DEVICE_REQUEST *Request,
IN EFI_USB_DATA_DIRECTION Direction,
IN UINT32 Timeout,
IN OUT VOID *Data OPTIONAL,
IN UINTN DataLength OPTIONAL,
OUT UINT32 *Status
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- Request
A pointer to the USB device request that will be sent to the USB device. See Related Definitions below.
- Direction
Indicates the data direction. See Related Definitions below for this type.
- Data
A pointer to the buffer of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- Timeout
Indicating the transfer should be completed within this time frame. The units are in milliseconds. If Timeout is 0, then the caller must wait for the function to be completed until EFI_SUCCESS or EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned.
- DataLength
The size, in bytes, of the data buffer specified by Data.
- Status
A pointer to the result of the USB transfer.
Related Definitions
typedef enum {
EfiUsbDataIn,
EfiUsbDataOut,
EfiUsbNoData
} EFI_USB_DATA_DIRECTION;
//
// Error code for USB Transfer Results
//
#define EFI_USB_NOERROR 0x0000
#define EFI_USB_ERR_NOTEXECUTE 0x0001
#define EFI_USB_ERR_STALL 0x0002
#define EFI_USB_ERR_BUFFER 0x0004
#define EFI_USB_ERR_BABBLE 0x0008
#define EFI_USB_ERR_NAK 0x0010
#define EFI_USB_ERR_CRC 0x0020
#define EFI_USB_ERR_TIMEOUT 0x0040
#define EFI_USB_ERR_BITSTUFF 0x0080
#define EFI_USB_ERR_SYSTEM 0x0100
typedef struct {
UINT8 RequestType;
UINT8 Request;
UINT16 Value;
UINT16 Index;
UINT16 Length;
} EFI_USB_DEVICE_REQUEST;
- RequestType
The field identifies the characteristics of the specific request.
- Request
This field specifies the particular request.
- Value
This field is used to pass a parameter to USB device that is specific to the request.
- Index
This field is also used to pass a parameter to USB device that is specific to the request.
- Length
This field specifies the length of the data transferred during the second phase of the control transfer. If it is 0, then there is no data phase in this transfer.
Description
This function allows a USB device driver to communicate with the USB device through a Control Transfer. There are three control transfer types according to the data phase. If the Direction parameter is EfiUsbNoData, Data is NULL, and DataLength is 0, then no data phase exists for the control transfer. If the Direction parameter is EfiUsbDataOut, then Data specifies the data to be transmitted to the device, and DataLength specifies the number of bytes to transfer to the device. In this case there is an OUT DATA stage followed by a SETUP stage. If the Direction parameter is EfiUsbDataIn, then Data specifies the data that is received from the device, and DataLength specifies the number of bytes to receive from the device. In this case there is an IN DATA stage followed by a SETUP stage. After the USB transfer has completed successfully, EFI_SUCCESS is returned. If the transfer cannot be completed due to timeout, then EFI_TIMEOUT is returned. If an error other than timeout occurs during the USB transfer, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned and the detailed status code is returned in Status.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The control transfer has been successfully executed. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
The parameter Direction is not valid. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Request is NULL. |
EFI-INVALID_PARAMETER |
Status is NULL. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The request could not be completed due to a lack of resources. |
EFI_TIMEOUT |
The control transfer fails due to timeout. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The transfer failed. The transfer status is returned in Status. |
17.2.7. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbBulkTransfer()¶
Summary
This function is used to manage a USB device with the bulk transfer pipe. Bulk Transfers are typically used to transfer large amounts of data to/from USB devices.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_BULK_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceEndpoint,
IN OUT VOID *Data,
IN OUT UINTN *DataLength,
IN UINTN Timeout,
OUT UINT32 *Status
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- DeviceEndpoint
The destination USB device endpoint to which the device request is being sent. DeviceEndpoint must be between 0x01 and 0x0F or between 0x81 and 0x8F, otherwise EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the endpoint is not a BULK endpoint, EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. The MSB of this parameter indicates the endpoint direction. The number “1” stands for an IN endpoint, and “0” stands for an OUT endpoint.
- Data
A pointer to the buffer of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
On input, the size, in bytes, of the data buffer specified by Data. On output, the number of bytes that were actually transferred.
- Timeout
Indicating the transfer should be completed within this time frame. The units are in milliseconds. If Timeout is 0, then the caller must wait for the function to be completed until EFI_SUCCESS or EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned.
- Status
This parameter indicates the USB transfer status.
Description
This function allows a USB device driver to communicate with the USB device through Bulk Transfer. The transfer direction is determined by the endpoint direction. If the USB transfer is successful, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned. If USB transfer cannot be completed within the Timeout frame, EFI_TIMEOUT is returned. If an error other than timeout occurs during the USB transfer, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned and the detailed status code will be returned in the Status parameter.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The bulk transfer has been successfully executed. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
If DeviceEndpoint is not valid. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Data is NULL. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
DataLength is NULL. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Status is NULL. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The request could not be completed due to a lack of resources. |
EFI_TIMEOUT |
The bulk transfer cannot be completed within Timeout timeframe. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The transfer failed other than timeout, and the transfer status is returned in Status. |
17.2.8. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer()¶
Summary
This function is used to manage a USB device with an interrupt transfer pipe. An Asynchronous Interrupt Transfer is typically used to query a device’s status at a fixed rate. For example, keyboard, mouse, and hub devices use this type of transfer to query their interrupt endpoints at a fixed rate.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_ASYNC_INTERRUPT_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceEndpoint,
IN BOOLEAN IsNewTransfer,
IN UINTN PollingInterval OPTIONAL,
IN UINTN DataLength OPTIONAL,
IN EFI_ASYNC_USB_TRANSFER_CALLBACK InterruptCallBack OPTIONAL,
IN VOID *Context OPTIONAL
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- DeviceEndpoint
The destination USB device endpoint to which the device request is being sent. DeviceEndpoint must be between 0x01 and 0x0F or between 0x81 and 0x8F, otherwise EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the endpoint is not an INTERRUPT endpoint, EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. The MSB of this parameter indicates the endpoint direction. The number “1” stands for an IN endpoint, and “0” stands for an OUT endpoint.
- IsNewTransfer
If TRUE, a new transfer will be submitted to USB controller. If FALSE, the interrupt transfer is deleted from the device’s interrupt transfer queue. If TRUE, and an interrupt transfer exists for the target end point, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
- PollingInterval
Indicates the periodic rate, in milliseconds, that the transfer is to be executed. This parameter is required when IsNewTransfer is TRUE. The value must be between 1 to 255, otherwise EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. The units are in milliseconds.
- DataLength
Specifies the length, in bytes, of the data to be received from the USB device. This parameter is only required when IsNewTransfer is TRUE.
- Context
Data passed to the InterruptCallback function. This is an optional parameter and may be NULL.
- InterruptCallback
The Callback function. This function is called if the asynchronous interrupt transfer is completed. This parameter is required when IsNewTransfer is TRUE. See Related Definitions for the definition of this type.
Related Definitions
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_ASYNC_USB_TRANSFER_CALLBACK) (
IN VOID *Data,
IN UINTN DataLength,
IN VOID *Context,
IN UINT32 Status
);
- Data
Data received or sent via the USB Asynchronous Transfer, if the transfer completed successfully.
- DataLength
The length of Data received or sent via the Asynchronous Transfer, if transfer successfully completes.
- Context
Data passed from EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer() request.
- Status
Indicates the result of the asynchronous transfer.
Description
This function allows a USB device driver to communicate with a USB device with an Interrupt Transfer. Asynchronous Interrupt transfer is different than the other four transfer types because it is a nonblocking transfer. The interrupt endpoint is queried at a fixed rate, and the data transfer direction is always in the direction from the USB device towards the system.
If IsNewTransfer is TRUE, then an interrupt transfer is started at a fixed rate. The rate is specified by PollingInterval, the size of the receive buffer is specified by DataLength, and the callback function is specified by InterruptCallback. If IsNewTransfer is TRUE, and an interrupt transfer exists for the target end point, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
If IsNewTransfer is FALSE, then the interrupt transfer is canceled.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The asynchronous USB transfer request has been successfully executed. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The asynchronous USB transfer request failed. When an interrupt transfer exists for the target end point and a new transfer is requested, EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. |
Examples
Below is an example of how an asynchronous interrupt transfer is used. The example shows how a USB Keyboard Device Driver can periodically receive data from interrupt endpoint.
EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *UsbIo;
EFI_STATUS Status;
USB_KEYBOARD_DEV *UsbKeyboardDevice;
EFI_USB_INTERRUPT_CALLBACK *KeyboardHandle;
. . .
Status = UsbIo->UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer(
UsbIo,
UsbKeyboardDevice->IntEndpointAddress,
TRUE,
UsbKeyboardDevice->IntPollingInterval,
8,
KeyboardHandler,
UsbKeyboardDevice
);
. . .
//
// The following is the InterruptCallback function. If there is
// any results got from Asynchronous Interrupt Transfer,
// this function will be called.
//
EFI_STATUS
KeyboardHandler(
IN VOID *Data,
IN UINTN DataLength,
IN VOID *Context,
IN UINT32 Result
)
{
USB_KEYBOARD_DEV *UsbKeyboardDevice;
UINTN I;
if(EFI_ERROR(Result))
{
//
// Something error during this transfer,
// just to some recovery work
//
. . .
. . .
return EFI_DEVICE_ERROR;
}
UsbKeyboardDevice = (USB_KEYBOARD_DEV *)Context;
for(I = 0; I < DataLength; I++)
{
ParsedData(Data[I]);
. . .
}
return EFI_SUCCESS;
}
17.2.9. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbSyncInterruptTransfer()¶
Summary
This function is used to manage a USB device with an interrupt transfer pipe. The difference between EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer() and UsbSyncInterruptTransfer() is that the Synchronous interrupt transfer will only be executed one time. Once it returns, regardless of its status, the interrupt request will be deleted in the system.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_SYNC_INTERRUPT_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceEndpoint,
IN OUT VOID *Data,
IN OUT UINTN *DataLength,
IN UINTN Timeout,
OUT UINT32 *Status
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- DeviceEndpoint
The destination USB device endpoint to which the device request is being sent. DeviceEndpoint must be between 0x01 and 0x0F or between 0x81 and 0x8F, otherwise EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the endpoint is not an INTERRUPT endpoint, EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. The MSB of this parameter indicates the endpoint direction. The number “1” stands for an IN endpoint, and “0” stands for an OUT endpoint.
- Data
A pointer to the buffer of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
On input, then size, in bytes, of the buffer Data. On output, the amount of data actually transferred.
- Timeout
The time out, in milliseconds, for this transfer. If Timeout is 0, then the caller must wait for the function to be completed until EFI_SUCCESS or EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned. If the transfer is not completed in this time frame, then EFI_TIMEOUT is returned.
- Status
This parameter indicates the USB transfer status.
Description
This function allows a USB device driver to communicate with a USB device through a synchronous interrupt transfer. The UsbSyncInterruptTransfer() differs from EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer() described in the previous section in that it is a blocking transfer request. The caller must wait for the function return, either successfully or unsuccessfully.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The sync interrupt transfer has been successfully executed. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
The parameter DeviceEndpoint is not valid. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Data is NULL. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
DataLength is NULL. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
Status is NULL. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The request could not be completed due to a lack of resources. |
EFI_TIMEOUT |
The transfer cannot be completed within Timeout timeframe. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The transfer failed other than timeout, and the transfer status is returned in Status. |
17.2.10. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbIsochronousTransfer()¶
Summary
This function is used to manage a USB device with an isochronous transfer pipe. An Isochronous transfer is typically used to transfer streaming data.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USB_IO_ISOCHRONOUS_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceEndpoint,
IN OUT VOID *Data,
IN UINTN DataLength,
OUT UINT32 *Status
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- DeviceEndpoint
The destination USB device endpoint to which the device request is being sent. DeviceEndpoint must be between 0x01 and 0x0F or between 0x81 and 0x8F, otherwise EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the endpoint is not an ISOCHRONOUS endpoint, EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. The MSB of this parameter indicates the endpoint direction. The number “1” stands for an IN endpoint, and “0” stands for an OUT endpoint.
- Data
A pointer to the buffer of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
The size, in bytes, of the data buffer specified by Data.
- Status
This parameter indicates the USB transfer status.
Description
This function allows a USB device driver to communicate with a USB device with an Isochronous Transfer. The type of transfer is different than the other types because the USB Bus Driver will not attempt to perform error recovery if transfer fails. If the USB transfer is completed successfully, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned. The isochronous transfer is designed to be completed within 1 USB frame time, if it cannot be completed, EFI_TIMEOUT is returned. If the transfer fails due to other reasons, then EFI_DEVICE_ERROR is returned and the detailed error status is returned in Status. If the data length exceeds the maximum payload per USB frame time, then it is this function’s responsibility to divide the data into a set of smaller packets that fit into a USB frame time. If all the packets are transferred successfully, then EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The isochronous transfer has been successfully executed. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
The parameter DeviceEndpoint is not valid. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The request could not be completed due to a lack of resources. |
EFI_TIMEOUT |
The transfer cannot be completed within the 1 USB frame time. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The transfer failed due to the reason other than timeout, The error status is returned in Status. |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The implementation doesn’t support an Isochronous transfer function. |
17.2.11. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbAsyncIsochronousTransfer()¶
Summary
This function is used to manage a USB device with an isochronous transfer pipe. An asynchronous Isochronous transfer is a nonblocking USB isochronous transfer.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_ASYNC_ISOCHRONOUS_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 DeviceEndpoint,
IN OUT VOID *Data,
IN UINTN DataLength,
IN EFI_ASYNC_USB_TRANSFER_CALLBACK IsochronousCallBack,
IN VOID *Context OPTIONAL
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- DeviceEndpoint
The destination USB device endpoint to which the device request is being sent. DeviceEndpoint must be between 0x01 and 0x0F or between 0x81 and 0x8F, otherwise EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the endpoint is not an ISOCHRONOUS endpoint, EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. The MSB of this parameter indicates the endpoint direction. The number “1” stands for an IN endpoint, and “0” stands for an OUT endpoint.
- Data
A pointer to the buffer of data that will be transmitted to USB device or received from USB device.
- DataLength
Specifies the length, in bytes, of the data to be sent to or received from the USB device.
- Context
Data passed to the IsochronoisCallback() in Protocols_USB_Support.rst function. This is an optional parameter and may be NULL.
- IsochronousCallback
The IsochronousCallback() function. This function is called if the requested isochronous transfer is completed. See the Related Definitions section of the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbAsyncInterruptTransfer() function description.
Description
This is an asynchronous type of USB isochronous transfer. If the caller submits a USB isochronous transfer request through this function, this function will return immediately. When the isochronous transfer completes, the IsochronoisCallback() function will be triggered, the caller can know the transfer results. If the transfer is successful, the caller can get the data received or sent in this callback function.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The asynchronous isochronous transfer has been successfully submitted to the system. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
The parameter DeviceEndpoint is not valid. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The request could not be submitted due to a lack of resources. |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The implementation doesn’t support an asynchronous Isochronous transfer function. |
17.2.12. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetDeviceDescriptor()¶
Summary
Retrieves the USB Device Descriptor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_GET_DEVICE_DESCRIPTOR) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT EFI_USB_DEVICE_DESCRIPTOR *DeviceDescriptor
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- DeviceDescriptor
A pointer to the caller allocated USB Device Descriptor. See Related Definitions for a detailed description.
Related Definitions
//
// See USB1.1 for detail description.
//
typedef struct {
UINT8 Length;
UINT8 DescriptorType;
UINT16 BcdUSB;
UINT8 DeviceClass;
UINT8 DeviceSubClass;
UINT8 DeviceProtocol;
UINT8 MaxPacketSize0;
UINT16 IdVendor;
UINT16 IdProduct;
UINT16 BcdDevice;
UINT8 StrManufacturer;
UINT8 StrProduct;
UINT8 StrSerialNumber;
UINT8 NumConfigurations;
} EFI_USB_DEVICE_DESCRIPTOR;
Description
This function is used to retrieve information about USB devices. This information includes the device class, subclass, and the number of configurations the USB device supports. If DeviceDescriptor is NULL, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the USB device descriptor is not found, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned. Otherwise, the device descriptor is returned in DeviceDescriptor, and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The device descriptor was retrieved successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
DeviceDescriptor is NULL. |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The device descriptor was not found. The device may not be configured. |
17.2.13. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetConfigDescriptor()¶
Summary
Retrieves the USB Device Configuration Descriptor.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_GET_CONFIG_DESCRIPTOR) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT EFI_USB_CONFIG_DESCRIPTOR *ConfigurationDescriptor
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- ConfigurationDescriptor
A pointer to the caller allocated USB Active Configuration Descriptor. See Related Definitions for a detailed description.
Related Definitions
//
// See USB1.1 for detail description.
//
typedef struct {
UINT8 Length;
UINT8 DescriptorType;
UINT16 TotalLength;
UINT8 NumInterfaces;
UINT8 ConfigurationValue;
UINT8 Configuration;
UINT8 Attributes;
UINT8 MaxPower;
} EFI_USB_CONFIG_DESCRIPTOR;
Description
This function is used to retrieve the active configuration that the USB device is currently using. If ConfigurationDescriptor is NULL, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the USB controller does not contain an active configuration, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned. Otherwise, the active configuration is returned in ConfigurationDescriptor, and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The active configuration descriptor was retrieved successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
ConfigurationDescriptor is NULL. |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
An active configuration descriptor cannot be found. The device may not be configured. |
17.2.14. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetInterfaceDescriptor()¶
Summary
Retrieves the Interface Descriptor for a USB Device Controller. As stated earlier, an interface within a USB device is equivalently to a USB Controller within the current configuration.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_GET_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT EFI_USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR *InterfaceDescriptor
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- InterfaceDescriptor
A pointer to the caller allocated USB Interface Descriptor within the configuration setting. See Related Definitions for a detailed description.
Related Definitions
//
// See USB1.1 for detail description.
//
typedef struct {
UINT8 Length;
UINT8 DescriptorType;
UINT8 InterfaceNumber;
UINT8 AlternateSetting;
UINT8 NumEndpoints;
UINT8 InterfaceClass;
UINT8 InterfaceSubClass;
UINT8 InterfaceProtocol;
UINT8 Interface;
} EFI_USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR;
Description
This function is used to retrieve the interface descriptor for the USB controller. If InterfaceDescriptor is NULL, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the USB controller does not contain an interface descriptor, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned. Otherwise, the interface descriptor is returned in InterfaceDescriptor, and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The interface descriptor retrieved successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
InterfaceDescriptor is NULL. |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The interface descriptor cannot be found. The device may not be correctly configured. |
17.2.15. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetEndpointDescriptor()¶
Summary
Retrieves an Endpoint Descriptor within a USB Controller.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_GET_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 EndpointIndex,
OUT EFI_USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR *EndpointDescriptor
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- EndpointIndex
Indicates which endpoint descriptor to retrieve. The valid range is 0..15.
- EndpointDescriptor
A pointer to the caller allocated USB Endpoint Descriptor of a USB controller. See Related Definitions for a detailed description.
Related Definitions
//
// See USB1.1 for detail description.
//
typedef struct {
UINT8 Length;
UINT8 DescriptorType;
UINT8 EndpointAddress;
UINT8 Attributes;
UINT16 MaxPacketSize;
UINT8 Interval;
} EFI_USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR;
Description
This function is used to retrieve an endpoint descriptor within a USB controller. If EndpointIndex is not in the range 0..15, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If EndpointDescriptor is NULL, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned. If the endpoint specified by EndpointIndex does not exist within the USB controller, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned. Otherwise, the endpoint descriptor is returned in EndpointDescriptor, and EFI_SUCCESS is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The endpoint descriptor was retrieved successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
EndpointIndex is not valid. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
EndpointDescriptor is NULL. |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The endpoint descriptor cannot be found. The device may not be correctly configured. |
Examples
The following code fragment shows how to retrieve all the endpoint descriptors from a USB controller.
EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *UsbIo;
EFI_USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR InterfaceDesc;
EFI_USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR EndpointDesc;
UINTN Index;
Status = UsbIo->GetInterfaceDescriptor (
UsbIo,
&InterfaceDesc
);
. . .
for(Index = 0; Index < InterfaceDesc.NumEndpoints; Index++) {
Status = UsbIo->GetEndpointDescriptor(
UsbIo,
Index,
&EndpointDesc
);
. . .
}
17.2.16. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetStringDescriptor()¶
Summary
Retrieves a string stored in a USB Device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_GET_STRING_DESCRIPTOR) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT16 LangID,
IN UINT8 StringID,
OUT CHAR16 **String
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- LangID
The Language ID for the string being retrieved. See the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetSupportedLanguages() function description for a more detailed description.
- StringID
The ID of the string being retrieved.
- String
A pointer to a buffer allocated by this function with EFI_BOOT_SERVICES.AllocatePool() to store the string. If this function returns EFI_SUCCESS, it stores the string the caller wants to get. The caller should release the string buffer with EFI_BOOT_SERVICES.FreePool() after the string is not used any more.
Description
This function is used to retrieve strings stored in a USB device. The string to retrieve is identified by a language and an identifier. The language is specified by LangID, and the identifier is specified by StringID. If the string is found, it is returned in String, and EFI_SUCCESS is returned. If the string cannot be found, then EFI_NOT_FOUND is returned. The string buffer is allocated by this function with AllocatePool(). The caller is responsible for calling FreePool() for String when it is no longer required.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The string was retrieved successfully. |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
The string specified by LangID and StringID was not found. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
There are not enough resources to allocate the return buffer String. |
17.2.17. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbGetSupportedLanguages()¶
Summary
Retrieves all the language ID codes that the USB device supports.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_GET_SUPPORTED_LANGUAGES) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT UINT16 **LangIDTable,
OUT UINT16 *TableSize
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
- LangIDTable
Language ID for the string the caller wants to get. This is a 16-bit ID defined by Microsoft. This buffer pointer is allocated and maintained by the USB Bus Driver, the caller should not modify its contents.
- TableSize
The size, in bytes, of the table LangIDTable.
Description
Retrieves all the language ID codes that the USB device supports.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The support languages were retrieved successfully. |
17.2.18. EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL.UsbPortReset()¶
Summary
Resets and reconfigures the USB controller. This function will work for all USB devices except USB Hub Controllers.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USB_IO_PORT_RESET) (
IN EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL *This
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL instance. Type EFI_USB_IO_PROTOCOL is defined in USB I/O Protocol .
Description
This function provides a reset mechanism by sending a RESET signal from the parent hub port. A reconfiguration process will happen (that includes setting the address and setting the configuration). This reset function does not change the bus topology. A USB hub controller cannot be reset using this function, because it would impact the downstream USB devices. So if the controller is a USB hub controller, then EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The USB controller was reset. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
If the controller specified by This is a USB hub. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
An error occurred during the reconfiguration process. |
17.3. USB Function Protocol¶
This section describes the USB Function Protocol, enabling a USB Function device with a UEFI driver that implements the protocol to communicate with a a USB Host device.
The USB Function Protocol provides an I/O abstraction for a USB Controller operating in Function mode (also commonly referred to as Device, Peripheral, or Target mode) and the mechanisms by which the USB Function can communicate with the USB Host. It is used by other UEFI drivers or applications to perform data transactions and basic USB controller management over a USB Function port.
This simple protocol only supports USB 2.0 bulk transfers on systems with a single configuration and a single interface. It does not support isochronous or interrupt transfers, alternate interfaces, or USB 3.0 functionality. Future revisions of this protocol may support these or additional features.
17.3.1. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL¶
Summary
Provides basic data transactions and basic USB controller management for a USB Function port.
GUID
// {32D2963A-FE5D-4f30-B633-6E5DC55803CC}
#define EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL_GUID \
{0x32d2963a, 0xfe5d, 0x4f30,\
{0xb6, 0x33, 0x6e, 0x5d, 0xc5, 0x58, 0x3, 0xcc}};
Revision Number
#define EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL_REVISION 0x00010001
Protocol Interface Structure
typedef struct _EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL {
UINT32 Revision;
EFI_USBFN_IO_DETECT_PORT DetectPort;
EFI_USBFN_IO_CONFIGURE_ENABLE_ENDPOINTS \
ConfigureEnableEndpoints;
EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_ENDPOINT_MAXPACKET_SIZE \
GetEndpointMaxPacketSize;
EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_DEVICE_INFO GetDeviceInfo;
EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_VENDOR_ID_PRODUCT_ID \
GetVendorIdProductId;
EFI_USBFN_IO_ABORT_TRANSFER AbortTransfer;
EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_ENDPOINT_STALL_STATE \
GetEndpointStallState;
EFI_USBFN_IO_SET_ENDPOINT_STALL_STATE \
SetEndpointStallState;
EFI_USBFN_IO_EVENTHANDLER EventHandler;
EFI_USBFN_IO_TRANSFER Transfer;
EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_MAXTRANSFER_SIZE \
GetMaxTransferSize;
EFI_USBFN_IO_ALLOCATE_TRANSFER_BUFFER AllocateTransferBuffer;
EFI_USBFN_IO_FREE_TRANSFER_BUFFER FreeTransferBuffer;
EFI_USBFN_IO_START_CONTROLLER StartController;
EFI_USBFN_IO_STOP_CONTROLLER StopController;
EFI_USBFN_IO_SET_ENDPOINT_POLICY SetEndpointPolicy;
EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_ENDPOINT_POLICY GetEndpointPolicy;
} EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL;
Parameters
- Revision
The revision to which the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL adheres. All future revisions must be backwards compatible. If a future version is not backwards compatible, a different GUID must be used.
- DetectPort
Returns information about the USB port type. See Related Definitions EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.DetectPort(), for more details.
- ConfigureEnableEndpoints
Initializes all endpoints based on supplied device and configuration descriptors. Enables the device by setting the run/stop bit.
- GetEndpointMaxPacketSize
Returns the maximum packet size of the specified endpoint.
- GetDeviceInfo
Returns device specific information based on the supplied identifier as a Unicode string.
- GetVendorIdProductId
Returns the vendor-id and product-id of the device.
- AbortTransfer
Aborts the transfer on the specified endpoint.
- GetEndpointStallState
Returns the stall state on the specified endpoint.
- SetEndpointStallState
Sets or clears the stall state on the specified endpoint.
- EventHandler
This function is called repeatedly to get information on USB bus states, receive-completion and transmit-completion events on the endpoints, and notification on setup packet on endpoint 0.
- Transfer
This function handles transferring data to or from the host on the specified endpoint, depending on the direction specified.
- GetMaxTransferSize
The maximum supported transfer size in bytes.
- AllocateTransferBuffer
Allocates a transfer buffer of the specified size that satisfies the controller requirements.
- FreeTransferBuffer
Deallocates the memory allocated for the transfer buffer by EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.AllocateTransferBuffer() function.
- StartController
This function initializes the hardware and the internal data structures. The port must not be activated by this function.
- StopController
This function disables the device by deactivating the port.
- SetEndpointPolicy
This function sets the configuration policy for the specified non-control endpoint. There are a few calling restrictions for this function. See the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.SetEndpointPolicy() function definition for more details.
- GetEndpointPolicy
This functions retrieves the configuration policy for the specified non-control endpoint.
Description
This protocol provides basic data transactions and USB controller management for a USB Function port. It provides a lightweight communication mechanism between a USB Host and a USB Function in the UEFI environment.
Like other UEFI device drivers, the entry point for a USB function driver attaches EFI_DRIVER_BINDING_PROTOCOL to image handle of EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL driver.
The driver binding protocol contains three services, Supported, Start and Stop.
The Supported function must test to see if this driver supports a given controller.
The Start function must supply power to the USB controller if needed, initialize hardware and internal data structures, and then return. The port must not be activated by this function.
The Stop function must disable the USB controller and power it off if needed.
17.3.2. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.DetectPort()¶
Summary
Returns information about what USB port type was attached.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_DETECT_PORT) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT EFI_USBFN_PORT_TYPE *PortType
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- PortType
Returns the USB port type. Refer to the Related Definitions for this function below for details.
Description
Returns information about the USB port type attached. Refer to the Related Definitions below for further details.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request or there is no USB port attached to the device |
Related Definitions
typedef enum _EFI_USBFN_PORT_TYPE {
EfiUsbUnknownPort = 0,
EfiUsbStandardDownstreamPort,
EfiUsbChargingDownstreamPort,
EfiUsbDedicatedChargingPort,
EfiUsbInvalidDedicatedChargingPort
} EFI_USBFN_PORT_TYPE;
- Unknown Port
Driver internal default port type, this is never returned by the driver with a success status code.
- Standard Downstream Port
Standard USB host; refer to USB Battery Charging Specification, Revision 1.2 in Appendix Q.1 for details and the link.
- Charging Downstream Port
Standard USB host with special charging properties; refer to USB Battery Charging Specification, Revision 1.2 in Appendix Q.1 ` for the details and link.
- Dedicated Charging Port
A wall-charger, not USB host; refer to USB Battery Charging Specification, Revision 1.2, in Appendix Q.1 for details and the link.
- Invalid Dedicated Charging Port -
Neither a USB host nor a dedicated charging port as defined by the USB Battery Charging Specification, Revision 1.2. in Appendix Q.1 for details and the link.) An example is a USB charger that raises the voltages on D+/D-, causing the charger to look like an SDP even though it will never issue a setup packet to the upstream facing port.
17.3.3. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.ConfigureEnableEndpoints()¶
Summary
Configures endpoints based on supplied device and configuration descriptors.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_CONFIGURE_ENABLE_ENDPOINTS) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_USB_DEVICE_INFO *DeviceInfo
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- DeviceInfo
A pointer to EFI_USBFN_DEVICE_INFO instance. Refer to the Related Definitions for this function below for details.
Description
Assuming that the hardware has already been initialized, this function configures the endpoints using the device information supplied by DeviceInfo, activates the port, and starts receiving USB events.
This function must ignore the bMaxPacketSize0 field of the Standard Device Descriptor and the wMaxPacketSize field of the Standard Endpoint Descriptor that are made available through DeviceInfo.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The request could not be completed due to lack of resources. |
Related Definitions
typedef struct {
EFI_USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR *InterfaceDescriptor;
EFI_USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR **EndpointDescriptorTable;
} EFI_USB_INTERFACE_INFO;
typedef struct {
EFI_USB_CONFIG_DESCRIPTOR *ConfigDescriptor*;
EFI_USB_INTERFACE_INFO **InterfaceInfoTable*;
} EFI_USB_CONFIG_INFO;
typedef struct {
EFI_USB_DEVICE_DESCRIPTOR *DeviceDescriptor*;
EFI_USB_CONFIG_INFO **ConfigInfoTable*;
} EFI_USB_DEVICE_INFO;
USB_DEVICE_DESCRIPTOR, USB_CONFIG_DESCRIPTOR, USB_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR, and USB_ENDPOINT_DESCRIPTOR are defined in Section USB I/O Protocol.
17.3.4. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GetEndpointMaxPacketSize()¶
Summary
Returns the maximum packet size of the specified endpoint type for the supplied bus speed.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_ENDPOINT_MAXPACKET_SIZE) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_USB_ENDPOINT_TYPE EndpointType,
IN EFI_USB_BUS_SPEED BusSpeed,
OUT UINT16 *MaxPacketSize
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- EndpointType
Endpoint type as defined as EFI_USB_ENDPOINT_TYPE in the Related Definitions for this function below for details.
- BusSpeed
Bus speed as defined as EFI_USB_BUS_SPEED in the Related Definitions for the EventHandle function for details.
- MaxPacketSize
The maximum packet size, in bytes, of the specified endpoint type.
Description
Returns the maximum packet size of the specified endpoint type for the supplied bus speed. If the BusSpeed is UsbBusSpeedUnknown, the maximum speed the underlying controller supports is assumed.
This protocol currently does not support isochronous or interrupt transfers. Future revisions of this protocol may eventually support it.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
Related Definitions
typedef enum _EFI_USB_ENDPOINT_TYPE
{
UsbEndpointControl = 0x00,
// UsbEndpointIsochronous = 0x01,
UsbEndpointBulk = 0x02,
// UsbEndpointInterrupt = 0x03
} EFI_USB_ENDPOINT_TYPE;
17.3.5. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GetDeviceInfo()¶
Summary
Returns device specific information based on the supplied identifier as a Unicode string.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_DEVICE_INFO) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN EFI_USBFN_DEVICE_INFO_ID Id,
IN OUT UINTN *BufferSize,
OUT VOID *Buffer OPTIONAL
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- Id
The requested information id. Refer to the Related Definitions for this function below for details.
- BufferSize
On input, the size of the Buffer in bytes. On output, the amount of data returned in Buffer in bytes.
- Buffer
A pointer to a buffer to return the requested information as a Unicode string.
Description
Returns device specific information based on the supplied identifier as a Unicode string. If the supplied Buffer isn’t large enough, or is NULL, the method fails with EFI_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL and the required size is returned through BufferSize. All returned strings are in Unicode format.
An Id of EfiUsbDeviceInfoUnknown is treated as an invalid parameter.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
One or more of the following conditions is TRUE:
• BufferSize is NULL.
• BufferSize1 is not 0 and Buffer is NULL.
• Id in invalid.
|
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
EFI_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL |
The buffer is too small to hold the buffer. |
1BufferSize has been updated with the size needed to hold the request string. |
Related Definitions
typedef enum _EFI_USBFN_DEVICE_INFO_ID
{
EfiUsbDeviceInfoUnknown = 0,
EfiUsbDeviceInfoSerialNumber,
EfiUsbDeviceInfoManufacturerName,
EfiUsbDeviceInfoProductName
} EFI_USBFN_DEVICE_INFO_ID;
17.3.6. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GetVendorIdProductId()¶
Summary
Returns the vendor-id and product-id of the device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_VENDOR_ID_PRODUCT_ID) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT UINT16 *Vid,
OUT UINT16 *Pid
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- Vid
Returned vendor-id of the device.
- Pid
Returned product-id of the device.
Description
Returns vendor-id and product-id of the device.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_NOT_FOUND |
Unable to return the vendor-id or the product-id |
Related Definitions
Vendor IDs (VIDs) are 16-bit numbers that represent the device’s vendor company and are assigned and maintained by the USB-IF. Product IDs (PIDs) are 16-bit numbers assigned by each vendor to the device.
17.3.7. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.AbortTransfer()¶
Summary
Aborts the transfer on the specified endpoint.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_ABORT_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 EndpointIndex,
IN EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION Direction
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- EndpointIndex
Indicates the endpoint on which the ongoing transfer needs to be canceled.
- Direction
Direction of the endpoint. Refer to the Related Definitions for this function (below) for details.
Description
Aborts the transfer on the specified endpoint. This function should fail with EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER if the specified direction is incorrect for the endpoint.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
Related Definitions
typedef enum _EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION
{
EfiUsbEndpointDirectionHostOut = 0,
EfiUsbEndpointDirectionHostIn,
EfiUsbEndpointDirectionDeviceTx = EfiUsbEndpointDirectionHostIn,
EfiUsbEndpointDirectionDeviceRx = EfiUsbEndpointDirectionHostOut
} EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION;
17.3.8. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GetEndpointStallState()¶
Summary
Returns the stall state on the specified endpoint.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_ENDPOINT_STALL_STATE) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 EndpointIndex,
IN EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION Direction,
IN OUT BOOLEAN *State
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- EndpointIndex
Indicates the endpoint.
- Direction
Direction of the endpoint. Refer to the Related Definitions for details see EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.AbortTransfer() .
- State
Boolean, true value indicates that the endpoint is in a stalled state, false otherwise.
Description
Returns the stall state on the specified endpoint. This function would fail with EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER if the specified direction is incorrect for the endpoint.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
17.3.9. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.SetEndpointStallState()¶
Summary
Sets or clears the stall state on the specified endpoint.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_SET_ENDPOINT_STALL_STATE) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 EndpointIndex,
IN EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION Direction,
IN BOOLEAN State
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- EndpointIndex
Indicates the endpoint.
- Direction
Direction of the endpoint. Refer to the Related Definitions for the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.ABORTTRANSFER() function for details.
- State
Requested stall state on the specified endpoint. TRUE value causes the endpoint to stall; FALSE value clears an existing stall.
Description
Sets or clears the stall state on the specified endpoint. This function would fail with EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER if the specified direction is incorrect for the endpoint.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
17.3.10. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.EventHandler()¶
Summary
This function is called repeatedly to get information on USB bus states, receive-completion and transmit-completion events on the endpoints, and notification on setup packet on endpoint 0.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_EVENTHANDLER) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT EFI_USBFN_MESSAGE *Message,
IN OUT UINTN *PayloadSize,
OUT EFI_USBFN_MESSAGE_PAYLOAD *Payload
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- Message
Indicates the event that initiated this notification. Refer to the Related Definitions for this function (below) for all possible types.
- PayloadSize
On input, the size of the memory pointed by Payload. On output, the amount of data returned in Payload.
- Payload
A pointer to EFI_USBFN_MESSAGE_PAYLOAD instance to return additional payload for current message. Refer to the Related Definitions for this function (below) for details on the type.
Description
This function is called repeatedly to get information on USB bus states, receive-completion and transmit-completion events on the endpoints, and notification on setup packet on endpoint 0. A class driver must call EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.EventHandler() repeatedly to receive updates on the transfer status and number of bytes transferred on various endpoints. Refer to Figure Sequence of Operations with Endpoint Policy Changes for details.
A few messages have an associated payload that is returned in the supplied buffer. The following table describes various messages and their payload:
Message |
Payload |
Description |
EfiUsbMsgSetupPacket |
EFI_USB_DEVICE_REQUEST |
SETUP packet was received. |
EfiUsbMsgEndpointStatusChangedRx |
EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_RESULT |
Some of the requested data has been transmitted to the host. It is the responsibility of the class driver to determine if any remaining data needs to be re-sent. The Buffer supplied to EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.Transfer() must be same as the Buffer field of the payload. |
EfiUsbMsgEndpointStatusChangedTx |
EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_RESULT |
Some of the requested data has been received from the host. It is the responsibility of the class driver to determine if it needs to wait for any remaining data. The Buffer supplied to EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.Transfer() must be same as the Buffer field of the payload. |
EfiUsbMsgBusEventReset |
None |
A RESET bus event was signaled. |
EfiUsbMsgBusEventDetach |
None |
A DETACH bus event was signaled. |
EfiUsbMsgBusEventAttach |
None |
An ATTACH bus event was signaled. |
EfiUsbMsgBusEventSuspend |
None |
A SUSPEND bus event was signaled. |
EfiUsbMsgBusEventResume |
None |
A RESUME bus event was signaled. |
EfiUsbMsgBusEventSpeed |
EFI_USB_BUS_SPEED |
A Bus speed update was signaled. |
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETE |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
EFI_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL |
The Supplied buffer is not large enough to hold the message payload. |
Related Definitions
typedef enum _EFI_USBFN_MESSAGE {
//
// Nothing
//
EfiUsbMsgNone = 0,
//
// SETUP packet is received, returned Buffer contains
// EFI_USB_DEVICE_REQUEST struct
//
EfiUsbMsgSetupPacket,
//
// Indicates that some of the requested data has been
// received from the host. It is the responsibility of the
// class driver to determine if it needs to wait for any
// remaining data. Returned Buffer contains
// EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_RESULT struct containing endpoint
// number, transfer status and count of bytes received.
//
EfiUsbMsgEndpointStatusChangedRx,
//
// Indicates that some of the requested data has been
// transmitted to the host. It is the responsibility of the
// class driver to determine if anyremaining data needs to be
// resent. Returned Buffer contains
// EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_RESULT struct containing endpoint
// number, transferstatus andcount of bytes sent.
//
EfiUsbMsgEndpointStatusChangedTx,
//
// DETACH bus event signaled
//
EfiUsbMsgBusEventDetach,
//
// ATTACH bus event signaled
//
EfiUsbMsgBusEventAttach,
//
// RESET bus event signaled
//
EfiUsbMsgBusEventReset,
//
// SUSPEND bus event signaled
//
EfiUsbMsgBusEventSuspend,
//
// RESUME bus event signaled
//
EfiUsbMsgBusEventResume,
//
// Bus speed updated, returned buffer indicated bus speed
// using following enumeration named EFI_USB_BUS_SPEED
//
EfiUsbMsgBusEventSpeed
} EFI_USBFN_MESSAGE;
typedef enum _EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_STATUS {
UsbTransferStatusUnknown = 0,
UsbTransferStatusComplete,
UsbTransferStatusAborted,
UsbTransferStatusActive,
UsbTransferStatusNone
} EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_STATUS;
typedef struct _EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_RESULT {
UINTN BytesTransferred;
EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_STATUS TransferStatus;
UINT8 EndpointIndex;
EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION Direction;
VOID *Buffer;
} EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_RESULT;
typedef enum _EFI_USB_BUS_SPEED {
UsbBusSpeedUnknown = 0,
UsbBusSpeedLow,
UsbBusSpeedFull,
UsbBusSpeedHigh,
UsbBusSpeedSuper,
UsbBusSpeedMaximum = UsbBusSpeedSuper
} EFI_USB_BUS_SPEED;
typedef union _EFI_USBFN_MESSAGE_PAYLOAD {
EFI_USB_DEVICE_REQUEST udr;
EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_RESULT utr;
EFI_USB_BUS_SPEED ubs;
} EFI_USBFN_MESSAGE_PAYLOAD;
17.3.11. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.Transfer()¶
Summary
This function handles transferring data to or from the host on the specified endpoint, depending on the direction specified.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI *EFI_USBFN_IO_TRANSFER) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 EndpointIndex,
IN EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION Direction,
IN OUT UINTN *BufferSize,
IN OUT VOID *Buffer
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- EndpointIndex
Indicates the endpoint on which TX or RX transfer needs to take place.
- Direction
Direction of the endpoint. Refer to the Related Definitions of the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.ABORTTRANSFER() function for details.
- BufferSize
If Direction is EfiUsbEndpointDirectionDeviceRx: On input, the size of the Buffer in bytes. On output, the amount of data returned in Buffer in bytes.
If Direction is EfiUsbEndpointDirectionDeviceTx: On input, the size of the Buffer in bytes. On output, the amount of data transmitted in bytes.
- Buffer
If Direction is EfiUsbEndpointDirectionDeviceRx: The Buffer to return the received data.
If Direction is EfiUsbEndpointDirectionDeviceTx: The Buffer that contains the data to be transmitted.
Note: This buffer is allocated and freed using the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.ABORTTRANSFER() and EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.FreeTransferBuffer() functions. The caller of this function must not free or reuse the buffer until EfiUsbMsgEndpointStatusChangedRx or EfiUsbMsgEndpointStatusChangedTx message was received along with the address of the transfer buffer as part of the message payload. Refer to the function definition for EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.EventHandler() for more information on various messages and their payloads.
Description
This function handles transferring data to or from the host on the specified endpoint, depending on the direction specified.
Direction |
Description |
EfiUsbEndpointDirectionDeviceTx |
Start a transmit transfer on the specified endpoint and return immediately. |
EfiUsbEndpointDirectionDeviceRx |
Start a receive transfer on the specified endpoint and return immediately with available data. |
A class driver must call EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.EventHandler() repeatedly to receive updates on the transfer status and the number of bytes transferred on various endpoints. Upon an update of the transfer status, the Buffer field of the EFI_USBFN_TRANSFER_RESULT structure (as described in the function description for EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.EventHandler() must be initialized with the Buffer pointer that was supplied to this method.
The overview of the call sequence is illustrated in Figure Sequence of Operations with Endpoint Policy Changes.
This function should fail with EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER if the specified direction is incorrect for the endpoint.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
17.3.12. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GetMaxTransferSize()¶
Summary
Returns the maximum supported transfer size.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_GET_MAXTRANSFER_SIZE) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
OUT UINTN *MaxTransferSize
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- MaxTransferSize
The maximum supported transfer size, in bytes.
Description
Returns the maximum number of bytes that the underlying controller can accommodate in a single transfer.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_NOT_READY |
The physical device is busy or not ready to process this request. |
17.3.13. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.AllocateTransferBuffer()¶
Summary
Allocates a transfer buffer of the specified size that satisfies the controller requirements.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_ALLOCATE_TRANSFER_BUFFER) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINTN Size,
OUT VOID **Buffer
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- Size
The number of bytes to allocate for the transfer buffer.
- Buffer
A pointer to a pointer to the allocated buffer if the call succeeds; undefined otherwise.
Description
The AllocateTransferBuffer() function allocates a memory region of Size bytes and returns the address of the allocated memory that satisfies the underlying controller requirements in the location referenced by Buffer.
The allocated transfer buffer must be freed using a matching call EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.FreeTransferBuffer() function.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_OUT_OF_RESOURCES |
The requested transfer buffer could not be allocated. |
17.3.14. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.FreeTransferBuffer()¶
Summary
Deallocates the memory allocated for the transfer buffer by the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.AllocateTransferBuffer() function.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_FREE_TRANSFER_BUFFER) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN VOID *Buffer
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- Buffer
A pointer to the transfer buffer to deallocate.
Description
The EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.FreeTransferBuffer() function deallocates the memory specified by Buffer. The Buffer that is freed must have been allocated by EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.AllocateTransferBuffer().
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
17.3.15. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.StartController()¶
Summary
This function supplies power to the USB controller if needed and initializes the hardware and the internal data structures. The port must not be activated by this function
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_START_CONTROLLER) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
Description
This function starts the hardware by supplying power to the USB controller if needed, and initializing the hardware and internal data structures. The port must not be activated by this function.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
17.3.16. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.StopController()¶
Summary
This function stops the USB hardware device.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_IO_STOP_CONTROLLER) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
17.3.16.1. Description¶
This function stops the USB hardware device
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
17.3.17. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.SetEndpointPolicy()¶
Summary
This function sets the configuration policy for the specified non-control endpoint. Refer to the description for calling restrictions.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_SET_ENDPOINT_POLICY) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 EndpointIndex
IN EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION Direction,
IN EFI_USBFN_POLICY_TYPE PolicyType,
IN UINTN BufferSize,
IN VOID *Buffer
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- EndpointIndex
Indicates the non-control endpoint for which the policy needs to be set.
- Direction
Direction of the endpoint. Refer to the Related Definitions for the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.AbortTransfer() function for details.
- PolicyType
Policy type the user is trying to set for the specified non-control endpoint. Refer to Related Definitions for this function below for details.
- BufferSize
The size of the Buffer in bytes.
- Buffer
The new value for the policy parameter that PolicyType specifies. Refer to Related Definitions for this function below for details.
Description
This function sets the configuration policy for the specified non-control endpoint. This function can only be called before EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.StartController() or after EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.StopController() has been called.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
Changing this policy value is not supported. |
Related Definitions
typedef enum _EFI_USBFN_POLICY_TYPE
{
EfiUsbPolicyUndefined = 0,
EfiUsbPolicyMaxTransactionSize,
EfiUsbPolicyZeroLengthTerminationSupport,
EfiUsbPolicyZeroLengthTermination
} EFI_USBFN_POLICY_TYPE;
- EfiUsbPolicyUndefined
Invalid policy value that must never be used across driver boundary. If used, the function must not return a success status code.
- EfiUsbPolicyMaxTransactionSize
EfiUsbPolicyMaxTransactionSize is only used with EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GETENDPOINTPOLICY(). It provides the size of the largest single transaction (delivery of service to an endpoint) supported by a controller. It must be greater than or equal to the maximum transfer size that can be retrieved by calling EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GETMAXTRANSFERSIZE().
GetEndpointPolicy |
SetEndpointPolicy |
|
BufferSize |
4 bytes, sizeof(UINT32) |
Not applicable |
Return Status |
EFI_STATUS |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
- EfiUsbPolicyZeroLengthTerminationSupport
- EfiUsbPolicyZeroLengthTerminationSupport is only used with XXXEFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GETENDPOINTPOLICY(). It is TRUE if the USB controller is capable of automatically handling zero length packets when the transfer size is a multiple of USB maximum packet size and FALSE if it is not supported by the controller.
GetEndpointPolicy |
SetEndpointPolicy |
|
BufferSize |
1 byte, sizeof (BOOLEAN) |
Not applicable |
Return Status |
EFI_STATUS |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
- EfiUsbPolicyZeroLengthTermination
When used with EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GETENDPOINTPOLICY() , a TRUE value is returned if the USB controller hardware is configured to automatically handle zero length packets when the transfer size is a multiple of USB maximum packet size; a FALSE value is returned if the controller hardware is not configured to do this.
Using EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.SETENDPOINTPOLICY() to set the EfiUsbPolicyZeroLengthTermination policy is only applicable to USB controller hardware capable of supporting automatic zero length packet termination. When this value is set to TRUE, the controller must be configured to handle zero length termination for the specified endpoint. When this value is set to FALSE, the controller must be configured to not handle zero length termination for the specified endpoint.
The USB controller’s default policy must not enable automatic zero length packet termination, even if the hardware is capable of supporting it.
GetEndpointPolicy |
SetEndpointPolicy |
|
BufferSize |
1 byte, sizeof (BOOLEAN) |
1 byte, sizeof (BOOLEAN) |
Return Status |
EFI_STATUS |
EFI_STATUS |
17.3.18. EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.GetEndpointPolicy()¶
Summary
This function retrieves the configuration policy for the specified non-control endpoint. There are no associated calling restrictions for this function.
Prototype
typedef
EFI_STATUS
(EFIAPI * EFI_USBFN_GET_ENDPOINT_POLICY) (
IN EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL *This,
IN UINT8 EndpointIndex
IN EFI_USBFN_ENDPOINT_DIRECTION Direction,
IN EFI_USBFN_POLICY_TYPE PolicyType,
IN OUT UINTN *BufferSize,
IN OUT VOID *Buffer
);
Parameters
- This
A pointer to the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL instance.
- EndpointIndex
Indicates the non-control endpoint for which the policy needs to be set.
- Direction
Direction of the endpoint. Refer to the Related Definitions for the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.Aborttransfer() function for details.
- PolicyType
Policy type the user is trying to retrieve for the specified non-control endpoint. Refer to the Related Definitions for the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.Setendpointpolicy() function for details.
- BufferSize
On input, the size of Buffer in bytes. On output, the amount of data returned in Buffer in bytes.
- Buffer
A pointer to a buffer to return requested endpoint policy value. Refer to the Related Definitions for the EFI_USBFN_IO_PROTOCOL.SetEndpointPolicy() function for size requirements of various policy types.
Description
This function retrieves the configuration policy for the specified non-control endpoint. This function has no calling restrictions.
Status Codes Returned
EFI_SUCCESS |
The function returned successfully. |
EFI_INVALID_PARAMETER |
A parameter is invalid. |
EFI_DEVICE_ERROR |
The physical device reported an error. |
EFI_UNSUPPORTED |
The specified policy value is not supported. |
EFI_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL |
Supplied buffer is not large enough to hold requested policy value. |